Abstract
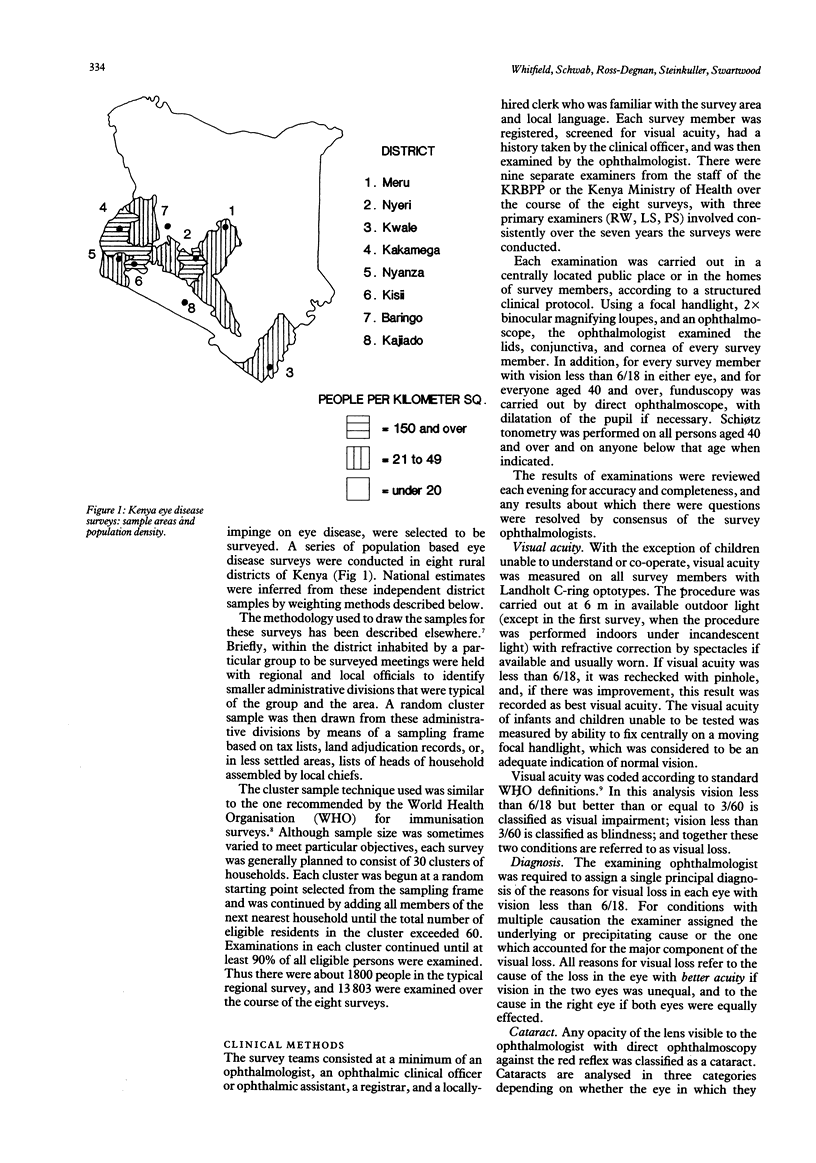
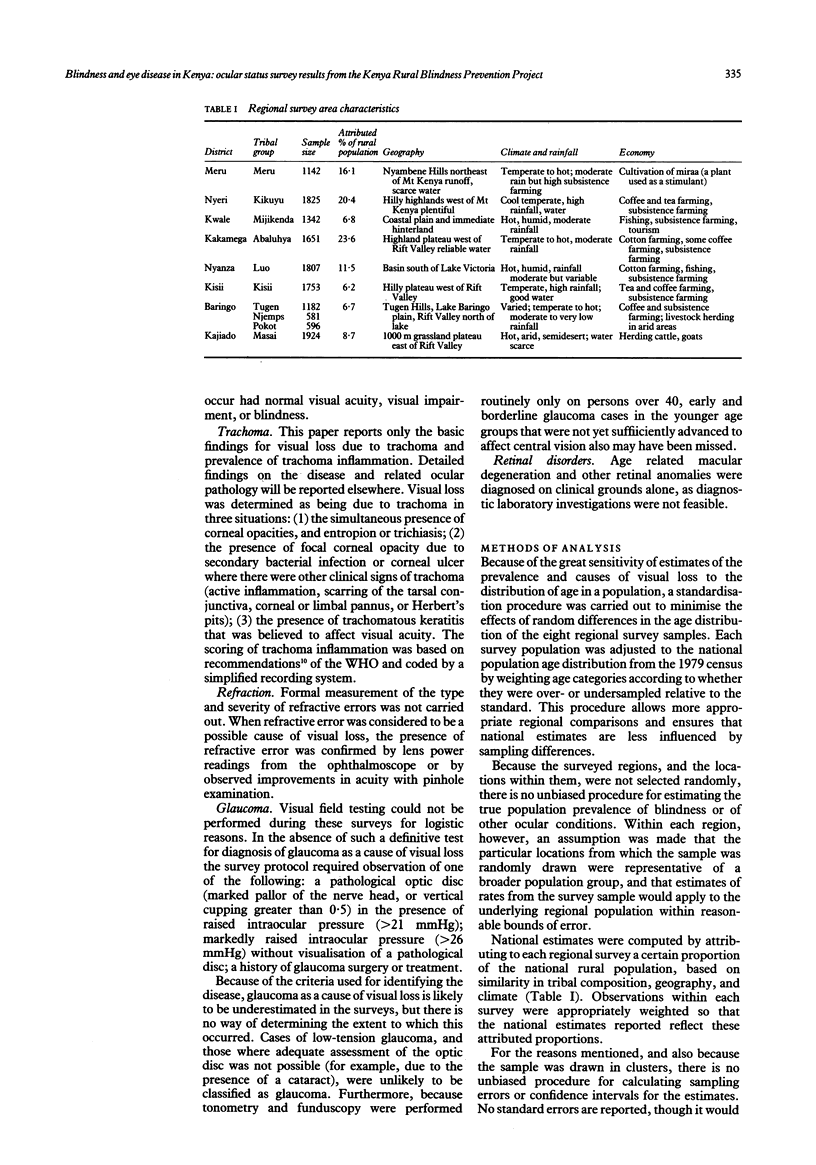
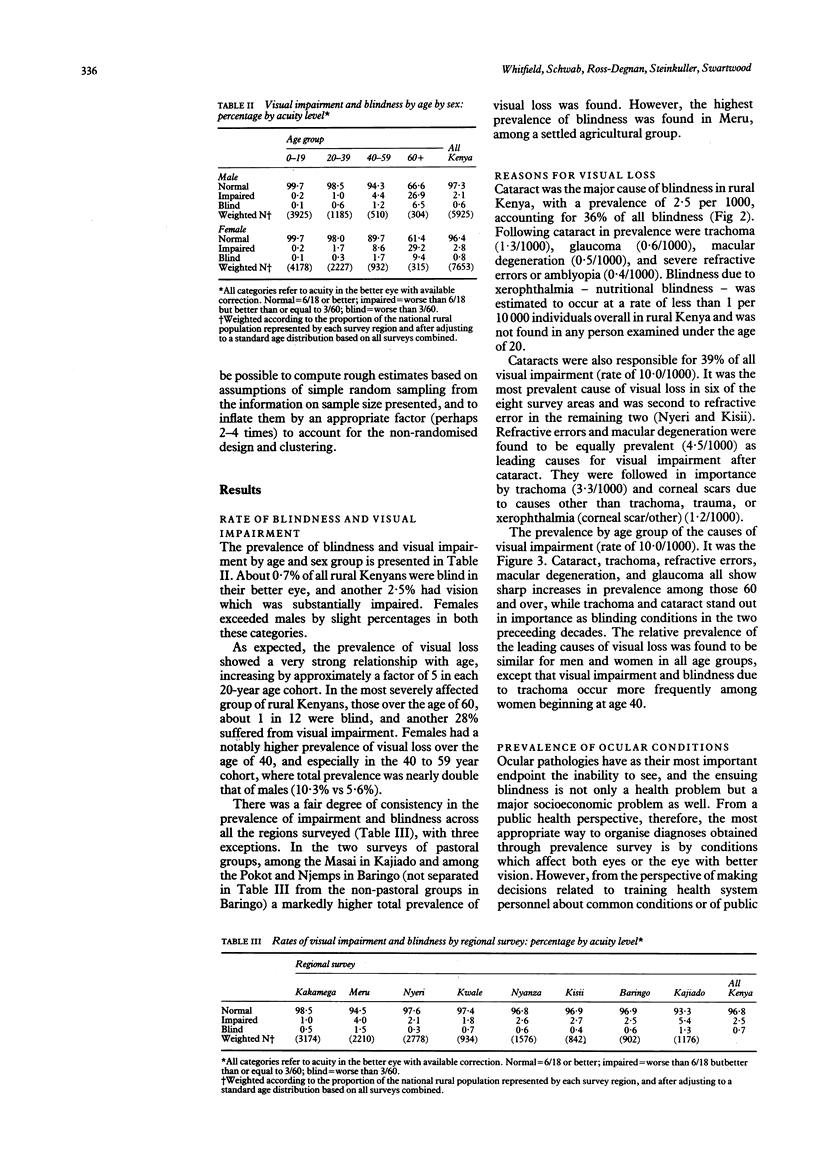
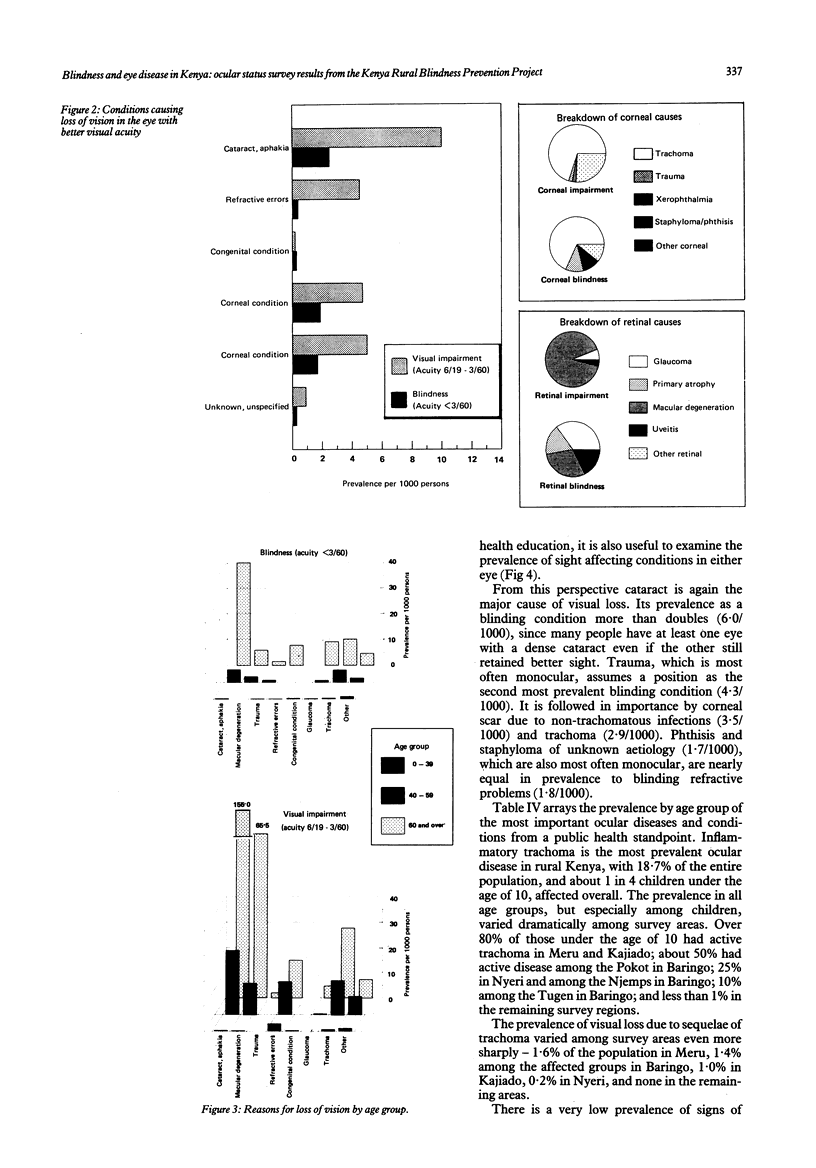
A series of eight regional eye surveys were conducted in Kenya as part of the Kenya Rural Blindness Prevention Project. Each survey consisted of clinical examinations of about 1800 individuals selected by a random cluster sampling technique in geographically distinct and culturally homogeneous rural areas; 13,803 examinations were completed in all. Together these surveys provide the basis for national estimates of the prevalence and aetiology of visual loss and ocular pathology. The results showed that 0.7% of rural Kenyans are blind in the better eye by WHO standards, and another 2.5% suffer significant visual impairment. Rates of visual loss tend to increase five-fold in each 20-year age cohort. Females have higher prevalence of visual loss than males over age 20, and certain geographical areas have markedly higher rates. The commonest cause of both blindness and visual impairment is cataract, accounting for 38% of all visual loss. Trachoma (a localised problem), glaucoma, macular degeneration, and severe refractive errors follow cataract as leading causes of blindness in the better eye. Trauma, corneal scars of various causes, phthisis, and staphyloma are important causes of monocular blindness. Nutritional eye disease does not appear to be a problem of any magnitude in rural Kenya.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbuckle R. D. The International Eye Foundation/Kenya Rural Blindness Prevention Project. Soc Sci Med. 1983;17(22):1789–1792. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(83)90393-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirambo M. C., Tielsch J. M., West K. P., Jr, Katz J., Tizazu T., Schwab L., Johnson G., Swartwood J., Taylor H. R., Sommer A. Blindness and visual impairment in southern Malawi. Bull World Health Organ. 1986;64(4):567–572. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. H., Sundaresan T. Cluster sampling to assess immunization coverage: a review of experience with a simplified sampling method. Bull World Health Organ. 1982;60(2):253–260. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross-Degnan D., Schwab L., Mburu F. M. Field methodology for ocular surveys in rural Africa. Soc Sci Med. 1983;17(22):1793–1796. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(83)90394-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinkuller P. G. Cataract: the leading cause of blindness and vision loss in Africa. Soc Sci Med. 1983;17(22):1693–1702. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(83)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabbara K. F., Ross-Degnan D. Blindness in Saudi Arabia. JAMA. 1986 Jun 27;255(24):3378–3384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thylefors B. Prevention of blindness: the current focus. WHO Chron. 1985;39(4):149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield R., Jr, Schwab L., Bakker N. J., Bisley G. G., Ross-Degnan D. Cataract and corneal opacity are the main causes of blindness in the Samburu tribe of Kenya. Ophthalmic Surg. 1983 Feb;14(2):139–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


