Abstract
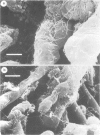
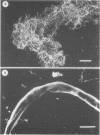
Within infected tissue Treponema pallidum shows a characteristic predilection for perivascular areas. After intact capillaries had been prepared from rabbit brain tissue treponemes were incubated with isolated capillaries and visualised by darkfield, phase contrast, and scanning electron microscopy. The organisms rapidly attached to the surface of the capillaries at the tip of the treponeme; attached organisms retained motility for longer periods than unattached organisms. Treponema pertenue also attached to capillaries. Heat-inactivated T pallidum and three non-pathogenic treponemes did not, however, attach to the capillaries. Immune rabbit serum contains a factor that blocks the attachment of T pallidum to capillaries. Compared with cultured mammalian cells capillaries should provide a better tool for investigating host-parasite relationships in syphilis.
Full text
PDF




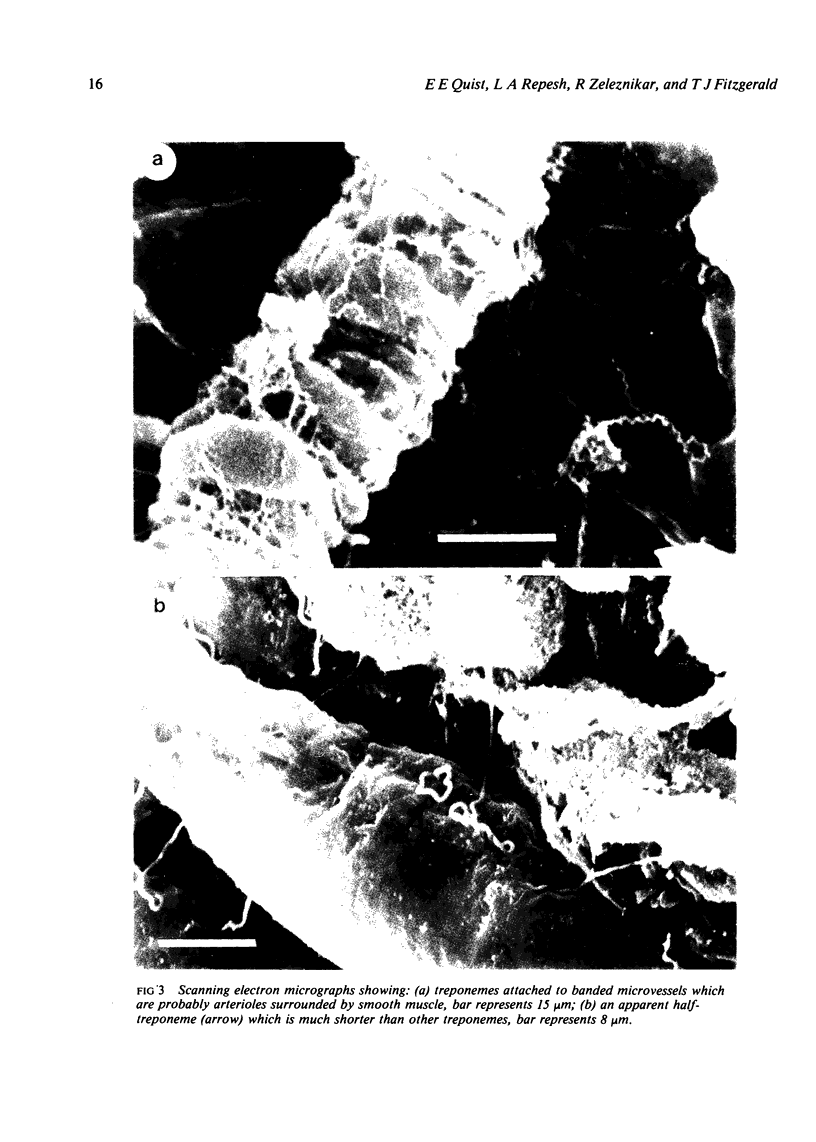


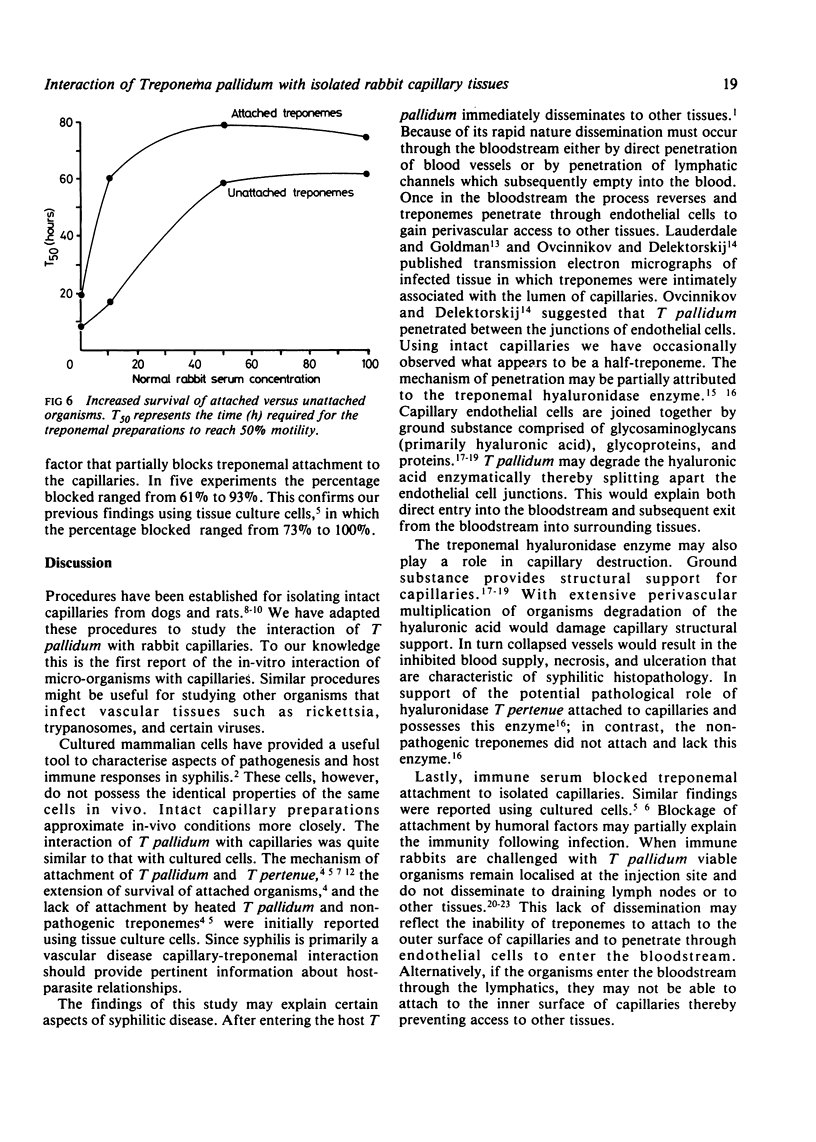

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brendel K., Meezan E., Carlson E. C. Isolated brain microvessels: a purified, metabolically active preparation from bovine cerebral cortex. Science. 1974 Sep 13;185(4155):953–955. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4155.953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewes L. D., Lidinsky W. A. Studies of cerebral capillary endothelial membrane. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1980;131:17–27. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3752-2_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieldsteel A. H., Stout J. G., Becker F. A. Comparative behavior of virulent strains of Treponema pallidum and Treponema pertenue in gradient cultures of various mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):337–345. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.337-345.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Cleveland P., Johnson R. C., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Scanning electron microscopy of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) attached to cultured mammalian cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1333–1344. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1333-1344.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Characterization of the attachment of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) to cultured mammalian cells and the potential relationship of attachment to pathogenicity. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):467–478. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.467-478.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C. Mucopolysaccharidase of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):261–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.261-268.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J. Pathogenesis and immunology of Treponema pallidum. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:29–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERSH I., CATCHPOLE H. R. The organization of ground substance and basement membrane and its significance in tissue injury disease and growth. Am J Anat. 1949 Nov;85(3):457-521, incl 7 pl. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000850304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes N. S., Muse K. E., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Parasitism by virulent Treponema pallidum of host cell surfaces. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):174–186. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.174-186.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joó F., Karnushina I. A procedure for the isolation of capillaries from rat brain. Cytobios. 1973 Sep-Oct;8(29):41–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauderdale V., Goldman J. N. Serial ultrathin sectioning demonstrating the intracellularity of T. Pallidum. An electron microscopic study. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Apr;48(2):87–96. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.2.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Fine structures of capillary and endocapillary layer as revealed by ruthenium red. Fed Proc. 1966 Nov-Dec;25(6):1773–1783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. II. Fine structural localization in animal tissues. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):369–415. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovcinnikov N. M., Delektorskij V. V. Electron microscopy of phagocytosis in syphilis and yaws. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Aug;48(4):227–248. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.4.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYKES J. A., MOORE E. B. A simple tissue culture chamber. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1960;18:288–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARING G. W., Jr, FLEMING W. L. The effect of partial immunity on the dissemination of infection in experimental syphilis. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1952 Jul;36(4):368–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]