Abstract
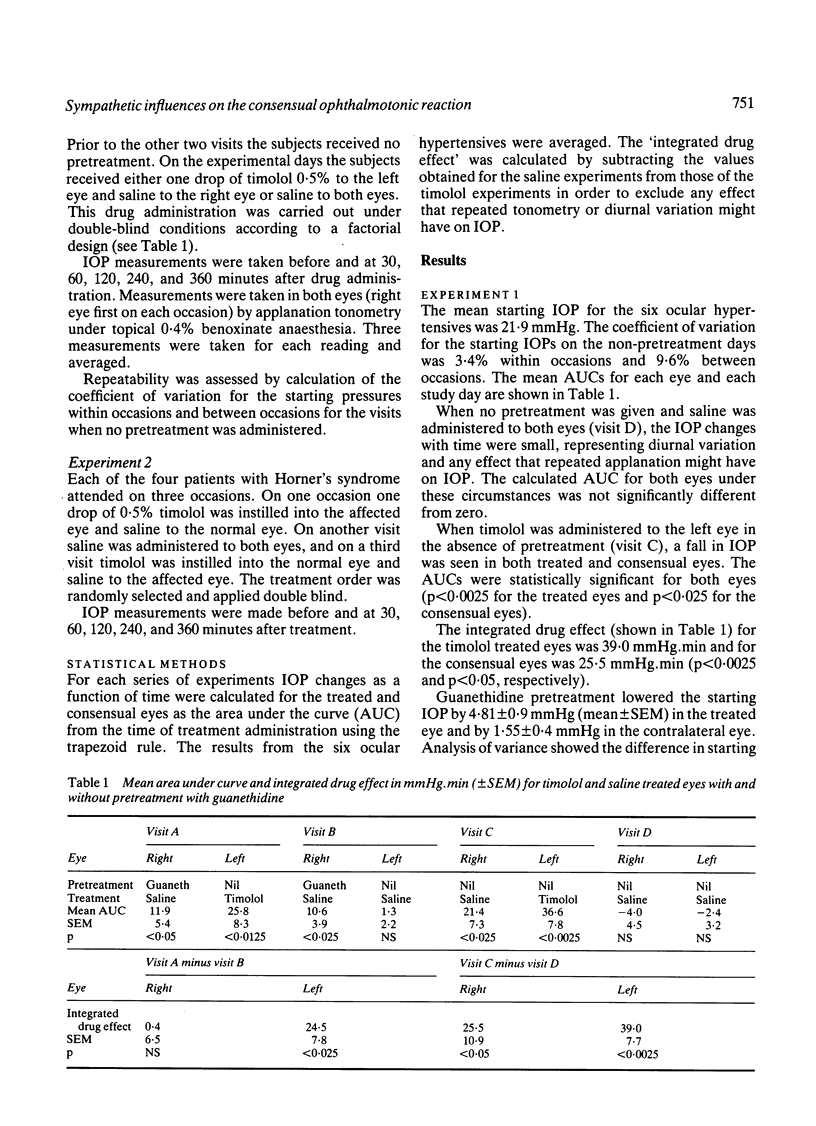
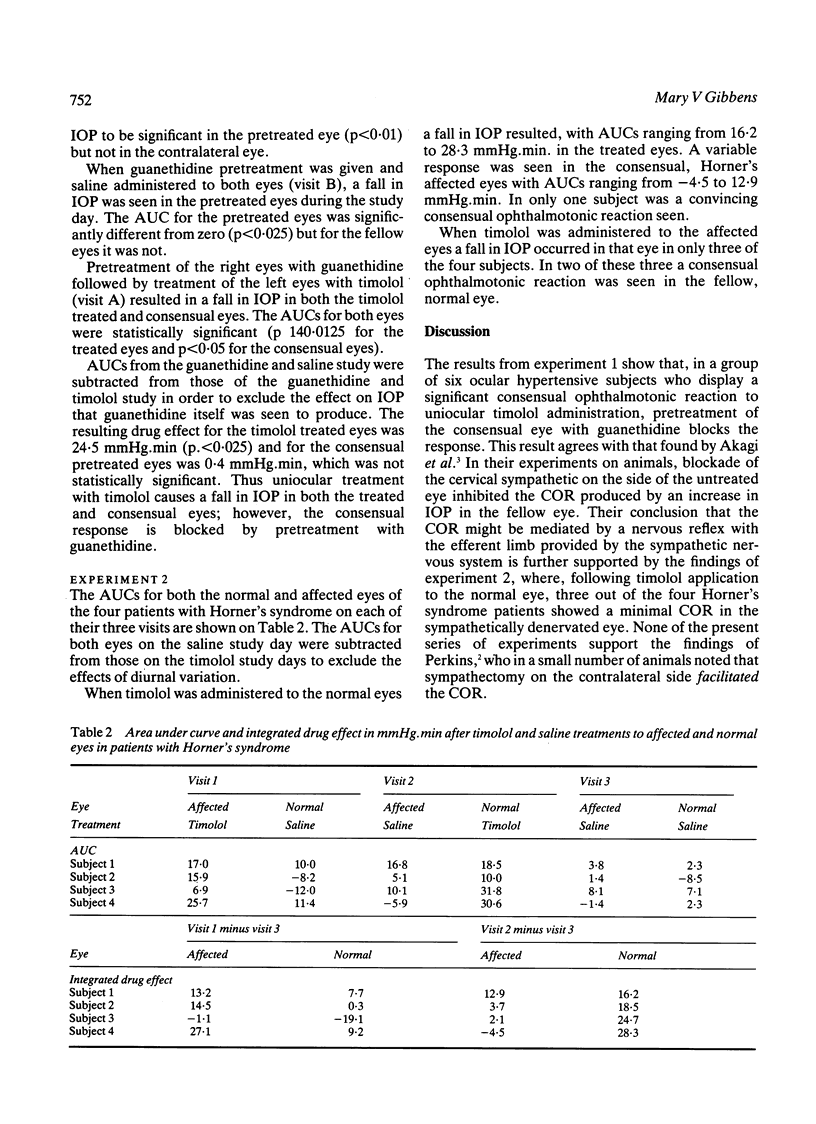
Six patients with intraocular hypertension received 0.5% timolol or saline uniocularly with saline to the other eye, and the intraocular pressure was measured by applanation tonometry at 0, 30, 60, 120, and 240 minutes. Falls in pressure were seen in both the timolol treated and consensual eyes. The same experiments were conducted after pretreatment of the consensual eyes with guanethidine 5%. The consensual ophthalmotonic reaction (COR) to timolol administration was blocked by pretreatment with guanethidine. Three out of four patients with Horner's syndrome also showed a reduced COR in the affected eye after timolol administration to the normal eye, suggesting that the COR is mediated by a nervous reflex with the efferent limb in the sympathetic nervous system.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- PERKINS E. S. Influence of the fifth cranial nerve on the intra-ocular pressure of the rabbit eye. Br J Ophthalmol. 1957 May;41(5):257–300. doi: 10.1136/bjo.41.5.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRIJOT E. L., STONE H. H. On the ophthalmotonic consensual reaction and its relationship to aqueous humor dynamics. Am J Ophthalmol. 1956 Jul;42(1):50–58. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(56)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth W. O., Brubaker R. F. Aqueous humor dynamics in a series of patients with third neuron Horner's syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1981 Sep;92(3):407–415. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(81)90533-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


