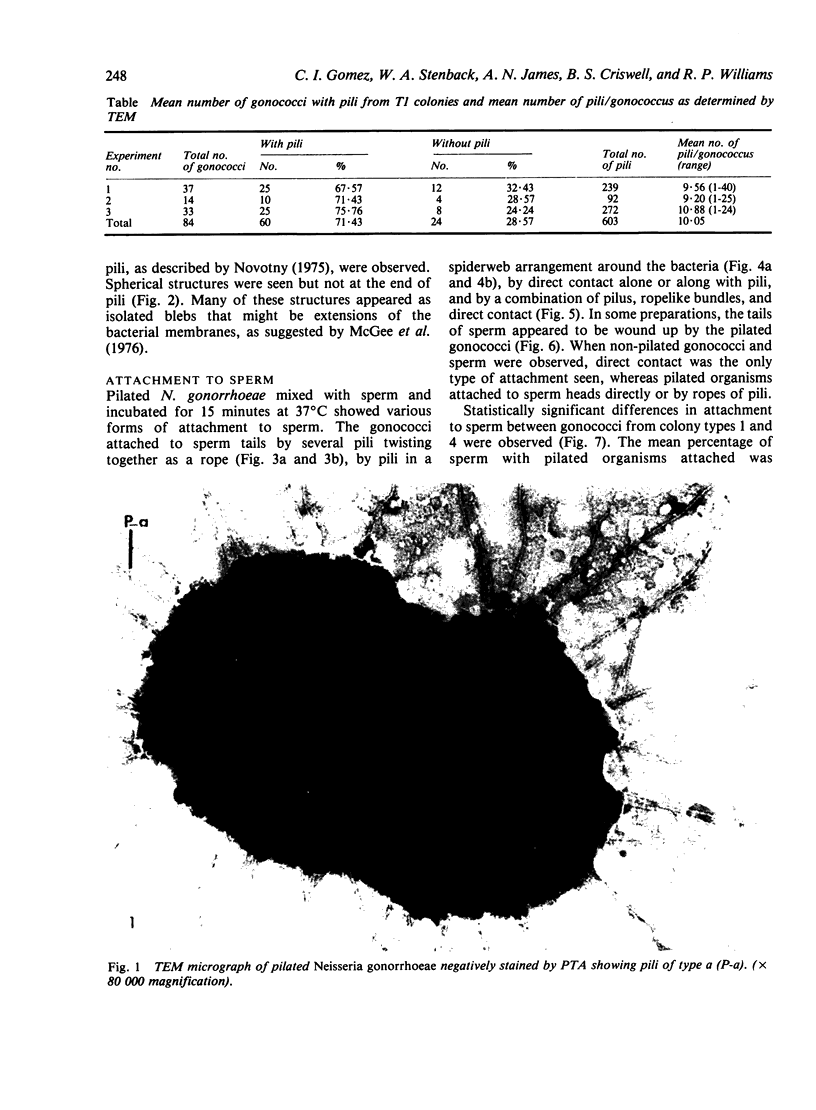
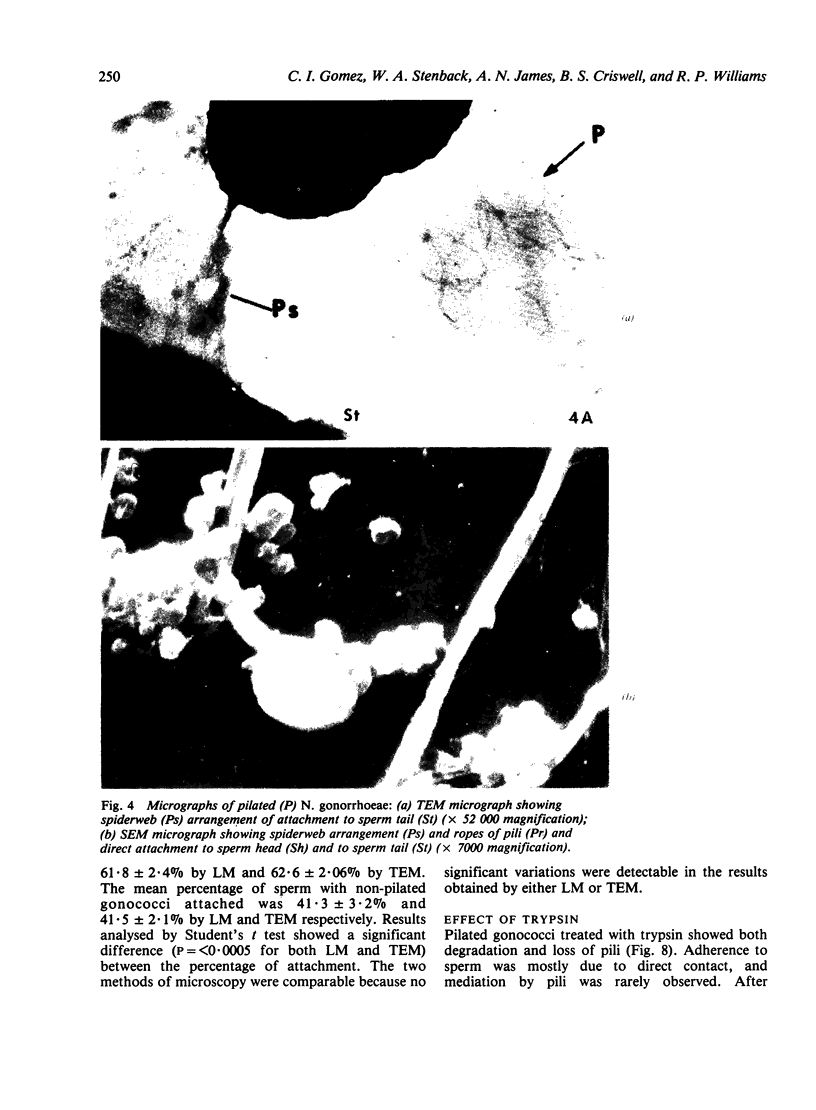
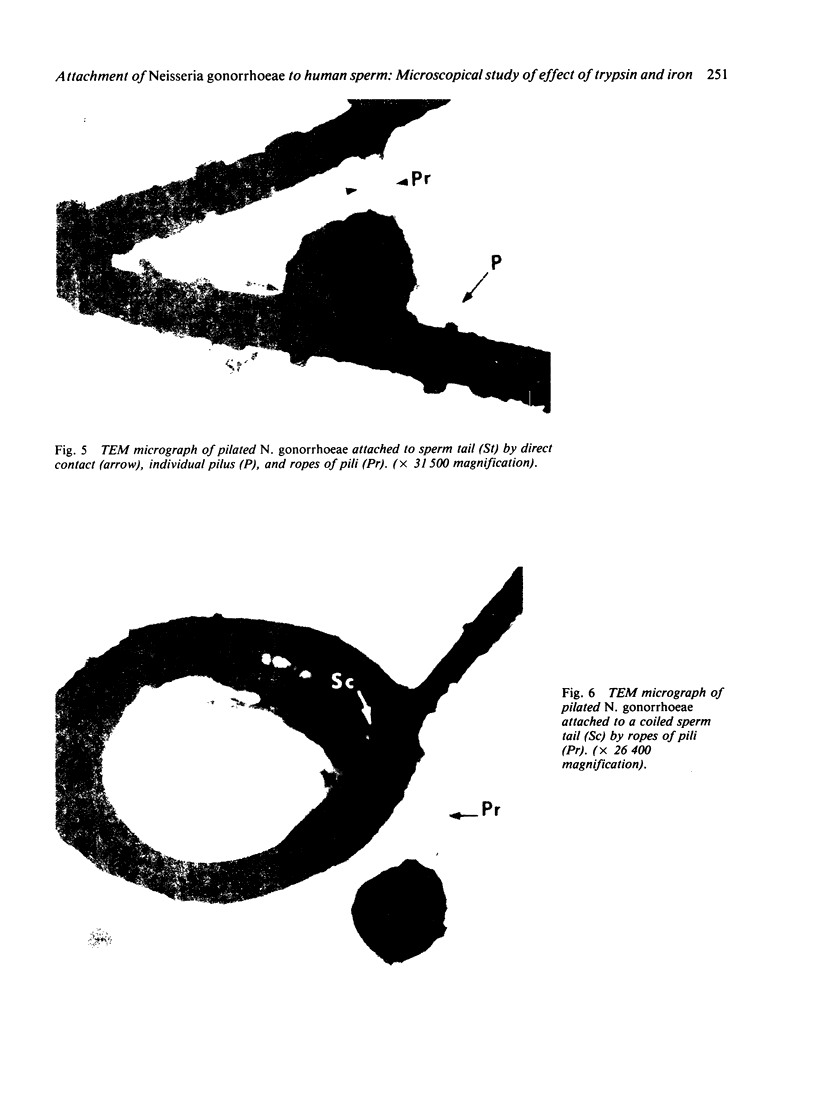
Abstract
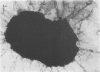
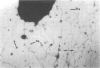
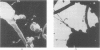
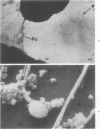
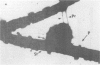
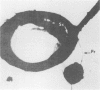
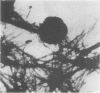
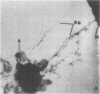
Pilated Neisseria gonorrhoeae of colony type 1 (T1) and non-pilated bacteria of colony type 4 (T4) were observed by transmission (TEM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). No pili were observed on T4 gonogocci, but two types of pili--straight, type a, and bent, type b--were seen on T1 by TEM. When incubated with human sperum and examined by either TEM or SEM, T1 gonococci were seen to attach by individual pili, by several pili wound together as a rope, or by direct contact. Gonococci from T4 colonies attached only by direct contact. Treatment with typsin (1 mg/ml) damaged or removed pili from gonococci. After incubation with trypsin, attachment of pilated gonococci to sperm was decreased significantly, but such treatment did not affect attachment of non-pilated gonococci. Incubation of gonococci from either colony type in 0.1 mmol/l ferric nitrate, followed by incubation with sperm, significantly increased attachment of only T4 bacteria. No pili were seen on T4 gonococci treated with ferric nitrate; thus, it appears that factors other than pili alone are concerned in attachment of these gonococci to sperm.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arya O. P., Nsanzumuhire H., Taber S. R. Clinical, cultural, and demographic aspects of gonorrhoea in a rural community in Uganda. Bull World Health Organ. 1973;49(6):587–595. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch R. G. Bacterial cytochromes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1968;22:181–200. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.22.100168.001145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Swanson J., Holmes K. K., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Quantitative determination of antibody to gonococcal pili. Changes in antibody levels with gonococcal infection. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2896–2909. doi: 10.1172/JCI107486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVoe I. W., Gilchrist J. E. Pili on meningococci from primary cultures of nasopharyngeal carriers and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with acute disease. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):297–305. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes D. M., Dooher G. B., O'Leary W. M. Evidence by scanning electron microscopy for an association between spermatozoa and T-mycoplasmas in men of infertile marriage. Fertil Steril. 1975 Dec;26(12):1203–1211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes D. M., MacLeod J., O'Leary W. M. T-mycoplasmas and human infertility: correlation of infection with alterations in seminal parameters. Fertil Steril. 1975 Dec;26(12):1212–1218. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)41537-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimble A., Armitage L. R. Surface structures of the gonococcus. Br J Vener Dis. 1974 Oct;50(5):354–359. doi: 10.1136/sti.50.5.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E., Blackett B., Everson J. S., Ward M. E. The influence of surface charge on the attachment of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to human cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Oct;96(2):359–364. doi: 10.1099/00221287-96-2-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard T. L. Bacterial hitch-hikers. J Urol. 1971 Jul;106(1):94–94. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)61232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James-Holmquest A. N., Swanson J., Buchanan T. M., Wende R. D., Williams R. P. Differential attachment by piliated and nonpiliated Neisseria gonorrhoeae to human sperm. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):897–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.897-902.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James A. N., Knox J. M., Williams R. P. Attachment of gonococci to sperm. Influence of physical and chemical factors. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Apr;52(2):128–135. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James A. N., Wende R. D., Williams R. P. Variation in colonial morphology of Neisseria gonorrhoeae after growth on media containing antimicrobial agents. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):248–251. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.248-251.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jephcott A. E., Reyn A., Birch-Andersen A. Neisseria gonorrhoeae 3. Demonstration of presumed appendages to cells from different colony types. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(3):437–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Thayer J. D. Virulence of gonococci. Annu Rev Med. 1969;20:323–328. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.20.020169.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny P., Short J. A., Hughes M., Miler J. J., Syrett C., Turner W. H., Harris J. R., MacLennan I. P. Studies on the mechanism of pathogenicity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Aug;10(3):347–365. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-3-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny P., Short J. A., Walker P. D. An electron-microscope study of naturally occurring and cultured cells of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Aug;8(3):413–427. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-3-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny P., Turner W. H. Immunological heterogeneity of pili of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jul;89(1):87–92. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H., Bisno A. L. Resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to phagocytosis: relationship to colonial morphology and surface pili. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):310–316. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. Pathogenesis and immunology of experimental gonococcal infection: role of iron in virulence. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1313–1318. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1313-1318.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A. P., Jr, Sawyer W. D. Role of pili in the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):255–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.255-263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. N., Vincent P., Ward M. E. The preparation and properties of gonococcal pili. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Sep;102(1):169–177. doi: 10.1099/00221287-102-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Studies on gonococcus infection. I. Pili and zones of adhesion: their relation to gonococcal growth patterns. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):886–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. IV. Pili: their role in attachment of gonococci to tissue culture cells. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):571–589. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Zeligs B. Studies on gonococcus infection. VI. Electron microscopic study on in vitro phagocytosis of gonococci by human leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):645–656. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.645-656.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Watt P. J. Adherence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to urethral mucosal cells: an electron-microscopic study of human gonorrhea. J Infect Dis. 1972 Dec;126(6):601–605. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.6.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistreich G. A., Baker R. F. The presence of fimbriae (pili) in three species of Neisseria. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Feb;65(2):167–173. doi: 10.1099/00221287-65-2-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]