Abstract
Eight hundred and twenty-three examinations were carried out on 662 homosexual patients. At each examination a blind anorectal swab and a rectal swab taken via a proctoscope were inoculated on to a culture plate. From a total of 100 gonococcal infections of the rectum 96 gave positive results from blind anorectal swabs and 99 from swabs taken via a proctoscope. Blind anorectal swabs proved to be a reliable method in the diagnosis of rectal gonorrhoea.
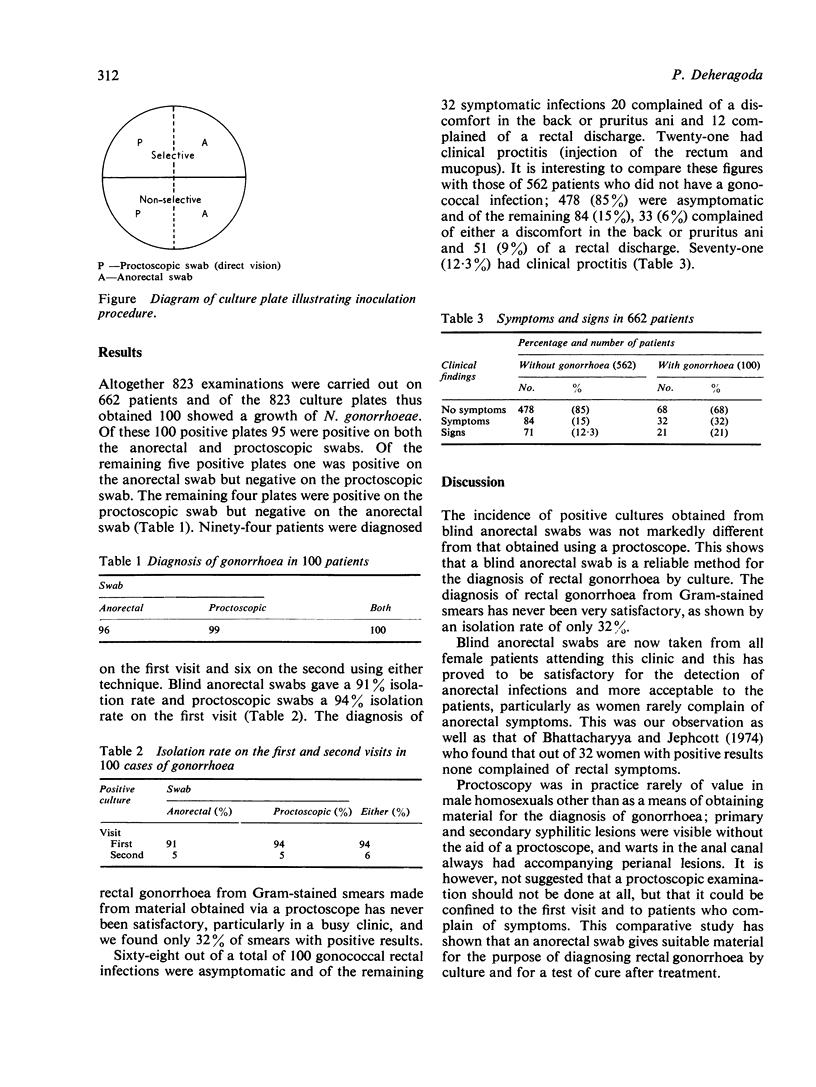
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharyya M. N., Jephcott A. E. Diagnosis of gonorrhoea in women. Role of the rectal sample. Br J Vener Dis. 1974 Apr;50(2):109–112. doi: 10.1136/sti.50.2.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odegaard K., Gundersen H., Gundersen T. Rectumgonoré hos kvinner. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 1971 Jul 10;91(19):1474–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeter A. L., Reynolds G. The rectal culture as a test of cure of gonorrhea in the female. J Infect Dis. 1972 May;125(5):499–503. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.5.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F., Yobs A. R., Billings T. E., Hackney J. F. Spectinomycin sulfate and aqueous procaine penicillin G in treatment of female gonorrhea. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1965;5:689–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


