Abstract
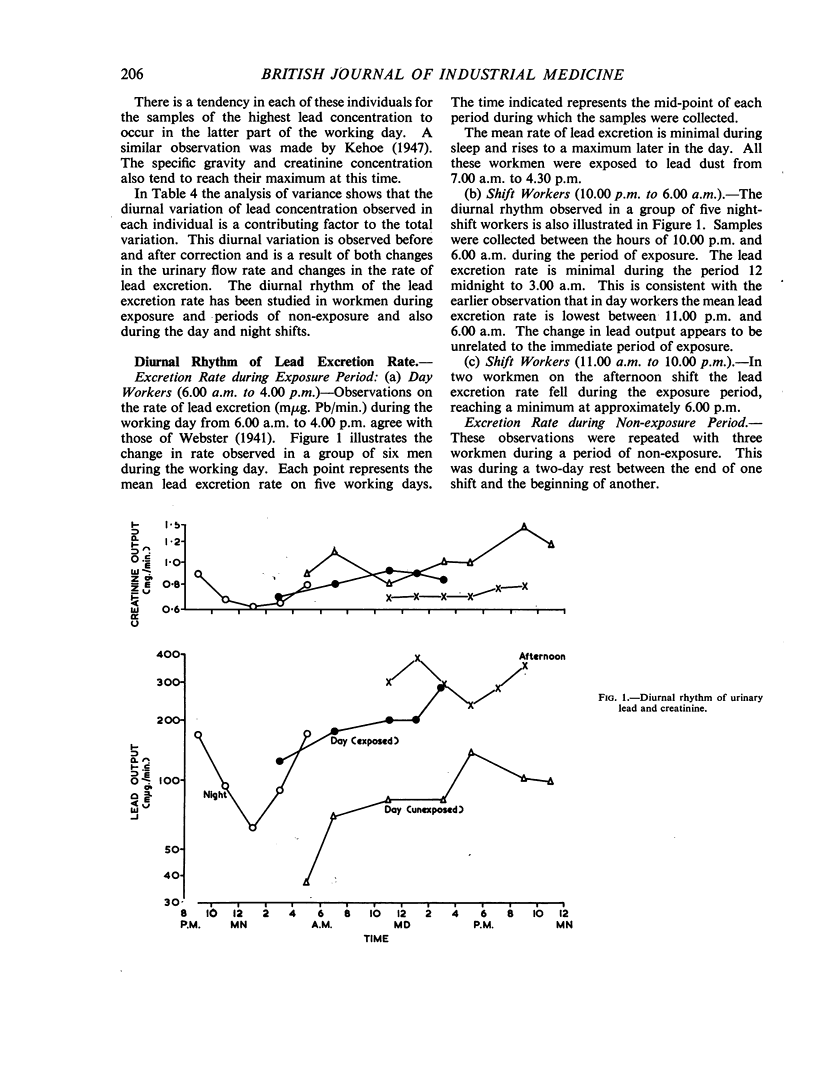
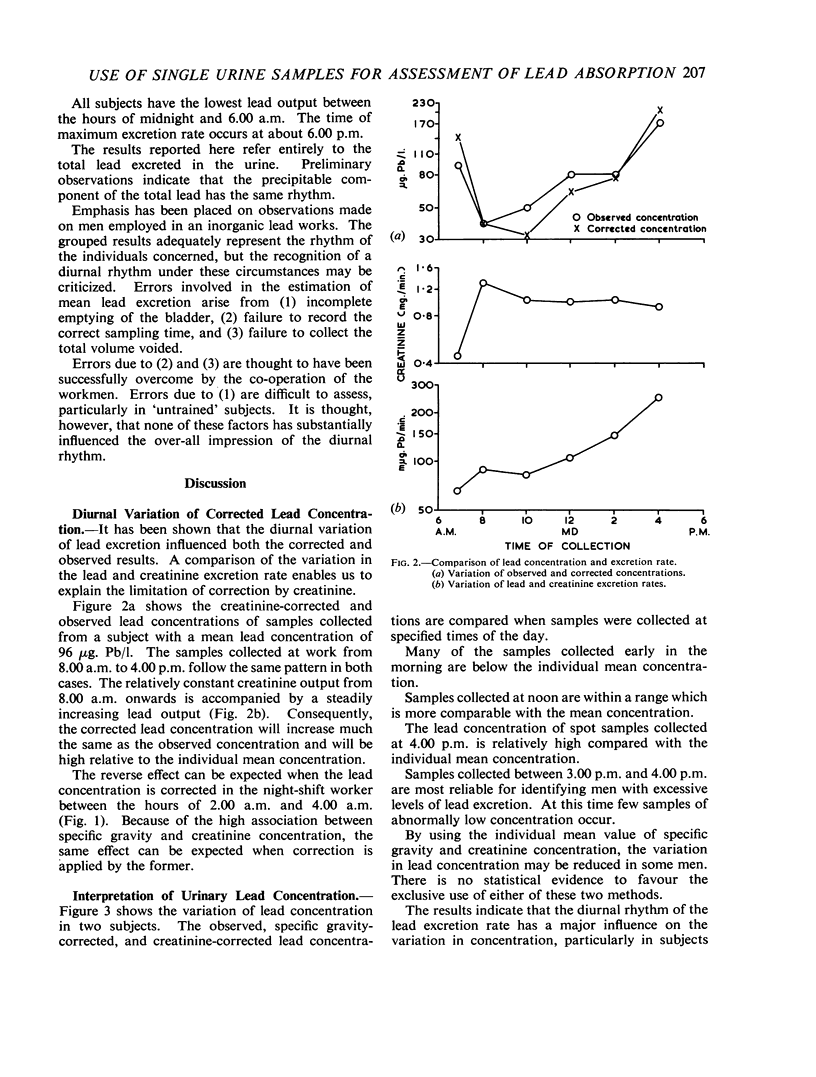
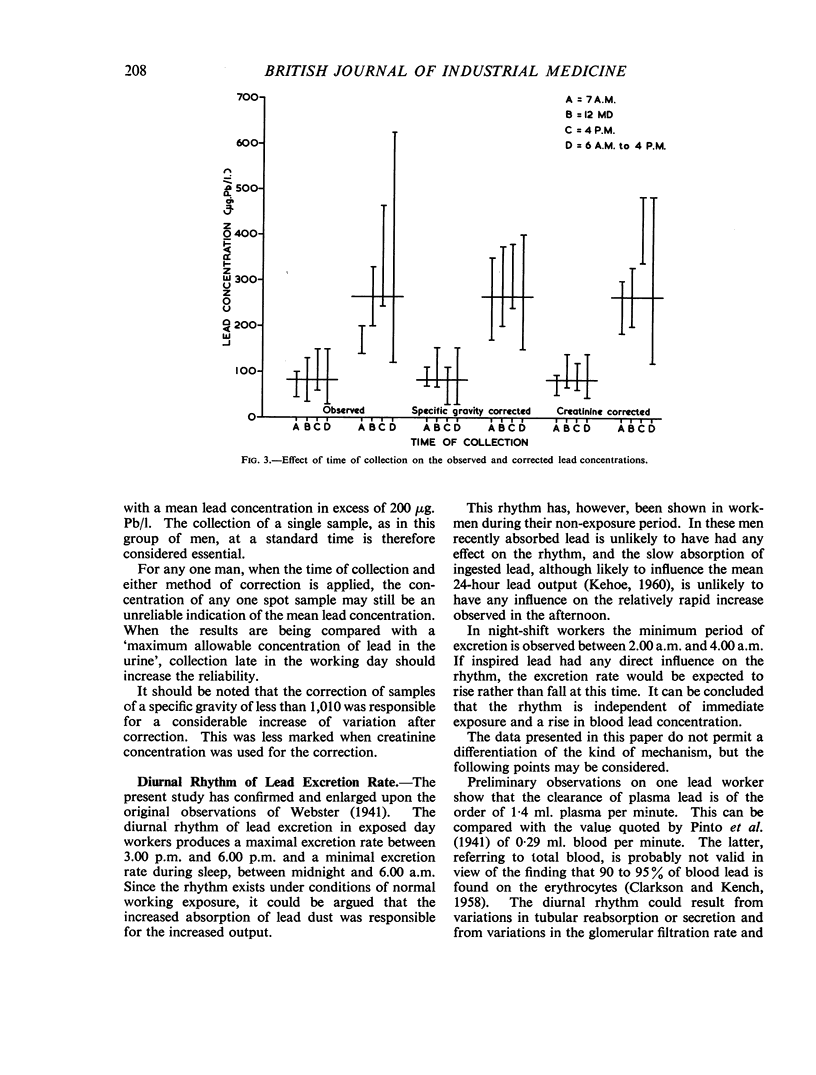
The variation of urinary lead concentration (μg. Pb/litre) of short-period samples has been studied in a group of men exposed to inorganic lead dust. The urinary specific gravity was used to correct for the variation in urinary volume, but the residual variation was still too great to assess the mean lead concentration. The effect of creatinine correction was studied as an alternative, but there is no statistical difference between either method of correction. It is shown that the variation of lead concentration is related to the time of day. The highest concentration occurs at approximately 4.00 p.m. in day workers.
The diurnal rhythm of the lead excretion rate (μg. Pb/minute) is described in day and night shift workers. The rate of excretion rises to a maximum at approximately 5.00 p.m. in the former but decreases in night workers, falling to a minimum at approximately 2.00 a.m. The rhythm is independent of immediate exposure and is thought to be physiological in origin. The plasma lead clearance is estimated at 1·4 ml. plasma per minute. This suggests that only a small proportion of plasma lead may be ultrafiltrable and that little lead is secreted by the tubules.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLARKSON T. W., KENCH J. E. Uptake of lead by human erythrocytes in vitro. Biochem J. 1958 Jul;69(3):432–439. doi: 10.1042/bj0690432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E., THOMPSON A. R. The measurement of lead absorption in industry. Ann Occup Hyg. 1961 Jun;3:247–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWEN J. A., IGGO B., SCANDRETT F. J., STEWART C. P. The determination of creatinine in plasma or serum, and in urine; a critical examination. Biochem J. 1954 Nov;58(3):426–437. doi: 10.1042/bj0580426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. C., KENCH J. E. Observations on urinary cadmium and protein excretion in men exposed to cadmium oxide dust and fume. Br J Ind Med. 1957 Oct;14(4):240–245. doi: 10.1136/oem.14.4.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


