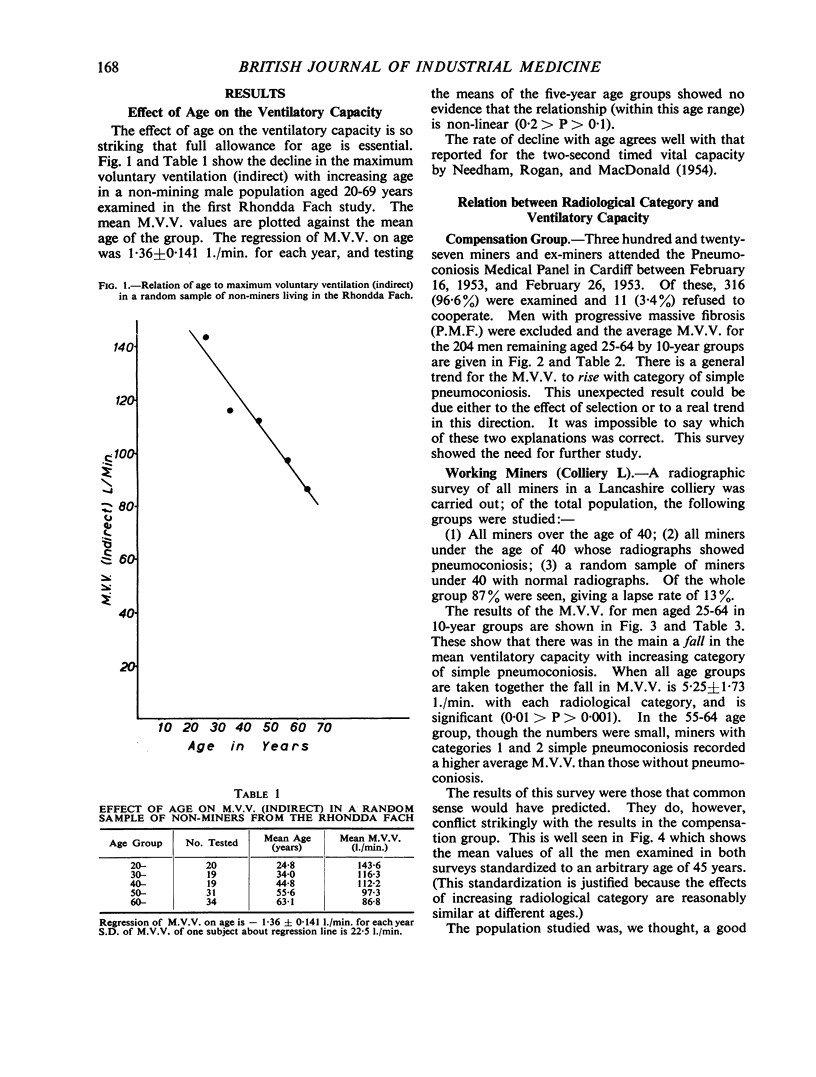
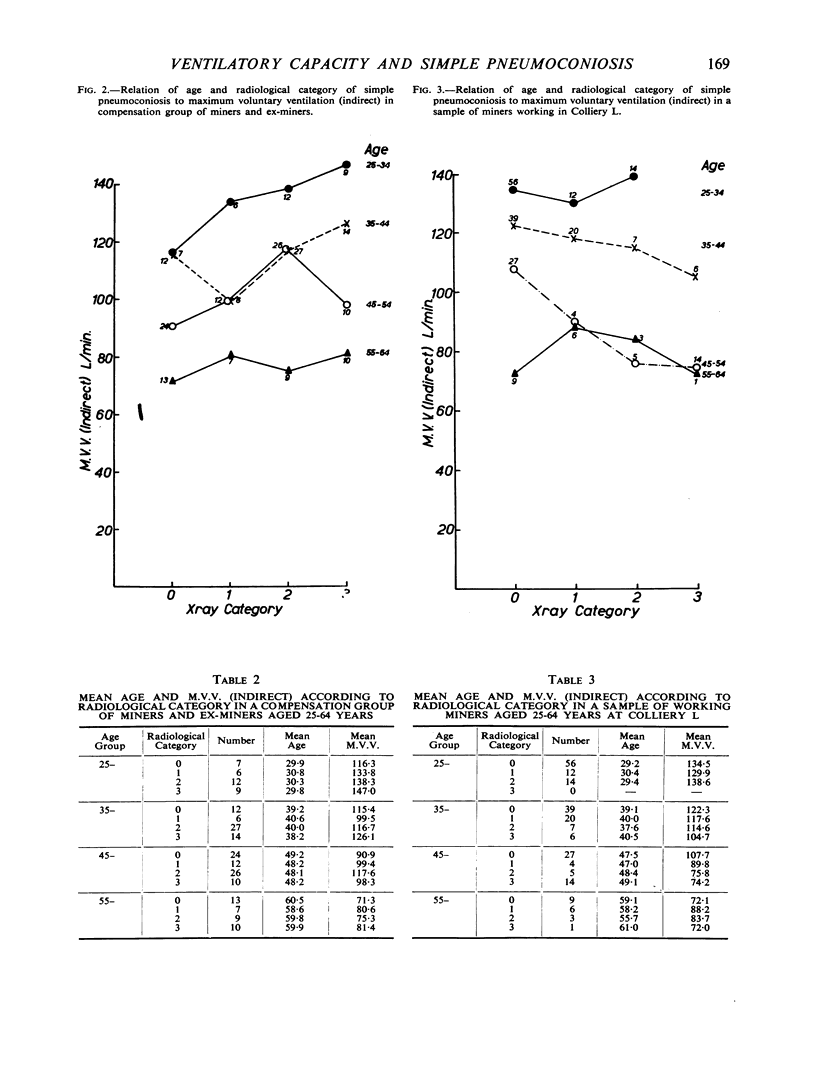
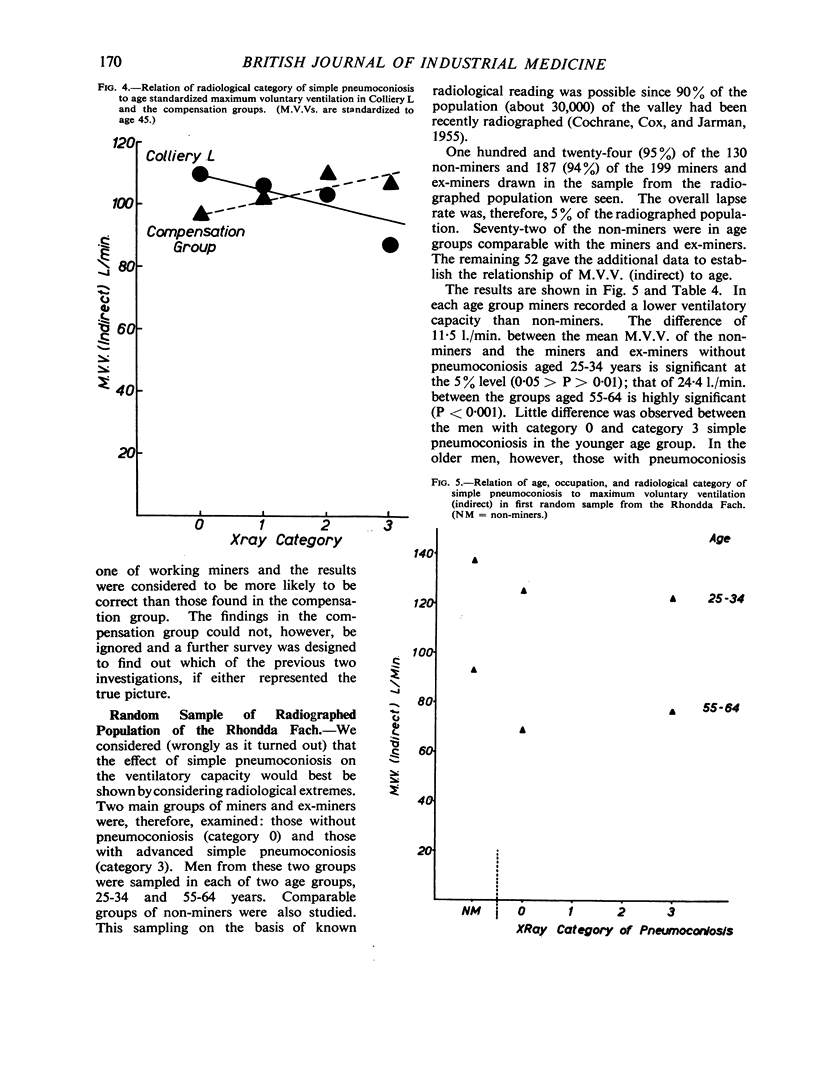
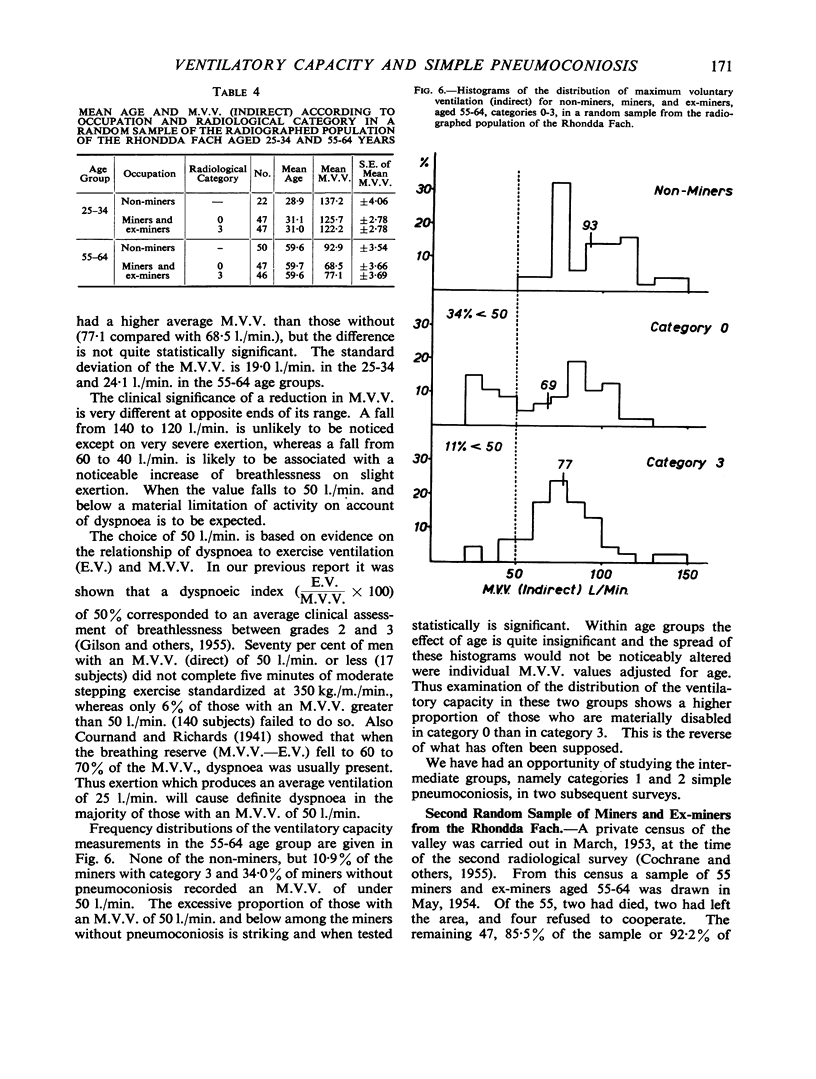
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNSTEIN L., KAZANTZIS G. The relation between the fast vital capacity curves and the maximum breathing capacity. Thorax. 1954 Dec;9(4):326–339. doi: 10.1136/thx.9.4.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARPENTER R. G., COCHRANE A. L., CLARKE W. G., JONATHAN G., MOORE F. Death rates of miners and ex-miners with and without coalworkers' pneumoconiosis in South Wales. Br J Ind Med. 1956 Apr;13(2):102–109. doi: 10.1136/oem.13.2.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCHRANE A. L., DAVIES I., FLETCHER C. M. "Entente radiologique": a step towards international agreement on the classification of radiographs in pneumoconiosis. Br J Ind Med. 1951 Oct;8(4):244–255. doi: 10.1136/oem.8.4.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLETCHER C. M. Pneumoconiosis of coal-miners. Br Med J. 1948 May 29;1(4560):1015–1022. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4560.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAENSLER E. A. An instrument for dynamic vital capacity measurements. Science. 1951 Oct 26;114(2965):444–446. doi: 10.1126/science.114.2965.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEPPLESTON A. G. The pathological anatomy of simple pneumokoniosis in coal workers. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):235–246. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY M. C. S. A practical measure of the maximum ventilatory capacity in health and disease. Thorax. 1953 Mar;8(1):73–83. doi: 10.1136/thx.8.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. J., MAGUIRE B. A., NAGELSCHMIDT G. Further studies of the dust in lungs of coal-miners. Br J Ind Med. 1956 Jan;13(1):9–23. doi: 10.1136/oem.13.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEUALLEN E. C., FOWLER W. S. Maximal midexpiratory flow. Am Rev Tuberc. 1955 Dec;72(6):783–800. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1955.72.6.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANN K. J. A radiological study of the relationship between tuberculosis and pneumokoniosis in coal miners. Thorax. 1951 Mar;6(1):43–55. doi: 10.1136/thx.6.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCALLUM R. I., BROWNE R. C. Coal miners' pneumoconiosis in four collieries in county Durham. Br J Ind Med. 1955 Oct;12(4):279–289. doi: 10.1136/oem.12.4.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McVITTIE J. C. Pneumoconiosis in coal miners. Postgrad Med J. 1949 Dec;25(290):618-31, illust. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.25.290.618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEEDHAM C. D., ROGAN M. C., McDONALD I. Normal standards for lung volumes, intrapulmonary gas-mixing, and maximum breathing capacity. Thorax. 1954 Dec;9(4):313–325. doi: 10.1136/thx.9.4.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROCHE L., THIVOLLET J. Exploration functionnelle du poumon dans l'expertise de la silicose. Arch Mal Prof. 1949;10(6):448–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THEODOS P. A., GORDON B. Studies in the clinical evaluation of disability of anthracosilicosis. Dis Chest. 1950 Mar;17(3):249–272. doi: 10.1378/chest.17.3.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS A. J., COTES J. E., HIGGINS I. T. Prevalence of coronary heart-disease in elderly coal-workers. Lancet. 1956 Apr 14;270(6920):414–420. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)90477-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIFFENEAU R., BOUSSER J., DRUTEL P. Capacité vitale et capacité pulmonaire utilisable à l'effort; critères statique et dynamique de laventilation pulmonaire. Paris Med. 1949 Dec 3;39(45):543–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


