Abstract
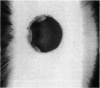
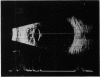
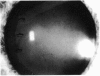
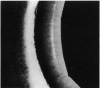
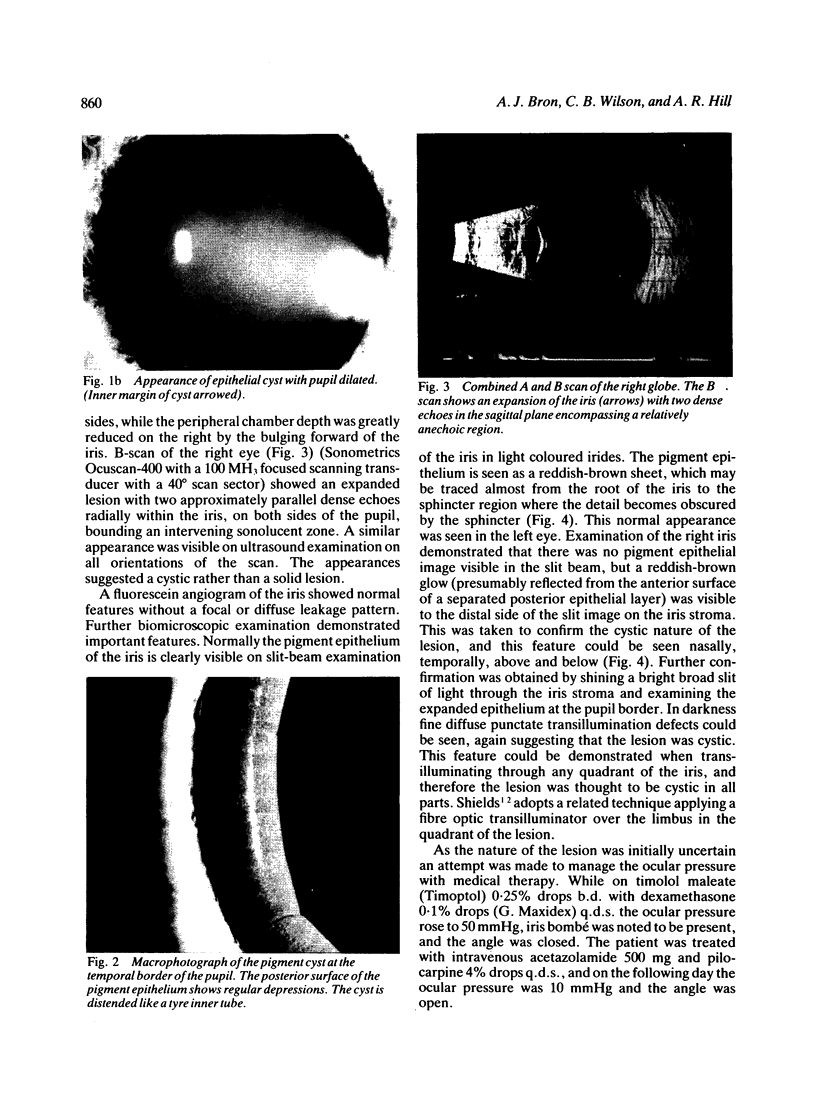
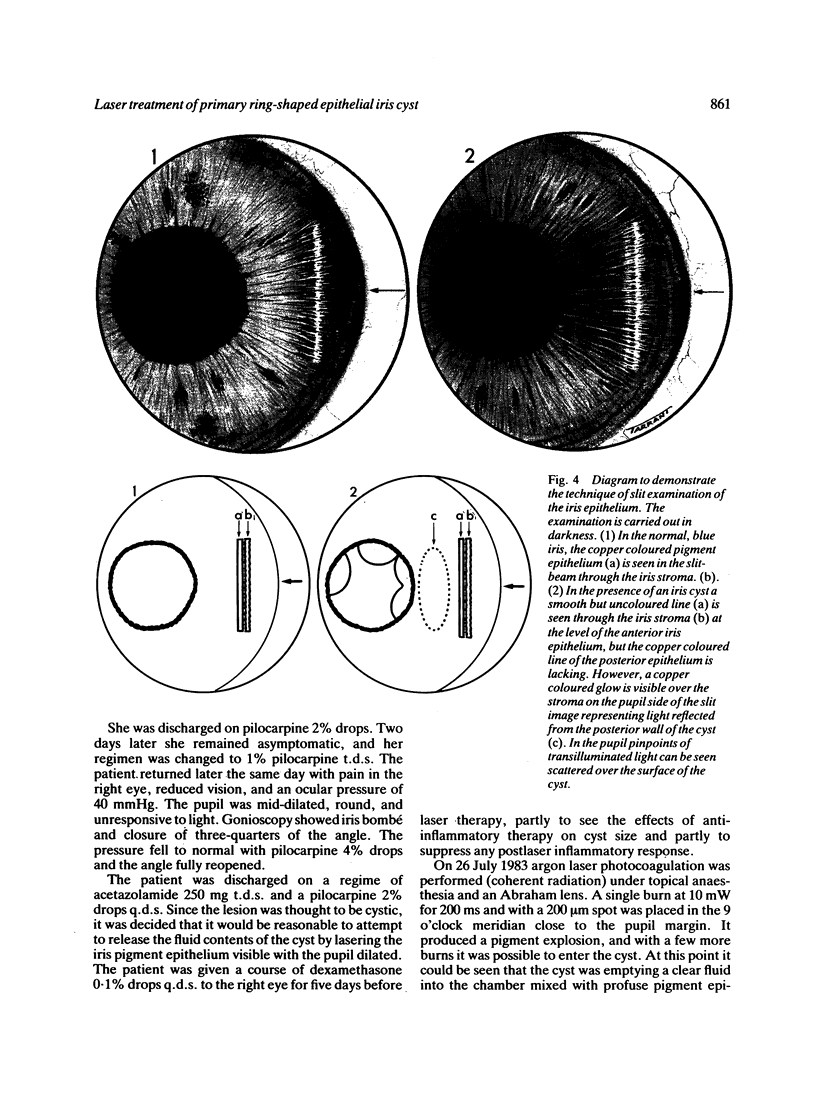
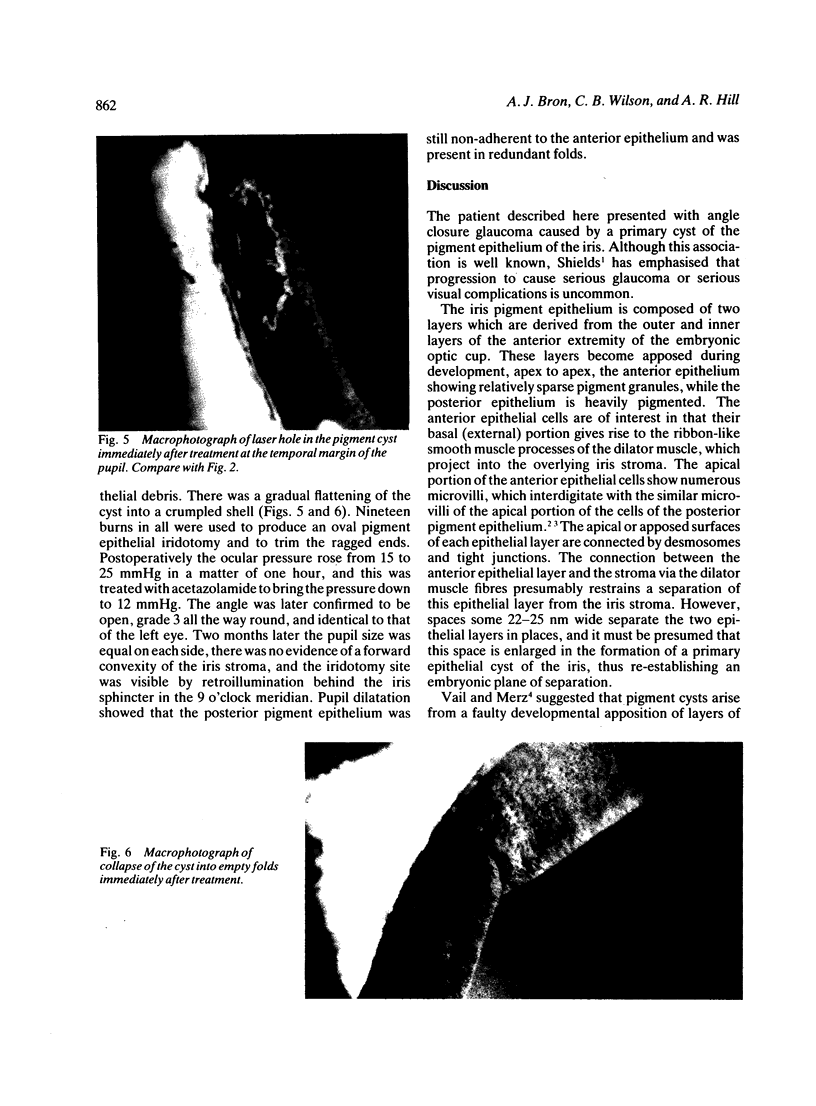
This is the first report of a ring-shaped, primary cyst of the iris pigment epithelium. The patient, a 28-year-old woman, presented with angle closure glaucoma. Ocular pressure was controlled medically, and the iris cyst was treated by argon laser photocoagulation. The derivation of the cyst, differential diagnosis, and mechanism of angle closure glaucoma are discussed.
Full text
PDF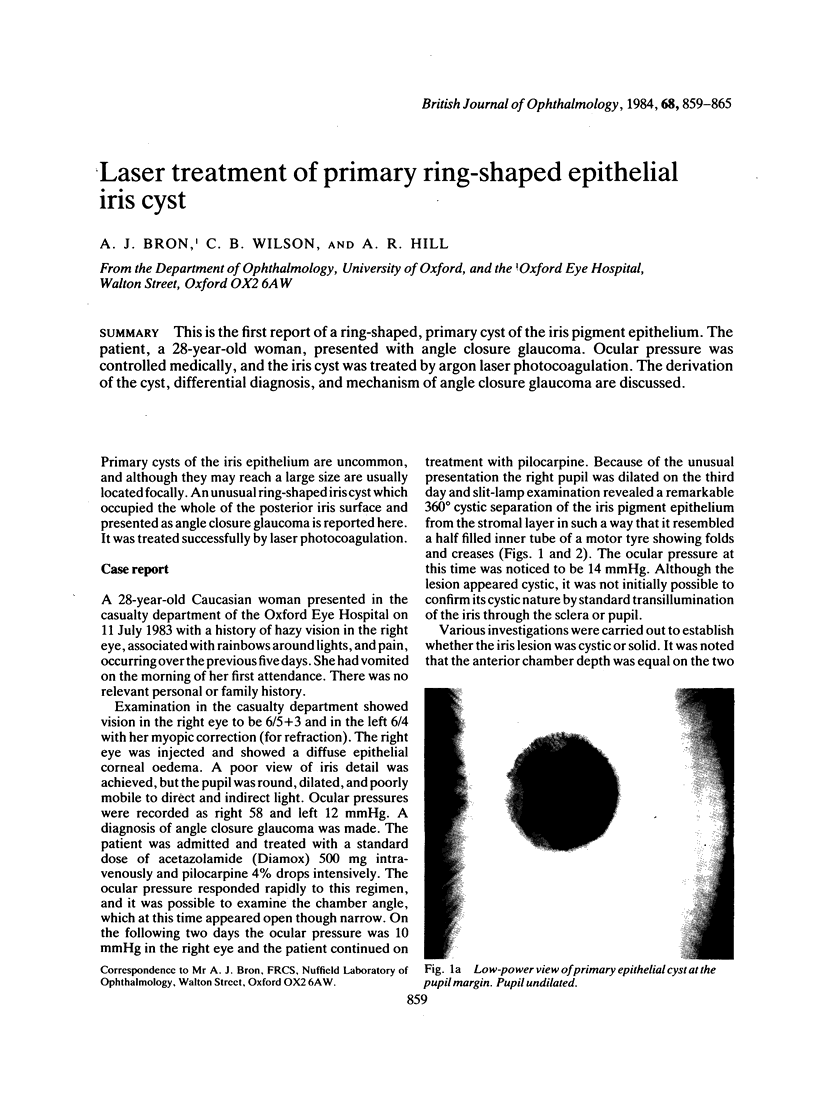



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernard J. A., Clay C. Photocoagulation au laser des kystes congénitaux du bord pupillaire. Bull Soc Ophtalmol Fr. 1981 Apr-May;81(4-5):463–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hvidberg-Hansen J. Light and electron microscopic studies of the marginal sinus (v. Szily) in the developing human eye. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol. 1971;182(2):134–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00413234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz R. T., Kelley J. S. Argon laser photocoagulation treatment of iris cysts following penetrating keratoplasty. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982 Jun;100(6):926–927. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1982.01030030934006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields J. A. Primary cysts of the iris. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1981;79:771–809. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAIL D., MERZ E. H. Embryonic intraepithelial cyst of the ciliary processes. Trans Am Soc Ophthalmol Otolaryngol Allergy. 1951;49:167–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]