Abstract
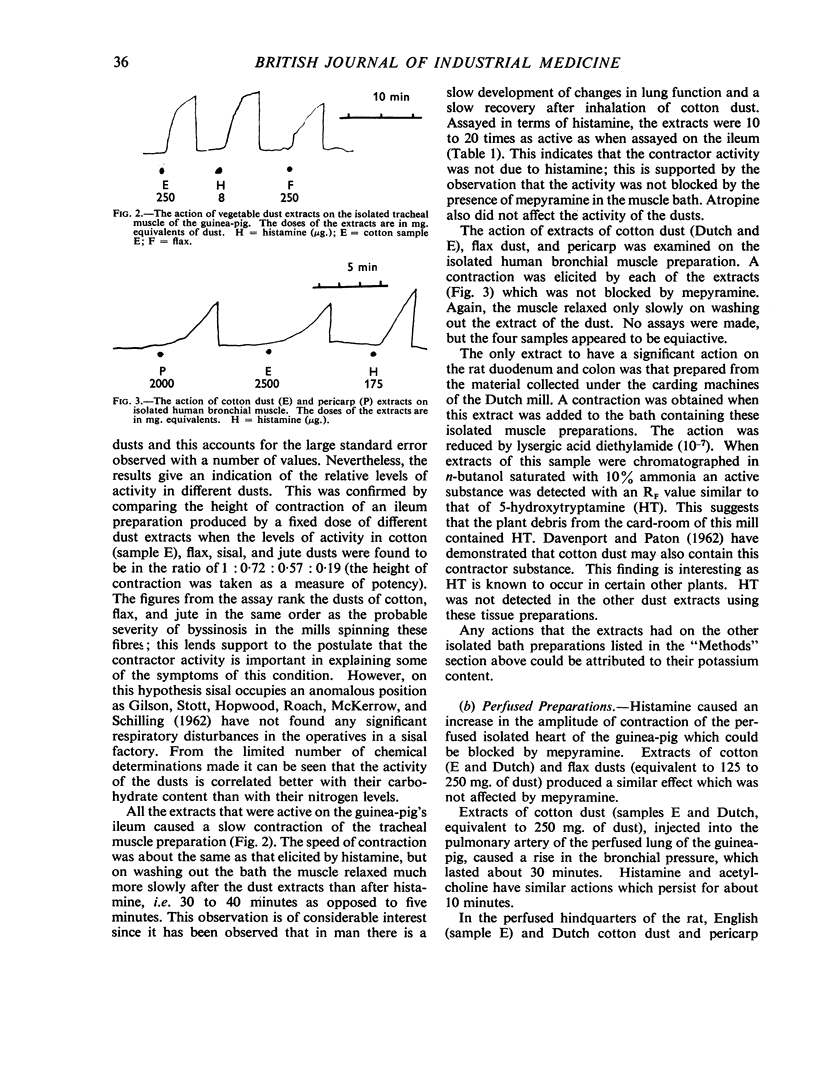
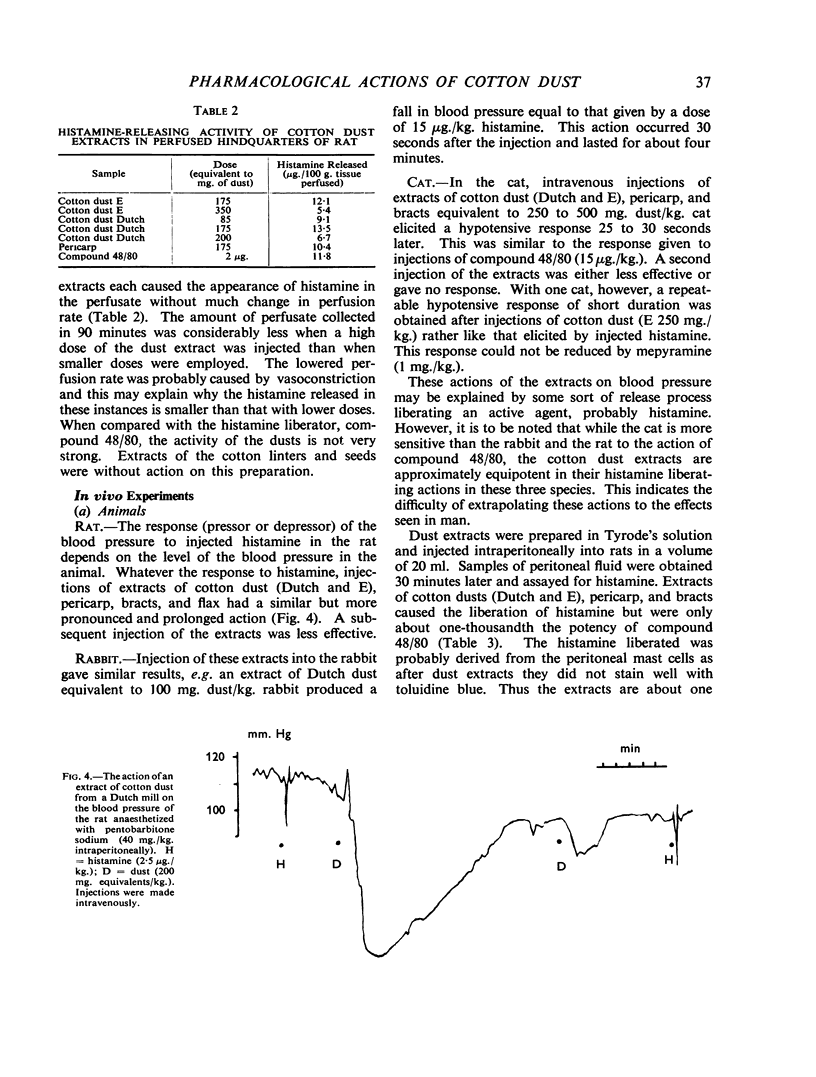
Aqueous extracts of cotton and other vegetable dusts cause contraction of the isolated ileum and tracheal muscle of the guinea-pig, and of isolated human bronchial muscle. The levels of this contractor activity place the dusts of cotton, flax, and jute in the order of the probable incidence of byssinosis occurring in the mills spinning these fibres.
Extracts of cotton dust possess a histamine-liberating activity and contain a permeability-increasing component. These actions are of plant origin and are found in the pericarp and bracts of the cotton boll. Histamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine have also been found in some cotton dust samples. The formation of histamine by bacterial action in cotton dust does not take place under conditions found in cotton mills. The smooth muscle contractor substance is organic in nature, relatively heat-stable, and dialysable. The relevance of these results to the symptoms of byssinosis is discussed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTWEILER H. [Experimental animal studies on the pathogenesis of byssinosis]. Arch Gewerbepathol Gewerbehyg. 1960;17:574–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOUHUYS A., LINDELL S. E., LUNDIN G. Experimental studies on byssinosis. Br Med J. 1960 Jan 30;1(5169):324–326. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5169.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAYTON H. R., FURNESS G., MAITLAND H. B. Studies on cotton dust in relation to byssinosis. II. Skin tests for allergy with extracts of cotton dust. Br J Ind Med. 1952 Jul;9(3):186–196. doi: 10.1136/oem.9.3.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAWCETT D. W. Cytological and pharmacological observations on the release of histamine by mast cells. J Exp Med. 1954 Aug 1;100(2):217–224. doi: 10.1084/jem.100.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., MONGAR J. L. Comparison of histamine release by compound 48/80 and octylamine in perfused tissues. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1954 Jun;9(2):197–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1954.tb00841.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GADDUM J. H., HORTON E. W. The extraction of human urinary kinin (substance Z) and its relation to the plasma kinins. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):117–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00937.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAWKINS D. F., SCHILD H. O. The action of drugs on isolated human bronchial chains. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1951 Dec;6(4):682–690. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1951.tb00680.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLENNAN A. P. Specific lipopolysaccharides of Bordetella. Biochem J. 1960 Feb;74:398–409. doi: 10.1042/bj0740398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILES A. A., MILES E. M. Vascular reactions to histamine, histamine-liberator and leukotaxine in the skin of guinea-pigs. J Physiol. 1952 Oct;118(2):228–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERNIS B., VIGLIANI E. C., CAVAGNA C., FINULLI M. The role of bacterial endotoxins in occupational diseases caused by inhaling vegetable dusts. Br J Ind Med. 1961 Apr;18:120–129. doi: 10.1136/oem.18.2.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


