Abstract
Twenty-two patients with lipid keratopathy were treated with argon laser photocoagulation to the feeder vessels. Two were grafted just over a week after treatment and the corneal discs examined histologically. The remainder of the patients were followed up for a least a year. In 6 cases the visual acuity improved, in 3 deteriorated, and in 10 did not change. The density and extent of the lipid deposition were diminished in 50% of cases. The commonest complications were bleeding into the lipid keratopathy and iris damage. The only serious problem was a disciform type of lipid keratopathy that flared up after treatment. Suggestions are made on improvements in the technique of laser application.
Full text
PDF


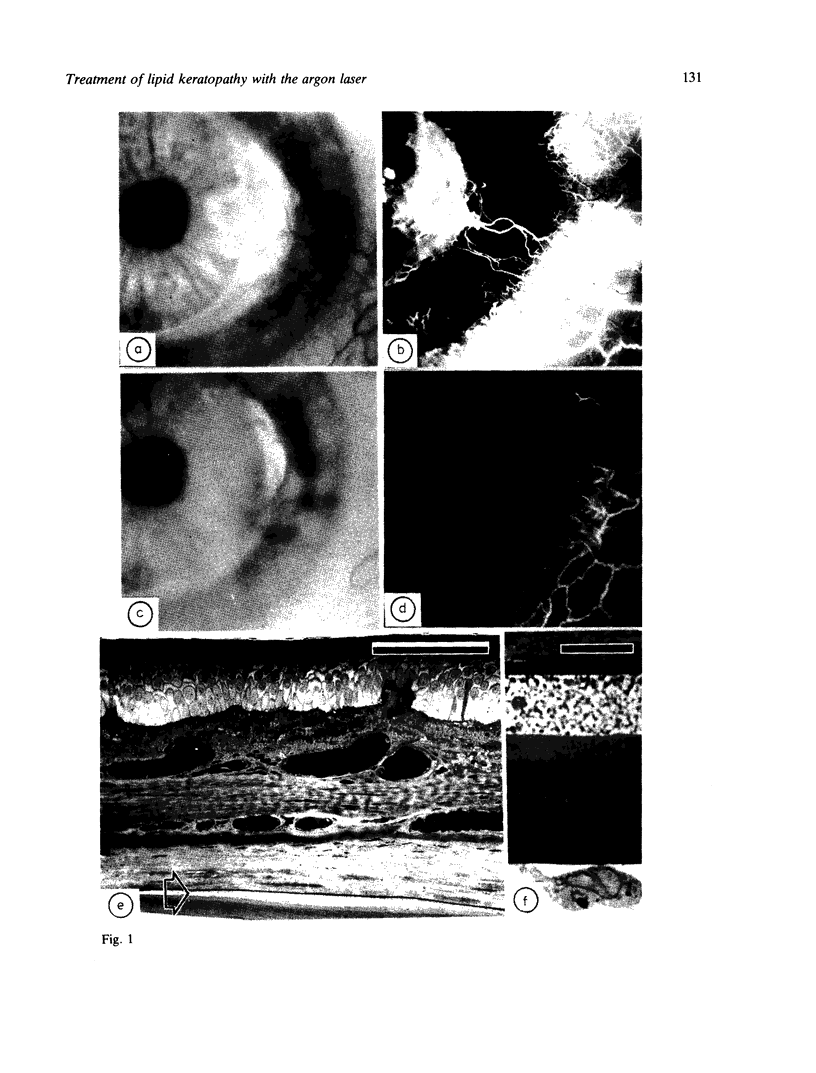

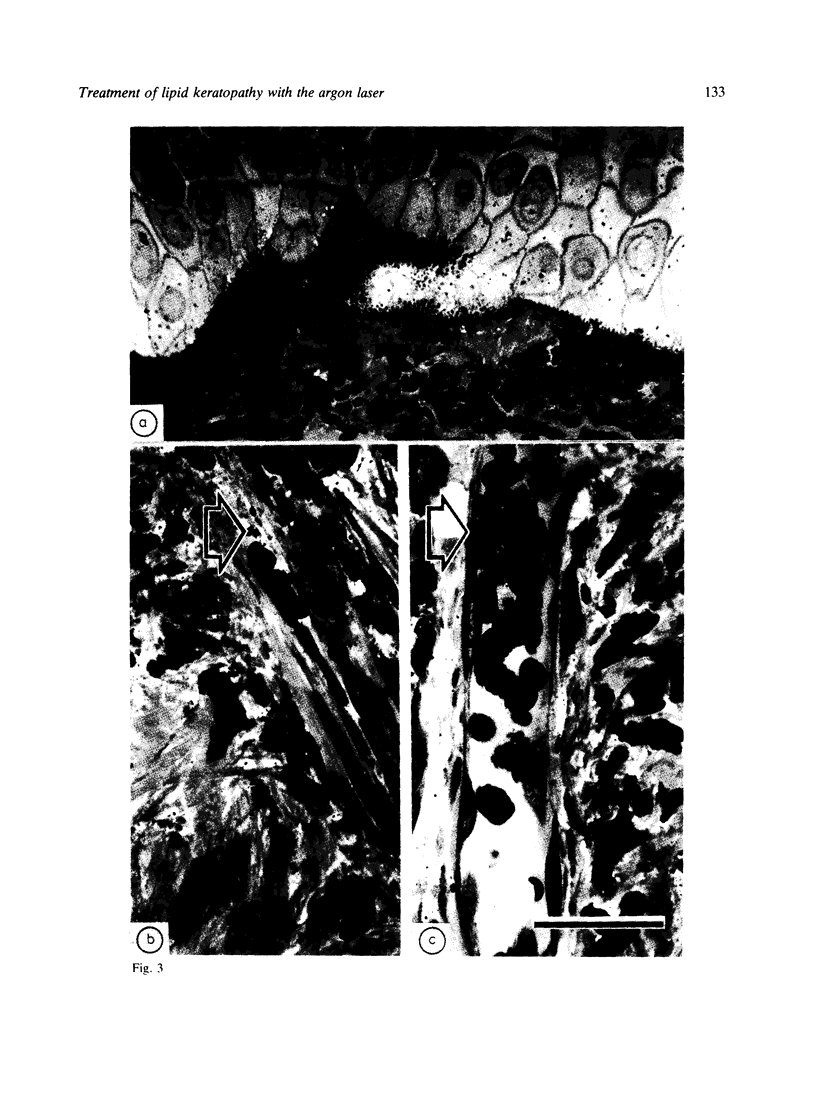


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AINSLIE D., SNELLING M. D., ELLIS R. E. Treatment of corneal vascularisation by strontium 90 beta plaque. Clin Symp. 1962 Jan;13:29–29. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(62)80005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apple D. J., Goldberg M. F., Wyhinny G. Histopathology and ultrastructure of the argon laser lesion in human retinal and choroidal vasculatures. Am J Ophthalmol. 1973 Apr;75(4):595–609. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(73)90812-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOK C., MacDONALD R. K. Effect of cortisone on the permeability of the blood-aqueous barrier to fluorescein. Br J Ophthalmol. 1951 Nov;35(11):730–740. doi: 10.1136/bjo.35.11.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry P. M., Faulkner J. D., Shaver R. P., Wise J. B., Witter S. L. Argon laser treatment of corneal neovascularization. Ann Ophthalmol. 1973 Aug;5(8):911–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUKE-ELDER S., ASHTON N. Action of cortisone on tissue reactions of inflammation and repair with special reference to the eye. Br J Ophthalmol. 1951 Nov;35(11):695–707. doi: 10.1136/bjo.35.11.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey R. C., Hughes W. F., Bloome M. A., Tallman C. B. Prevention of corneal vascularization. Am J Ophthalmol. 1968 Dec;66(6):1118–1131. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(68)90821-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser H., Naunton W. J. TREATMENT OF NON-MALIGNANT CORNEAL CONDITIONS WITH RADIOACTIVE ISOTOPES: A 5-YEAR SURVEY. Br J Ophthalmol. 1961 May;45(5):358–364. doi: 10.1136/bjo.45.5.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton A. M., Blach R. K. The technique and indications for photocoagulation in diabetic retinopathy. II. The treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Int Ophthalmol. 1979 Feb;1(2):85–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00154195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGHAM M. E. The inhibition of corneal vascularization by triethylene thiophosphoramide. Am J Ophthalmol. 1960 May;49:1111–1117. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(60)91621-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGLEY R. K., MORTIMER C. B., MCCULLOCH C. The experimental production of cataracts by exposure to heat and light. Arch Ophthalmol. 1960 Mar;63:473–488. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1960.00950020475006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAVERGNE G., COLMANT I. A. COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE ACTION OF THIOTEPA AND TRIAMCINOLONE ON CORNEAL VASCULARIZATION IN RABBITS. Br J Ophthalmol. 1964 Aug;48:416–422. doi: 10.1136/bjo.48.8.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDRAS G. La bétathérapie en ophtalmologie. Arch Ophtalmol Rev Gen Ophtalmol. 1956 Dec;16(8):811–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh R. J., Ford S. M. Cine photography and video recording of anterior segment fluorescein angiography. Br J Ophthalmol. 1978 Sep;62(9):657–659. doi: 10.1136/bjo.62.9.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer W. Cryotherapy in corneal vascularization. Arch Ophthalmol. 1967 May;77(5):637–641. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1967.00980020639013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. W., Fromer C., Klintworth G. K. Induced corneal vascularization remission with argon laser therapy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1975 Oct;93(10):1017–1019. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1975.01010020797012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sliney D. H., Wolborsht M. L. Safety standards and measurement techniques for high intensity light sources. Vision Res. 1980;20(12):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(80)90051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger W. G., Brown N. A., Edwards J. Response of the human eye to laser irradiation of the iris. Br J Ophthalmol. 1977 Feb;61(2):148–153. doi: 10.1136/bjo.61.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]