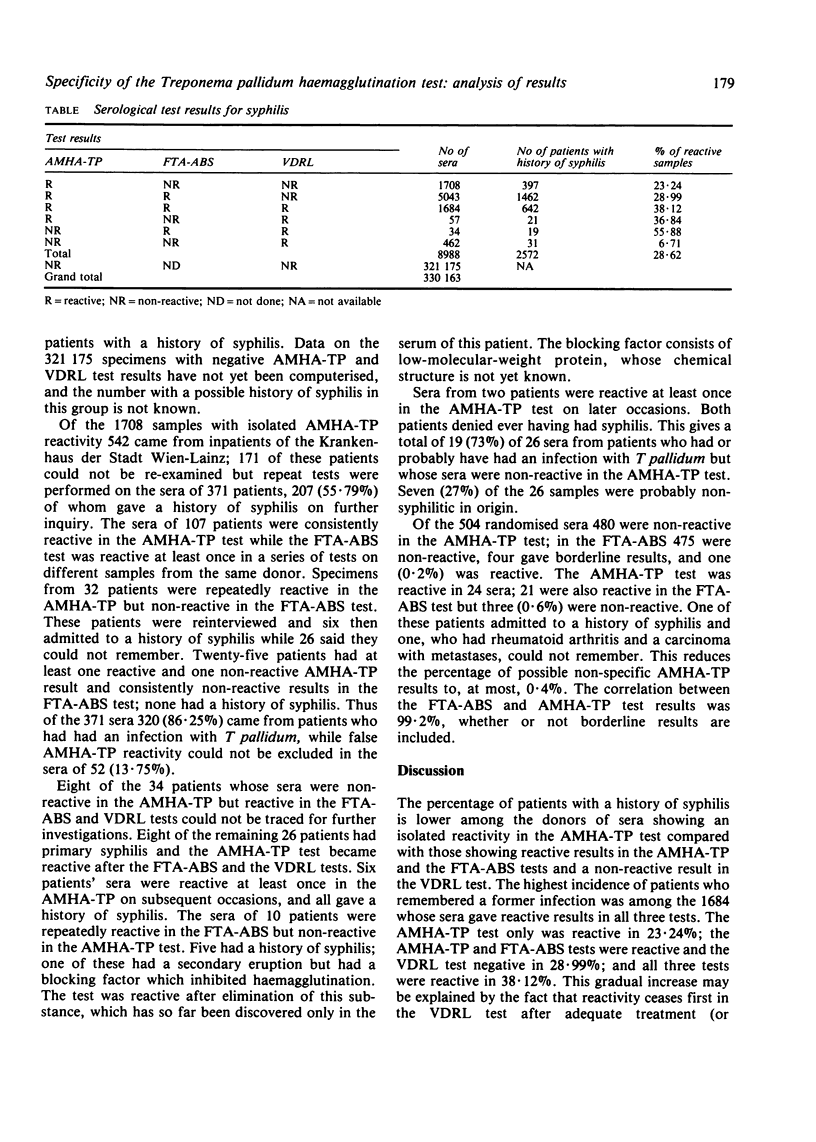
Abstract
The automated haemagglutination assay using Treponema pallidum antigen (AMHA-TP) and the Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) test were used to examine 330 163 sera. Reactive results were checked by the fluorescent treponemal antibody-absorption (FTA-ABS) test. When isolated reactivity or non-reactivity in the AMHA-TP test was investigated an estimated margin of error of 0.7% probably wrongly non-reactive and 0.008% presumably false non-reactive results were found. These figures were confirmed by randomised FTA-ABS tests on 504 sera with repeat AMHA-TP tests. The latter is therefore still the most reliable and practicable method for mass screening for syphilis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Luger A., Schmidt B., Spendlingwimmer I., Horn F. Recent observations on the serology of syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1980 Feb;56(1):12–16. doi: 10.1136/sti.56.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


