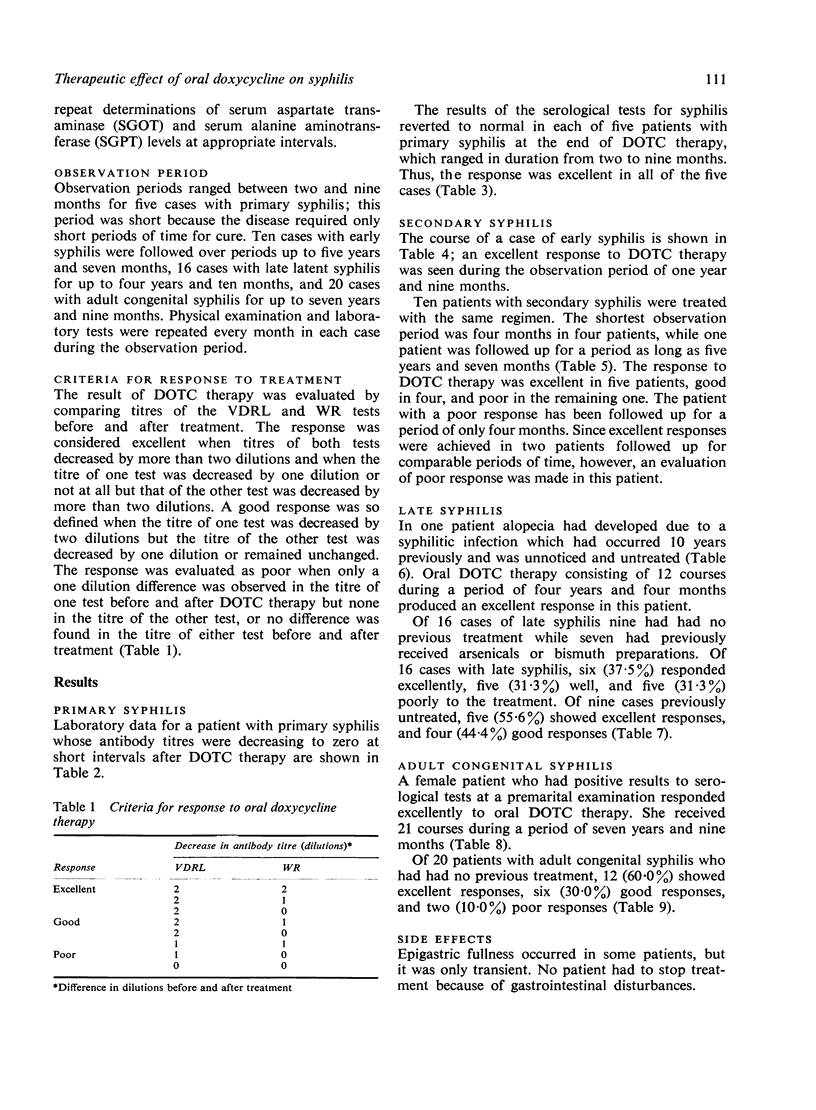
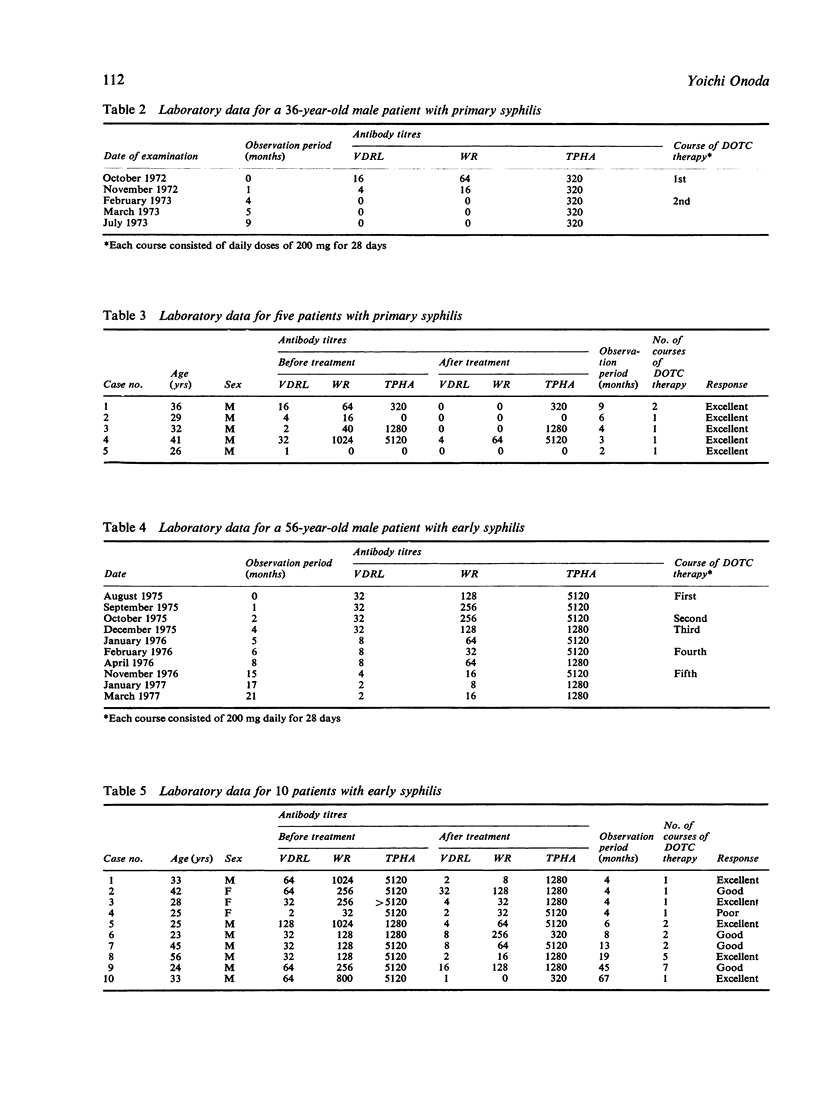
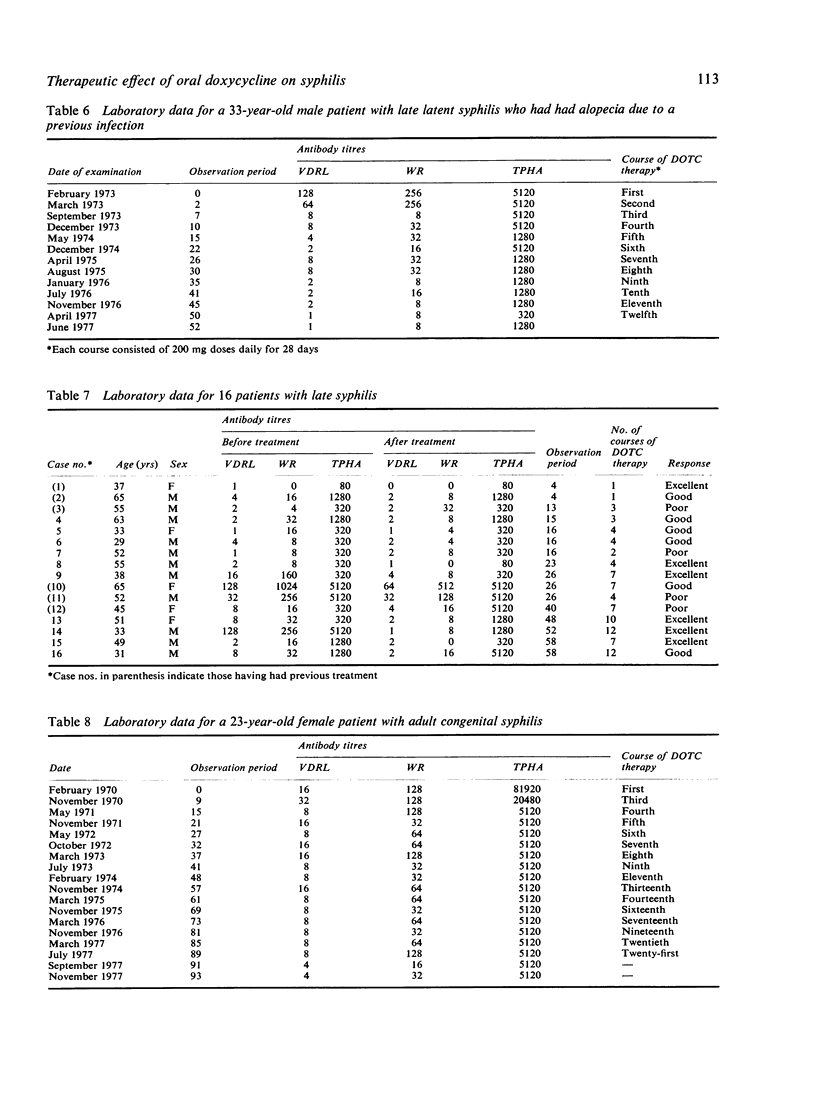
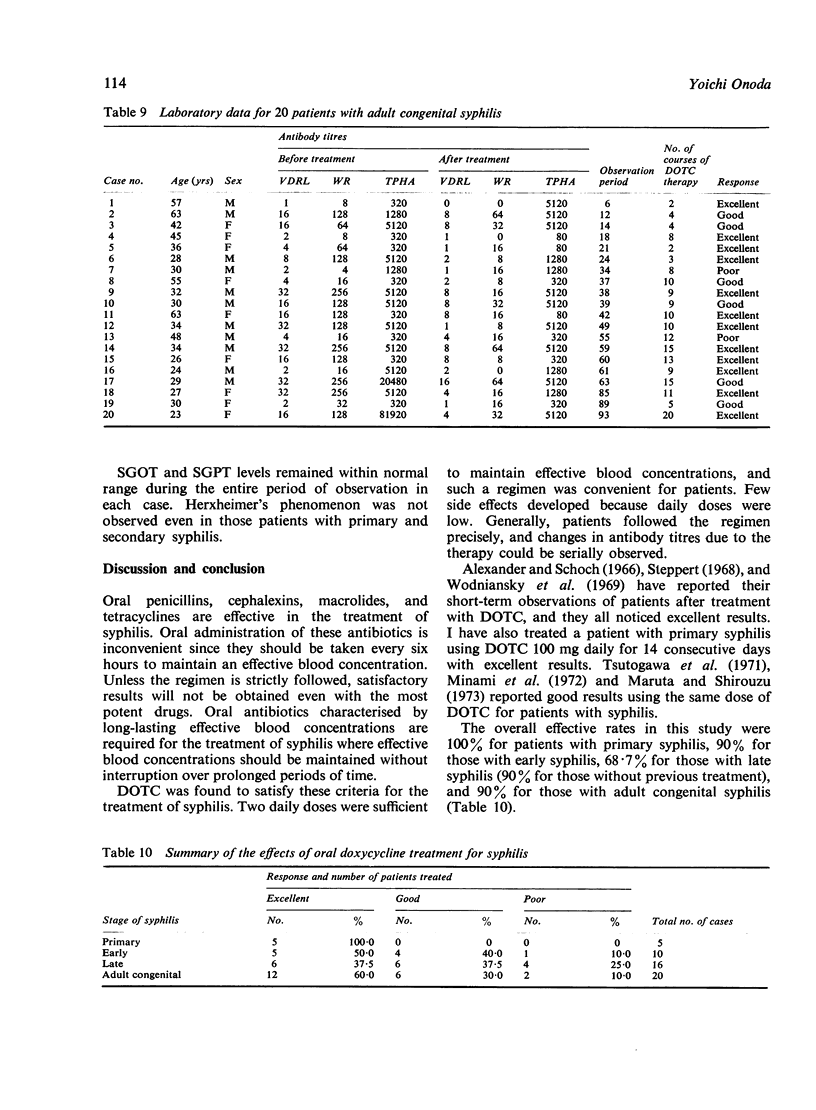
Abstract
Fifty-one patients with syphilis were treated with oral doxycycline. A course of the antibiotic treatment consisted of 200 mg of doxycycline daily in two divided doses for 28 days. The courses were repeated three to four times a year with an interval of several months. Quantitative Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL), Wassermann reaction (WR), and Treponema pallidum haemagglutination assay (TPHA) tests were performed monthly to evaluate the therapeutic effect of doxycycline treatment. The response rate was 100% for primary, 90% for early, 68% for late, and 90% for congenital syphilis in adults. No notable side effects were encountered except for epigastric fullness in one patient, which did not require the treatment to be discontinued. No abnormalities were detected in the results of laboratory tests.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Steppert A. Zur Therapei bakterieller Hautinfektionen und venerischer Erkrankungen. Wien Med Wochenschr. 1968 Jun 22;118(25):599–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


