Abstract
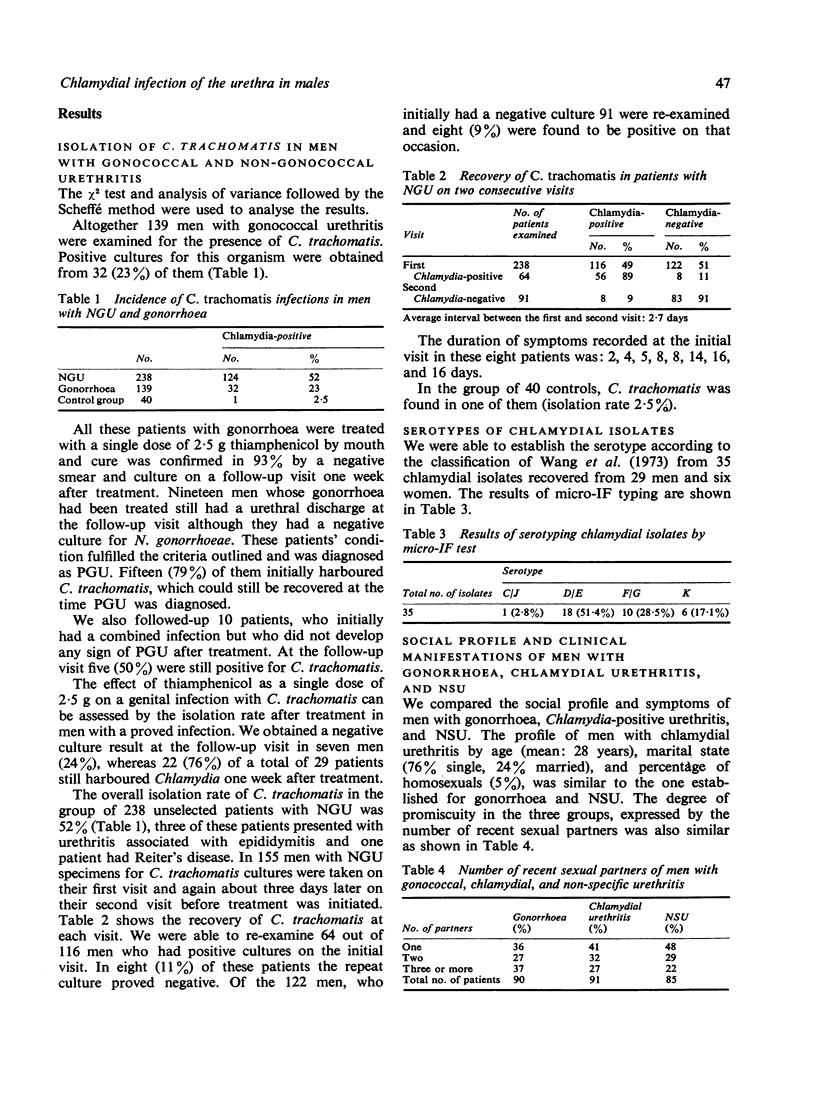
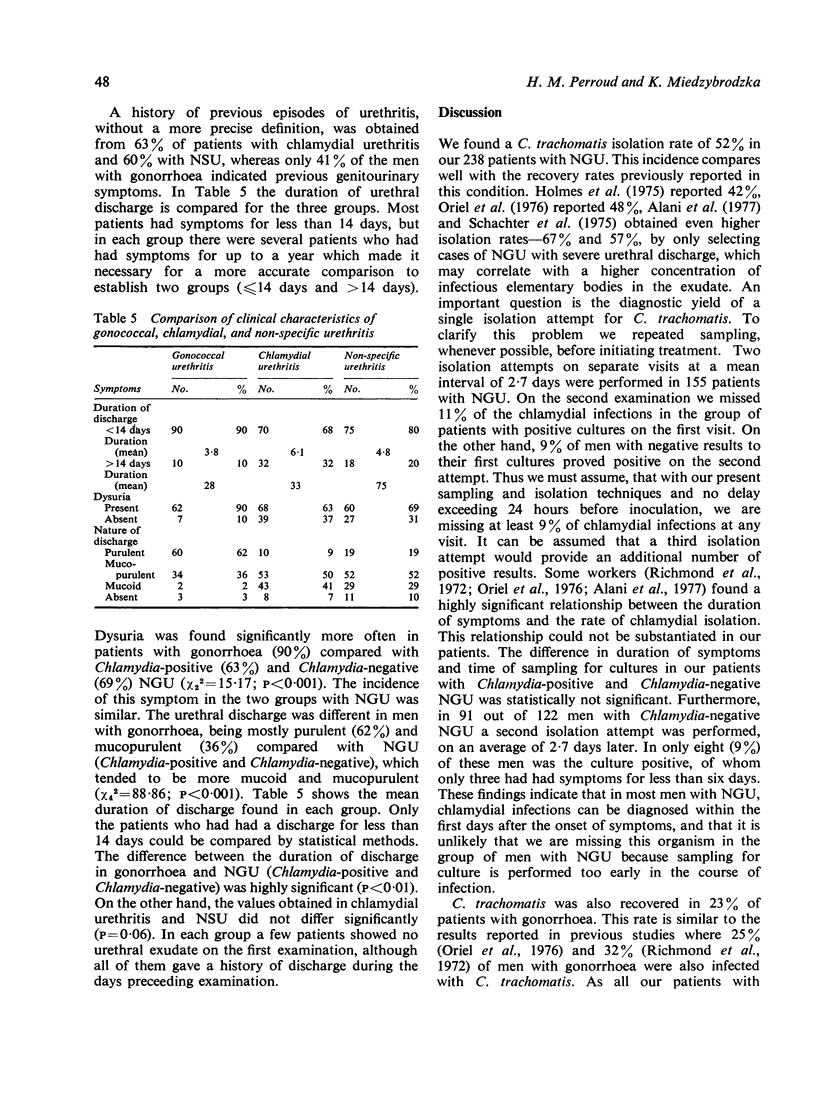
Chlamydia trachomatis was isolated from the uretha of 125 (52%) of 238 men with non-gonococcal urethritis (NGU). Repeat isolation attempts in 155 of these patients were successful in eight men in whom results had been negative on the initial visit, but they were unsuccessful in eight men who initially had had positive cultures. We must assume that with our present isolation techniques we are missing, at any single visit, at least 9% of chlamydial infections. C. trachomatis was also found in 32 (23%) of 139 men with gonorrhoea. Positive cultures were obtained from 15 (79%) of 19 men, who later developed post-gonococcal urethritis (PGU). Thiamphenicol, used for the treatment of gonorrhoea, was shown to have very little effect on C. trachomatis, which could still be recovered after treatment in 76% of the patients who initially had had a combined infection. The typing of 35 genital isolates by micro-immunofluorescence confirms the previously reported distribution of chlamydial serotypes. In this study a social profile is given of our patients with urethritis and a comparison is made of the duration of symptoms and the nature of discharge in men with gonococcal, chlamydial, and non-specific urethritis. We were able to show a clear difference in clinical symptoms in men with gonorrhoea and NGU, taken as a whole, but found only a slight difference between men with chlamydial and non-specific urethritis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alani M. D., Darougar S., Burns D. C., Thin R. N., Dunn H. Isolation of Chlamydia trachomatis from the male urethra. Br J Vener Dis. 1977 Apr;53(2):88–92. doi: 10.1136/sti.53.2.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. K., Handsfield H. H., Wang S. P., Wentworth B. B., Turck M., Anderson J. B., Alexander E. R. Etiology of nongonococcal urethritis. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jun 5;292(23):1199–1205. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197506052922301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs N. F., Kraus S. J. Gonococcal and nongonococcal urethritis in men. Clinical and laboratory differentiation. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jan;82(1):7–12. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-1-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McChesney J. A., Zedd A., King H., Russell C. M., Hendley J. O. Acute urethritis in male college students. JAMA. 1973 Oct 1;226(1):37–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriel J. D., Reeve P., Thomas B. J., Nicol C. S. Infection with Chlamydia group A in men with urethritis due to Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):376–382. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriel J. D., Reeve P., Wright J. T., Owen J. Chlamydial infection of the male urethra. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Feb;52(1):46–51. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perroud H. M. Die Chlamydien-Urethritis. Schweiz Rundsch Med Prax. 1977 Sep 20;66(38):1213–1217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve P., Owen J., Oriel J. D. Laboratory procedures for the isolation of chlamydia trachomatis from the human genital tract. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Nov;28(11):910–914. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.11.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond S. J., Hilton A. L., Clarke S. K. Chlamydial infection. Role of Chlamydia subgroup A in non-gonococcal and post-gonococcal urethritis. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Dec;48(6):437–444. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.6.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J., Hanna L., Hill E. C., Massad S., Sheppard C. W., Conte J. E., Jr, Cohen S. N., Meyer K. F. Are chlamydial infections the most prevalent venereal disease? JAMA. 1975 Mar 24;231(12):1252–1255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treharne J. D., Davey S. J., Gray S. J., Jones B. R. Immunological classification of TRIC agents and of some recently isolated LGV agents by the micro-immunofluorescence test. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Feb;48(1):18–25. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Kuo C. C., Grayston J. T. A simplified method for immunological typing of trachoma-inclusion conjunctivitis-lymphogranuloma venereum organisms. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):356–360. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.356-360.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


