Error in Figure/Table
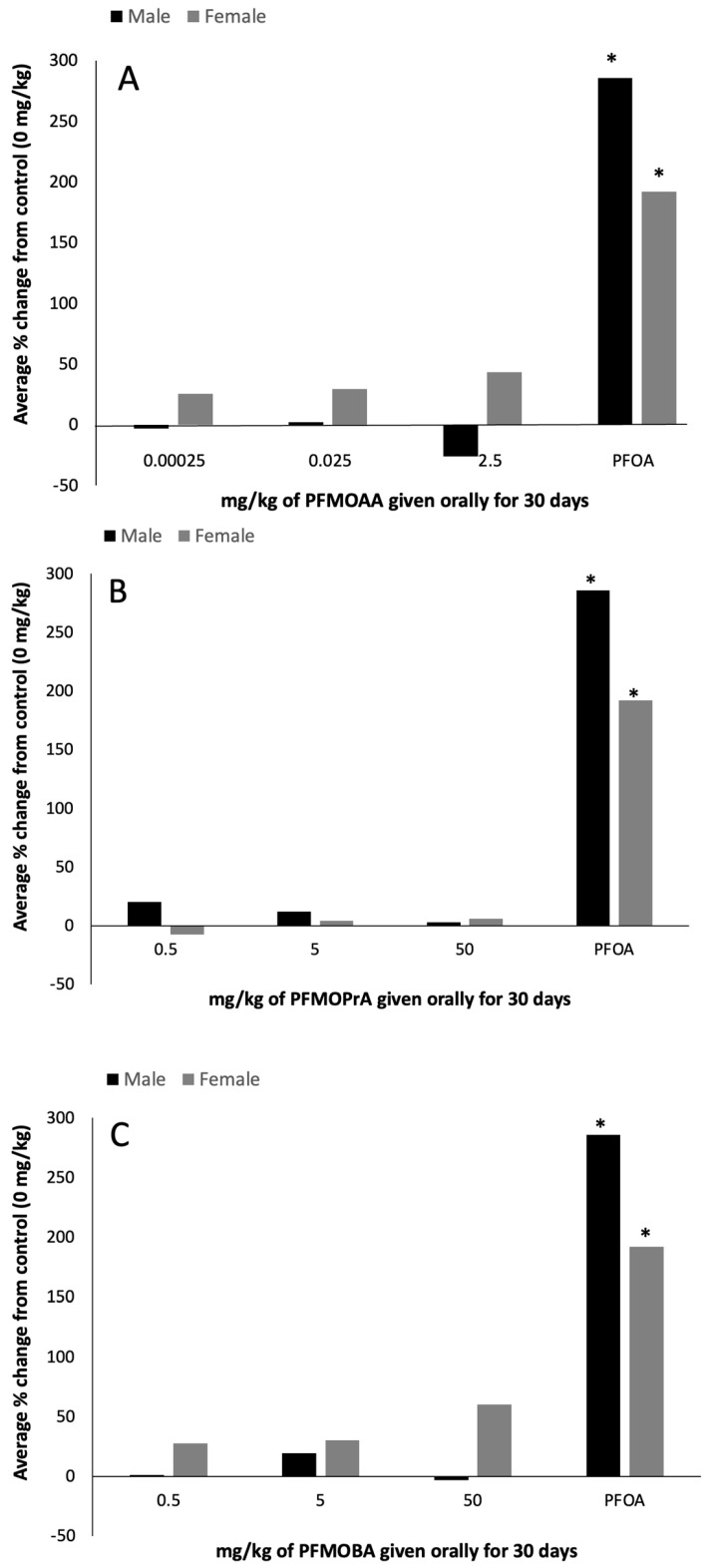
Error in figure x-axis (Figure 1A: Hepatic peroxisome proliferation). In the original publication [1] there was a mistake in Figure 1A as published. The x-axis was supposed to be labeled with the following doses: 0, 0.00025, 0.025, or 2.5 PFOA. The authors state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
Figure 1.
Hepatic peroxisome proliferation (percent change from 0 mg/kg control) of male and female C57BL/6 mice orally exposed to (A): PFMOAA, (B): PFMOPrA, or (C): PFMOBA for 30 days. Acyl-CoA oxidase activity was measured in livers that had been collected from animals one day after exposure ended. n = 4–6/dose for PFMOAA, PFMOPrA, PFMOBA, and PFOA-positive control (note that the PFOA-positive control was included from animals evaluated in a separate PFAS study). No error bars are present due to how the data were calculated. Abbreviations: perfluoro-2-methoxyacetic acid (PFMOAA), perfluoro-2-methoxypropanoic acid (PFMOPrA), perfluoro-4-methoxybutanioc acid (PFMOBA), and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA). * p < 0.05 from same-sex control group.
Footnotes
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
Reference
- 1.Woodlief T., Vance S., Hu Q., DeWitt J. Immunotoxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Insights into Short-Chain PFAS Exposure. Toxics. 2021;9:100. doi: 10.3390/toxics9050100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]