Abstract
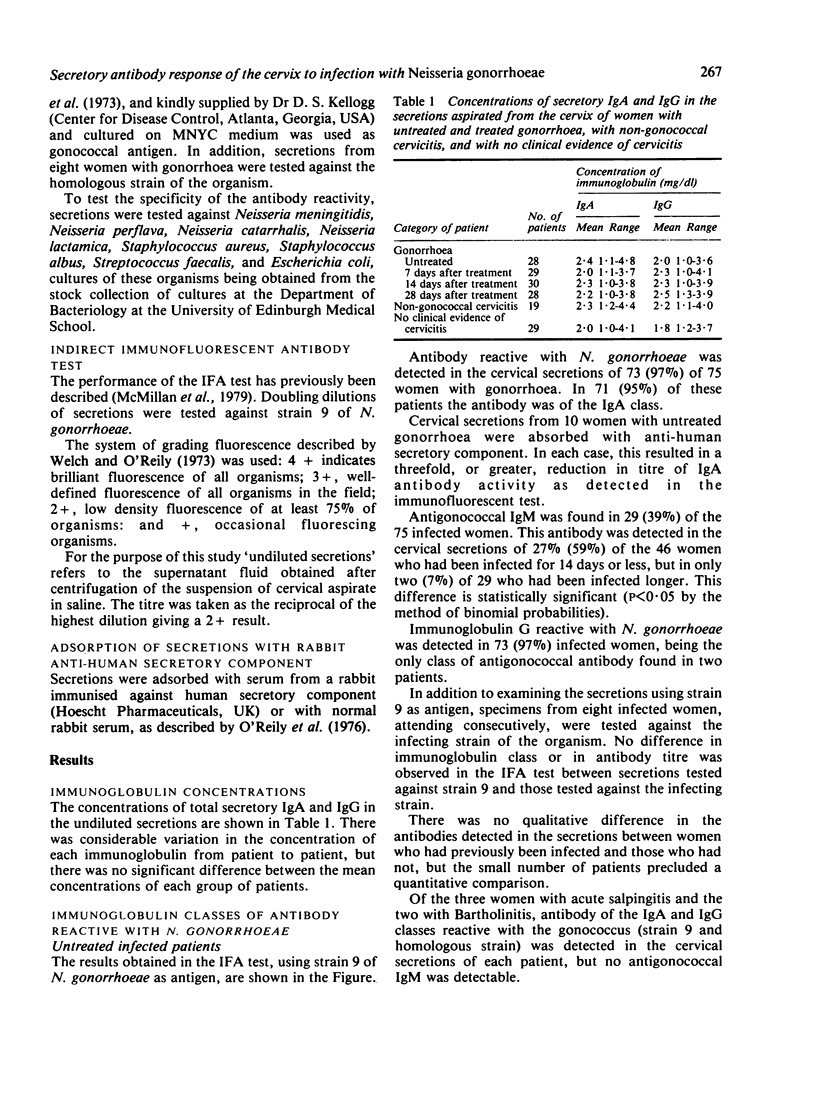
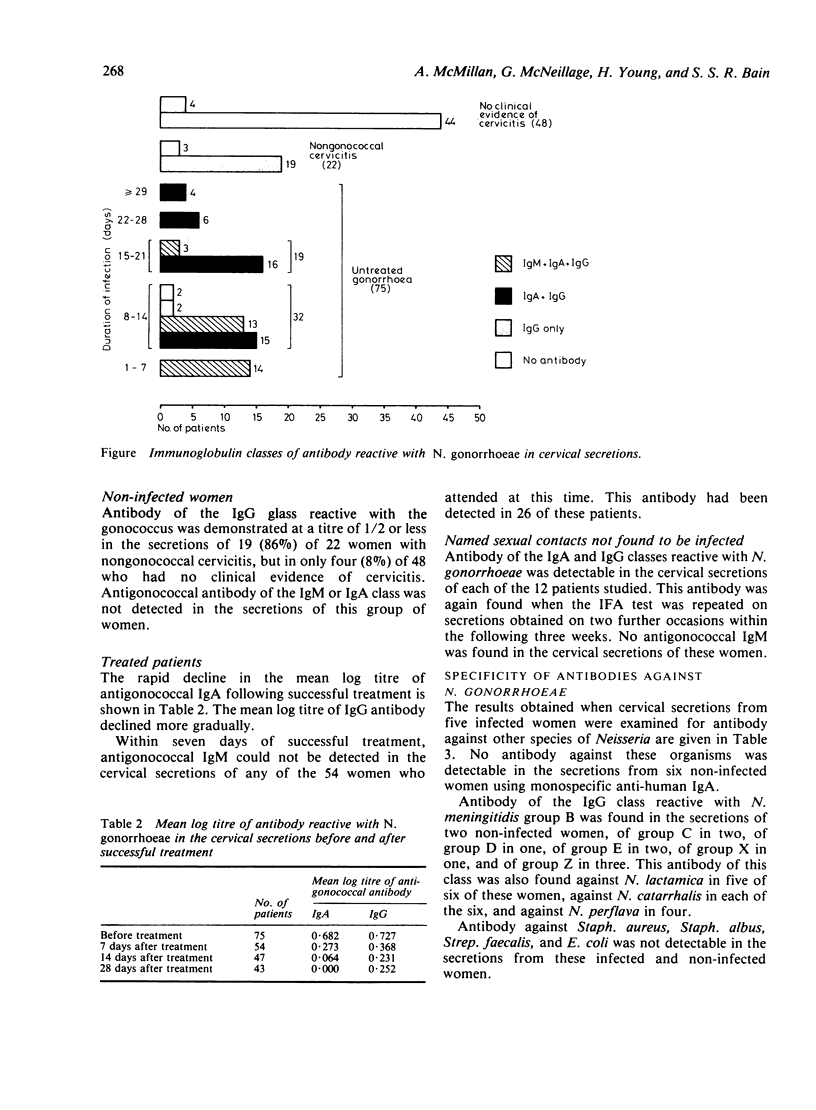
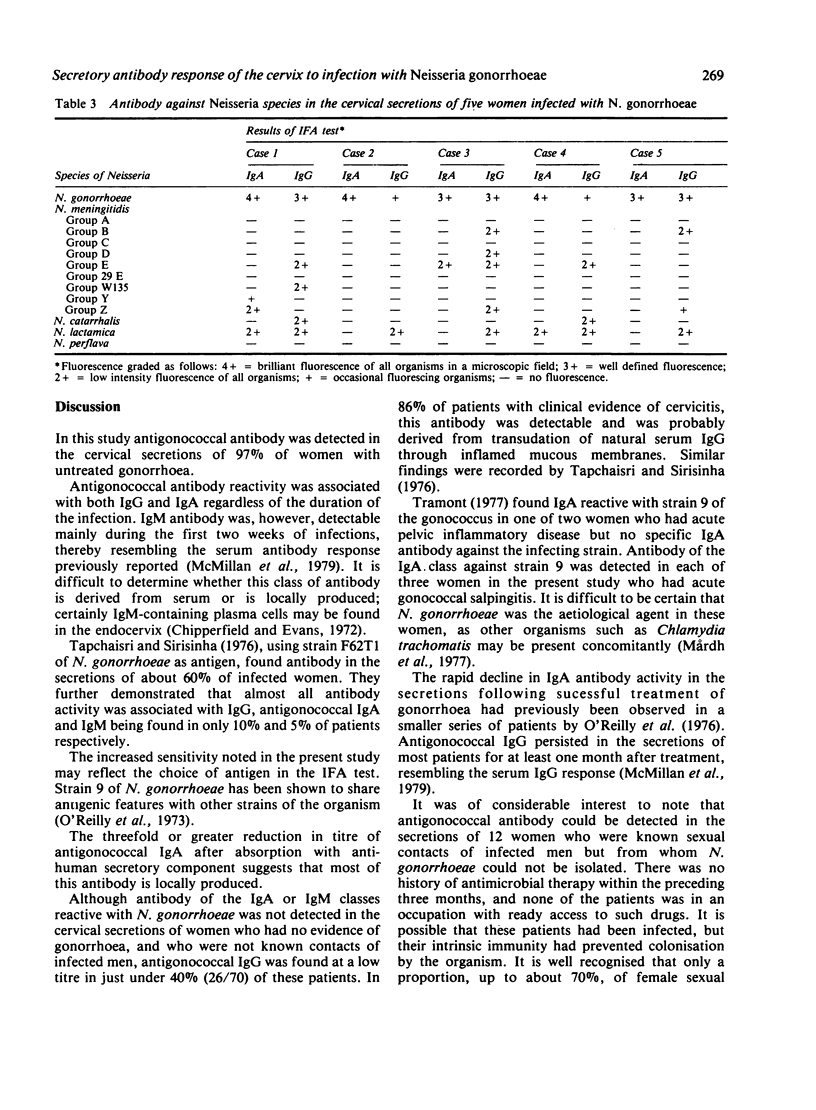
Cervical secretions from 157 women were examined for antibody against Neisseria gonorrhoeae by an indirect immunofluorescent antibody test. Antigonococcal antibody was detected in 73 (97%) of 75 infected women, being of the IgG class in 73 (97%), of the IgA class in 71 (95%), and of the IgM class in 29 (39%). IgM antibody was nearly always associated with infections of less than 15 days' duration. Immunoglobulin G, reactive with N. gonorrhoeae, was found in 23 (33%) of 70 non-infected women; of these, 19 had non-gonococcal cervicitis. Neither IgA nor IgM antibodies were detected in these women. Antigonoccal IgA and IgG was found in each of 12 women who had no evidence of infection but were contacts of infected men. Successful treatment resulted in a rapid decline in IgA antibody activity but a more gradual decrease in IgG reactivity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackers J. P., Lumsden W. H., Catterall R. D., Coyle R. Antitrichomonal antibody in the vaginal secretions of women infected with T. vaginalis. Br J Vener Dis. 1975 Oct;51(5):319–323. doi: 10.1136/sti.51.5.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipperfield E. J., Evans B. A. The influence of local infection on immunoglobulin formation in the human endocervix. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Jun;11(2):219–233. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan A., McNeillage G., Young H., Bain S. R. Serum immunoglobulin response in uncomplicated gonorrhoea. Br J Vener Dis. 1979 Feb;55(1):5–9. doi: 10.1136/sti.55.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly R. J., Lee L., Welch B. G. Secretory IgA antibody responses to Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the genital secretions of infected females. J Infect Dis. 1976 Feb;133(2):113–125. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.2.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly R. J., Welch B. G., Kellogg D. S., Jr An indirect fluorescent-antibody technique for study of uncomplicated gonorrhea. II. Selection and characterization of the strain of Neisseria gonorrhoeae used as antigen. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jan;127(1):77–83. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogra P. L., Ogra S. S. Local antibody response to poliovaccine in the human female genital tract. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1307–1311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebello R., Green F. H., Fox H. A study of the secretory immune system of the female genital tract. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1975 Oct;82(10):812–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson R. R., McClelland D. B., Shearman D. J. Studies on the quantitation of immunoglobulin in human intestinal secretions. Gut. 1973 Aug;14(8):616–626. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.8.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapchaisri P., Sirisinha S. Serum and secretory antibody responses to Neisseria gonorrhoeae in patients with gonococcal infections. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Dec;52(6):374–380. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.6.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjokronegoro A., Sirisinha S. Quantitative analysis of immunoglobulins and albumin in secretion of female reproductive tract. Fertil Steril. 1975 May;26(5):413–417. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)41112-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C. Inhibition of adherence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by human genital secretions. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):117–124. doi: 10.1172/JCI108608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin J. Gonorrhoea in 1972. A 1-year study of patients attending the VD Unit in Uppsala. Br J Vener Dis. 1975 Feb;51(1):41–47. doi: 10.1136/sti.51.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch B. G., O'Reilly R. J. An indirect fluorescent-antibody technique for study of uncomplicated gonorrhea. I. Methodology. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jan;127(1):69–76. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. Cultural diagnosis of gonorrhoea with modified New York City (MNYC) medium. Br J Vener Dis. 1978 Feb;54(1):36–40. doi: 10.1136/sti.54.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


