Abstract
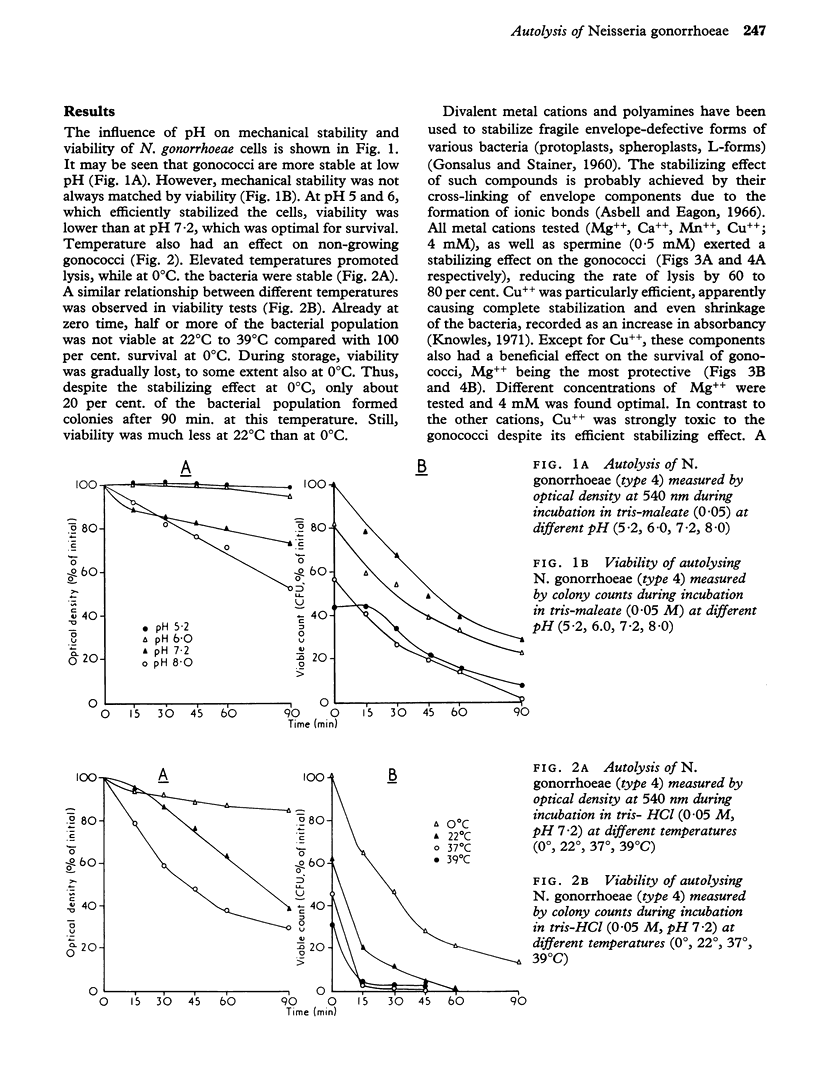
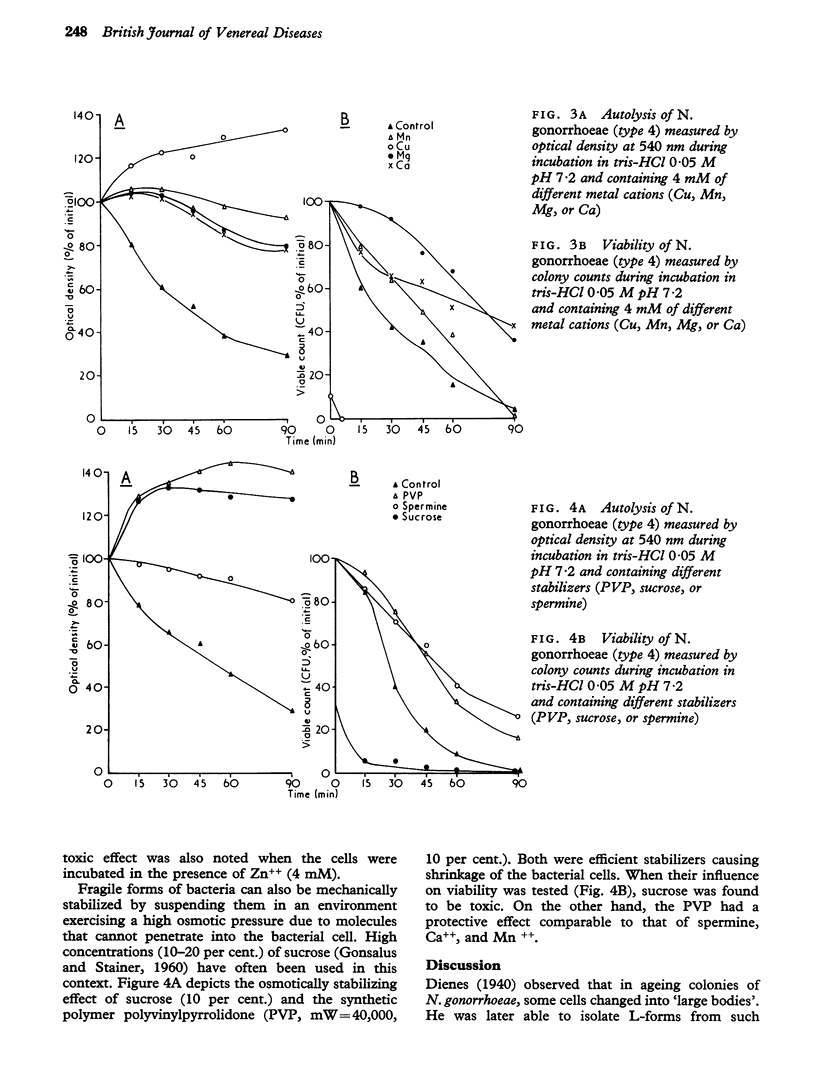
The relationship between the mechanical stability and the viability of N. gonorrhoeae (Type 4) in suspension was investigated. A correlation between viability and optical density recordings was often found. However, in spite of increased mechanical stability in solutions with low pH (5-2) or containing Cu++ or sucrose (10 per cent.), these environments were toxic to the gonococci. A viability preserving effect by Mg++ (4 mM), Ca++ (4 mM), spermine (0-5 mM), polyvinylpyrrolidone (10 per cent.), and low temperature (4 degrees C) was demonstrated. The possibility of improving transport media for gonococci is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asbell M. A., Eagon R. G. Role of Multivalent Cations in the Organization, Structure, and Assembly of the Cell Wall of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;92(2):380–387. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.2.380-387.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIENES L., BANDUR B. M., MADOFF S. DEVELOPMENT OF L-TYPE GROWTH IN NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE CULTURES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1471–1476. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1471-1476.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmros T., Hörstedt P., Winblad B. Scanning electron microscopic study of virulent and avirulent colonies of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):630–637. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.630-637.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiscina B., Oster G. K., Oster G., Swanson J. Gonococcicidal action of capper in vitro. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1973 May 1;116(1):86–90. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(73)90889-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M. Use of bacteriolytic enzymes in determination of wall structure and their role in cell metabolism. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 2):425–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnarpe H., Wallin J., Forsgren A. Studies in venereal disease. I. Isolation of L-phase organisms of N. gonorrhoeae from patients with gonorrhoea. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Dec;48(6):496–499. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.6.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebeler B. H., Young F. E. Autolysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):385–392. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.385-392.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosty T. S., Freear M. A., Baker C., Holston J. Comparison of transportation media for the culturing of N. gonorrhoeae. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Sep;62(3):435–437. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/62.3.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles C. J. Salt induces changes of turbidity and volume of E. coli. Nat New Biol. 1971 Feb 3;229(5):154–155. doi: 10.1038/newbio229154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spellacy W. N., Hiser B. J., Birk S. A. The effect of copper intrauterine devices on endocervical gonococcal cultures. Fertil Steril. 1974 Sep;25(9):772–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


