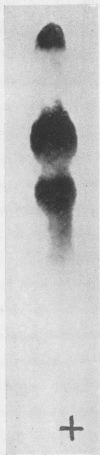
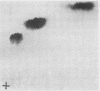
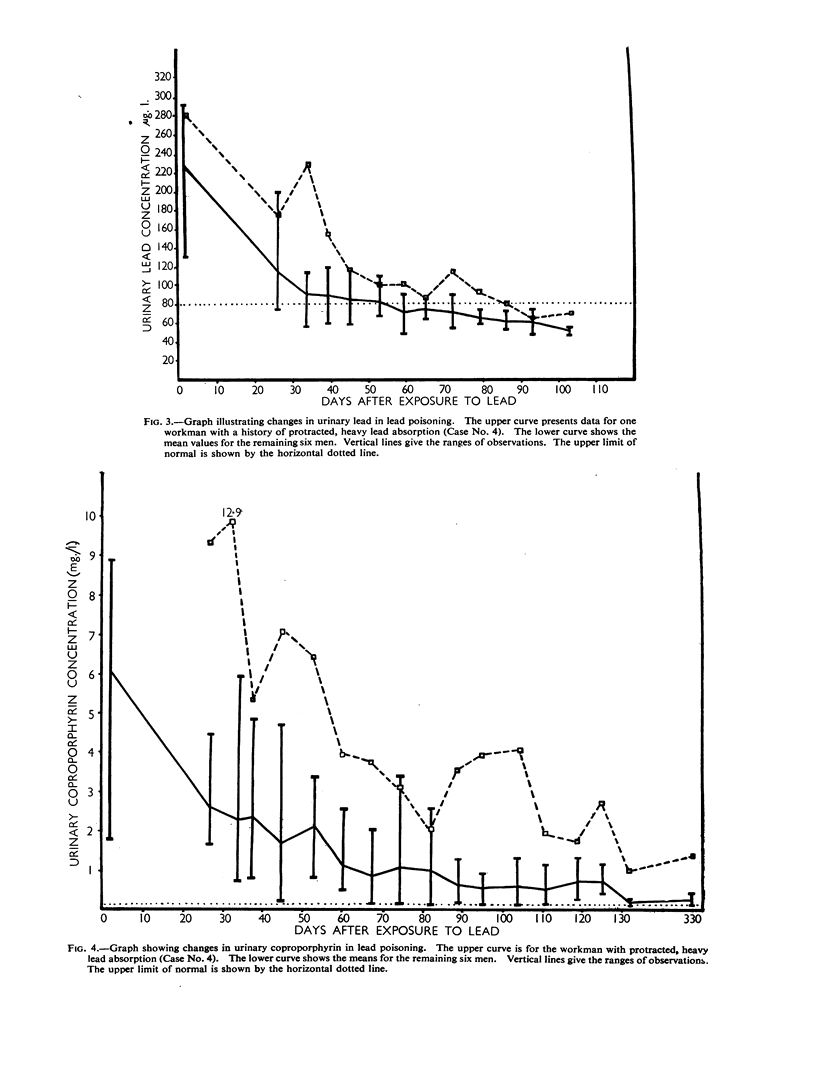
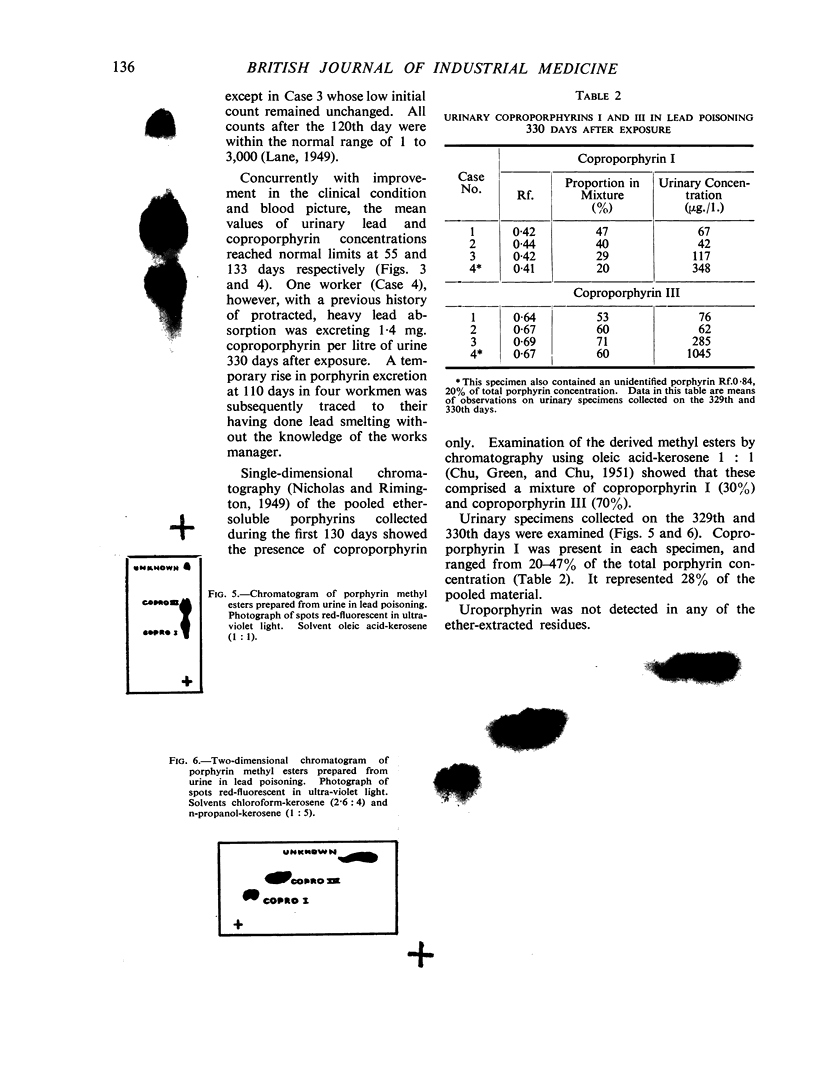
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRICH R. A., HAWKINSON V., GRINSTEIN M., WATSON C. J. Photosensitive or congenital porphyria with hemolytic anemia. I. Clinical and fundamental studies before and after splenectomy. Blood. 1951 Aug;6(8):685–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHU T. C., SISTER A A GREEN, CHU E. J. Paper chromatography of methyl esters of porphyrins. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jun;190(2):643–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobriner K., Rhoads C. P. THE EXCRETION OF COPROPORPHYRIN I FOLLOWING HEMORRHAGE IN DOGS. J Clin Invest. 1938 Jan;17(1):105–108. doi: 10.1172/JCI100921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kench J. E., Gillam A. E., Lane R. E. Haemopoiesis in lead poisoning. Biochem J. 1942 Apr;36(3-4):384–388. doi: 10.1042/bj0360384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kench J. E. The determination of minute amounts of lead in urine. Biochem J. 1940 Sep;34(8-9):1245–1247. doi: 10.1042/bj0341245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson C. J. CONCERNING THE NATURALLY OCCURRING PORPHYRINS. IV. THE URINARY PORPHYRIN IN LEAD POISONING AS CONTRASTED WITH THAT EXCRETED NORMALLY AND IN OTHER DISEASES. J Clin Invest. 1936 May;15(3):327–334. doi: 10.1172/JCI100783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]