Abstract
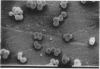
We have demonstrated, with an in vitro model, that Staphylococcus epidermidis is able to colonise intraocular lenses. Adherent organisms were quantitated by light microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and viable counting. Bacterial adherence was associated with production of a polysaccharide glycocalyx. Organisms which were attached to the lenses were resistant to apparently bactericidal concentrations of antibiotics, as determined by conventional testing. We speculate on the role of colonisation in the pathogenesis of endophthalmitis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore R. S., Mitchell M. Immunologic investigations of mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of susceptibility to opsonic antibody in mucoid and nonmucoid strains. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):238–247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore R. S., Mitchell M. Immunologic investigations of mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of susceptibility to opsonic antibody in mucoid and nonmucoid strains. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):238–247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bee J. A., Hay R. A., Lamb E. M., Devore J. J., Conrad G. W. Positional specificity of corneal nerves during development. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1986 Jan;27(1):38–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohigian G. M., Olk R. J. Factors associated with a poor visual result in endophthalmitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1986 Mar 15;101(3):332–341. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(86)90829-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Adherence of slime-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):318–326. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.318-326.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwack K. D., Petit T., Ohnson B. L., Jr, Johnson B. L., Jr Penetration of gentamicin. Administered intramuscularly and subconjunctivally into aqueous humor. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969 Nov;82(5):687–693. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1969.00990020681018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheth N. K., Franson T. R., Sohnle P. G. Influence of bacterial adherence to intravascular catheters on in-vitro antibiotic susceptibility. Lancet. 1985 Dec 7;2(8467):1266–1268. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91552-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vafidis G. C., Marsh R. J., Stacey A. R. Bacterial contamination of intraocular lens surgery. Br J Ophthalmol. 1984 Aug;68(8):520–523. doi: 10.1136/bjo.68.8.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenton M. J., Brubaker R. F., Allen H. F. Staphylococcus epidermidis (albus) endophthalmitis. Report of two cases after cataract extraction. Arch Ophthalmol. 1973 Feb;89(2):94–96. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1973.01000040096004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]