Abstract
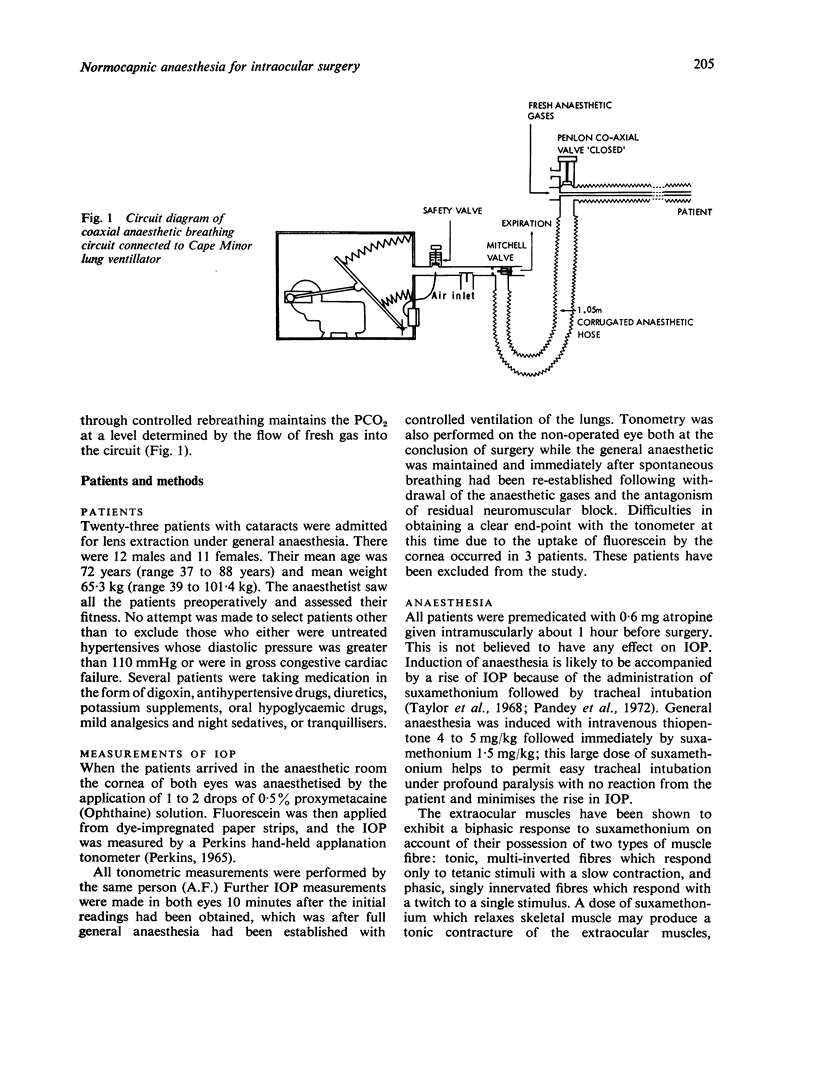
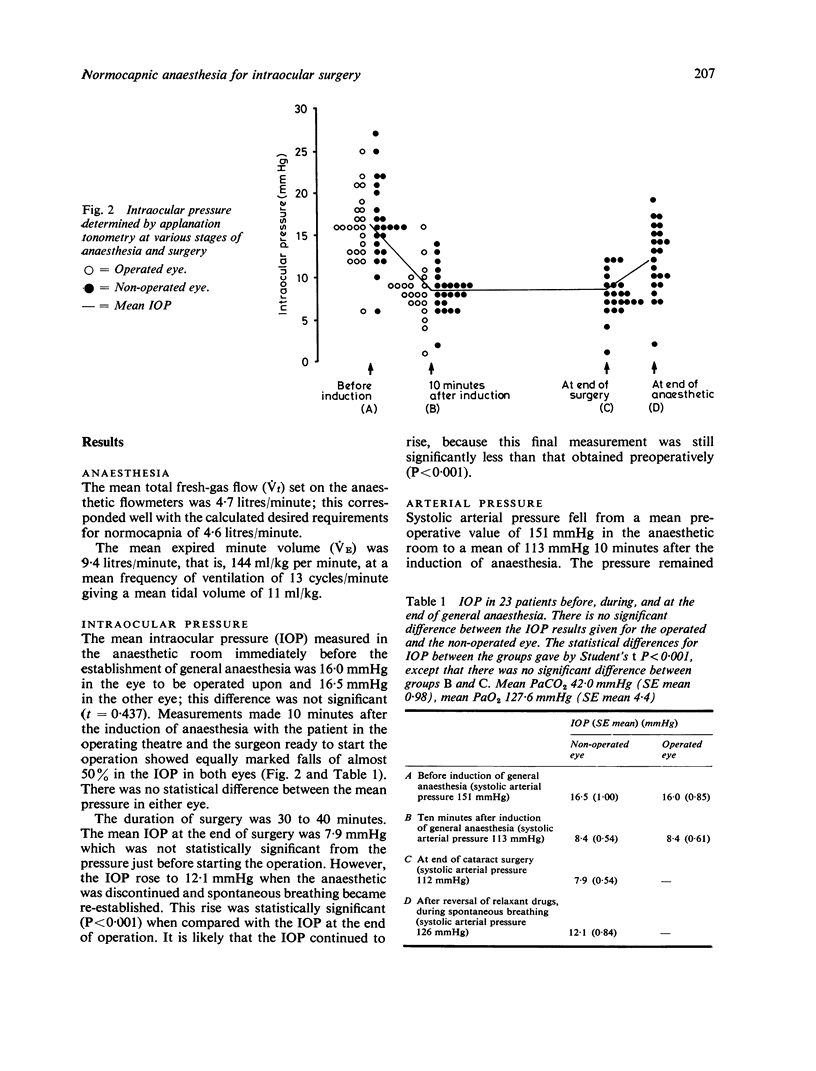
Measurement of intraocular pressure (IOP) by applanation tonometry in 23 patients undergoing lens extraction showed that a normocapnic general anaesthetic technique with controlled ventilation of the lungs (IPPV) reliably reduced the IOP by 50% for the duration of the operative period. This was not associated with large falls in systemic arterial pressure which are often a feature of spontaneously breathing halothane anaesthesia for eye surgery. Normocapnia and IPPV were easy to achieve by use of the single-limb coaxial Bain anaesthetic breathing circuit in conjunction with an electrically driven, small, and inexpensive ventilator while the anesthetic mixture of 33% oxygen and 0.5% halothane in nitrous oxide was delivered at a rate of 70 ml/kg body weight per minute.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A. K., Barnett K. C. Anaesthesia and intraocular pressure. Anaesthesia. 1966 Apr;21(2):202–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1966.tb02599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams A. P., Fordham R. M. General anesthesia in adults. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1973 Summer;13(2):83–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams A. P. The Bain circuit. Prevention of anaesthetic mixture dilution when using mechanical ventilators delivering non-anaesthetic gases. Anaesthesia. 1977 Jan;32(1):46–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1977.tb11557.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Abrak M. H., Samuel J. R. Effects of general anaesthesia on the intraocular pressure in man. Trichloroethylene in nitrous oxide and oxygen. Br J Ophthalmol. 1975 Feb;59(2):107–110. doi: 10.1136/bjo.59.2.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausinsch B., Rayburn R. L., Munson E. S., Levy N. S. Ketamine and intraocular pressure in children. Anesth Analg. 1976 Nov-Dec;55(6):773–775. doi: 10.1213/00000539-197611000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bain J. A., Spoerel W. E. Flow requirements for a modified Mapleson D system during controlled ventilation. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1973 Sep;20(5):629–636. doi: 10.1007/BF03026260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen D. J., McGrand J. C., Palmer R. J. Intraocular pressures after suxamethonium and endotracheal intubation in patients pretreated with pancuronium. Br J Anaesth. 1976 Dec;48(12):1201–1205. doi: 10.1093/bja/48.12.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAYTHORNE N. W., ROTTENSTEIN H. S., DRIPPS R. D. The effect of succinylcholine on intraocular pressure in adults, infants and children during general anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1960 Jan-Feb;21:59–63. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196001000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carballo A. S. Succinylcholine and acetazolamide (diamox) in anaesthesia for ocular surgery. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1965 Sep;12(5):486–498. doi: 10.1007/BF03004410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis J. M. Three simple ventilators. An assessment. Anaesthesia. 1967 Oct;22(4):598–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1967.tb10157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway C. M., Leigh J. M., Preston T. D., Walters F. J., Webb D. A. An assessment of three electronic respirometers. Br J Anaesth. 1974 Nov;46(11):885–891. doi: 10.1093/bja/46.11.885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUCKWORTH S. I. The Oxford non-kinking endotracheal tube. Results of its use in about 18,000 cases. Anaesthesia. 1962 Apr;17:208–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1962.tb13453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delilkan A. E., Chandran S. A three-year review of anesthesia for cataract extractions. Anesth Analg. 1972 Jul-Aug;51(4):506–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncalf D., Foldes F. F. Effect of anesthetic drugs and muscle relaxants on intraocular pressure. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1973 Summer;13(2):21–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen S., Bramsen T., Hommelgaard P. Some aspects of ocular function after precurarization. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1977;21(5):385–389. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1977.tb01236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibb D. B. Suxamethonium--a review. Pharmacological actions of suxamethonium apart from its neuromuscular blocking effect. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1974 Feb;2(1):9–26. doi: 10.1177/0310057X7400200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henville J. D., Adams A. P. A co-axial breathing circuit and scavenging valve. Anaesthesia. 1976 Mar;31(2):257–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1976.tb11799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henville J. D., Adams A. P. The Bain anaesthetic system. An assessment during controlled ventilation. Anaesthesia. 1976 Mar;31(2):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1976.tb11798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway K. B. Factors affecting intraocular pressure. Proc R Soc Med. 1977 Feb;70(2):144–144. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IVES J. Combined local and general analgesia for cataract operations. Br Med J. 1959 Mar 28;1(5125):821–823. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5125.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones W. M., Samis W. D., Macdonald D., Boyes H. W. Neuroleptanalgesia for intraocular surgery. Can J Ophthalmol. 1969 Apr;4(2):163–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi C., Bruce D. L. Thiopental and succinylcholine: Action on intraocular pressure. Anesth Analg. 1975 Jul-Aug;54(4):471–475. doi: 10.1213/00000539-197507000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L. General anaesthesia in ophthalmology. Proc R Soc Med. 1967 Dec;60(12):1275–1280. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelman G. R., Nunn J. F. Nomograms for correction of blood Po2, Pco2, pH, and base excess for time and temperature. J Appl Physiol. 1966 Sep;21(5):1484–1490. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.5.1484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch S., Wolf G. L., Berlin I. General anesthesia for cataract surgery: a comparative review of 2217 consecutive cases. Anesth Analg. 1974 Nov-Dec;53(6):909–913. doi: 10.1213/00000539-197453060-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGORA F., COLLINS V. J. The influence of general anesthetic agents on intraocular pressure in man. The effect of common nonexplosive agents. Arch Ophthalmol. 1961 Dec;66:806–811. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1961.00960010808006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. D., Way W. L., Hickey R. F. Inhibition of succinylcholine-induced increased intraocular pressure by non-depolarizing muscle relaxants. Anesthesiology. 1968 Jan-Feb;29(1):123–126. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196801000-00031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey K., Badola R. P., Kumar S. Time course of intraocular hypertension produced by suxamethonium. Br J Anaesth. 1972 Feb;44(2):191–196. doi: 10.1093/bja/44.2.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins E. S. Hand-held applanation tonometer. Br J Ophthalmol. 1965 Nov;49(11):591–593. doi: 10.1136/bjo.49.11.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peuler M., Glass D. D., Arens J. F. Ketamine and intraocular pressure. Anesthesiology. 1975 Nov;43(5):575–578. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197511000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prys-Roberts C., Kelman G. R., Greenbaum R., Robinson R. H. Circulatory influences of artificial ventilation during nitrous oxide anaesthesia in man. II. Results: the relative influence of mean intrathoracic pressure and arterial carbon dioxide tension. Br J Anaesth. 1967 Jul;39(7):533–548. doi: 10.1093/bja/39.7.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prys-Roberts C., Meloche R., Foëx P. Studies of anaesthesia in relation to hypertension. I. Cardiovascular responses of treated and untreated patients. Br J Anaesth. 1971 Feb;43(2):122–137. doi: 10.1093/bja/43.2.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz R. S., Salmonsen P. C. Expulsive choroidal effusion. A complication of intraocular surgery. Arch Ophthalmol. 1976 Jan;94(1):69–70. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1976.03910030027008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvatore A. J., Sullivan S. F., Papper E. M. Postoperative hypoventilation and hypoxemia in man after hyperventilation. N Engl J Med. 1969 Feb 27;280(9):467–470. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196902272800903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel J. R., Beaugié A. Effect of carbon dioxide on the intraocular pressure in man during general anaesthesia. Br J Ophthalmol. 1974 Jan;58(1):62–67. doi: 10.1136/bjo.58.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scullica L., Montanini S., Sinardi A., De Salvo R. Sui vantaggi della ipotensione arteriosa nella chirurgia oculare. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1973 Aug 15;49(15):938–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I., Beveridge M. E., Wyllie A. M. 4-Hydroxybutyrate narcosis for ophthalmic surgery. Br J Ophthalmol. 1972 May;56(5):429–435. doi: 10.1136/bjo.56.5.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow J. C., Sensel S. A review of cataract extraction under local and general anesthesia at the Massachusetts eye and ear infirmary. Anesth Analg. 1966 Nov-Dec;45(6):742–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor T. H., Mulcahy M., Nightingale D. A. Suxamethonium chloride in intraocular surgery. Br J Anaesth. 1968 Feb;40(2):113–118. doi: 10.1093/bja/40.2.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T. M., Le May M., Holloway K. B., Strang R., McKenzie E. Experimental and clinical study of factors influencing choroidal blood flow. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1974 Jul;94(2):378–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wislicki L. Factors affecting Intraocular Pressure. Proc R Soc Med. 1976 Dec;69(12):952–952. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa K., Murai Y. The effect of ketamine on intraocular pressure in children. Anesth Analg. 1971 Mar-Apr;50(2):199–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Abrak M. H., Samuel J. R. Further observations on the effects of general anaesthesia on intraocular pressure in man: halothane in nitrous oxide and oxygen. Br J Anaesth. 1974 Oct;46(10):756–759. doi: 10.1093/bja/46.10.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


