Abstract
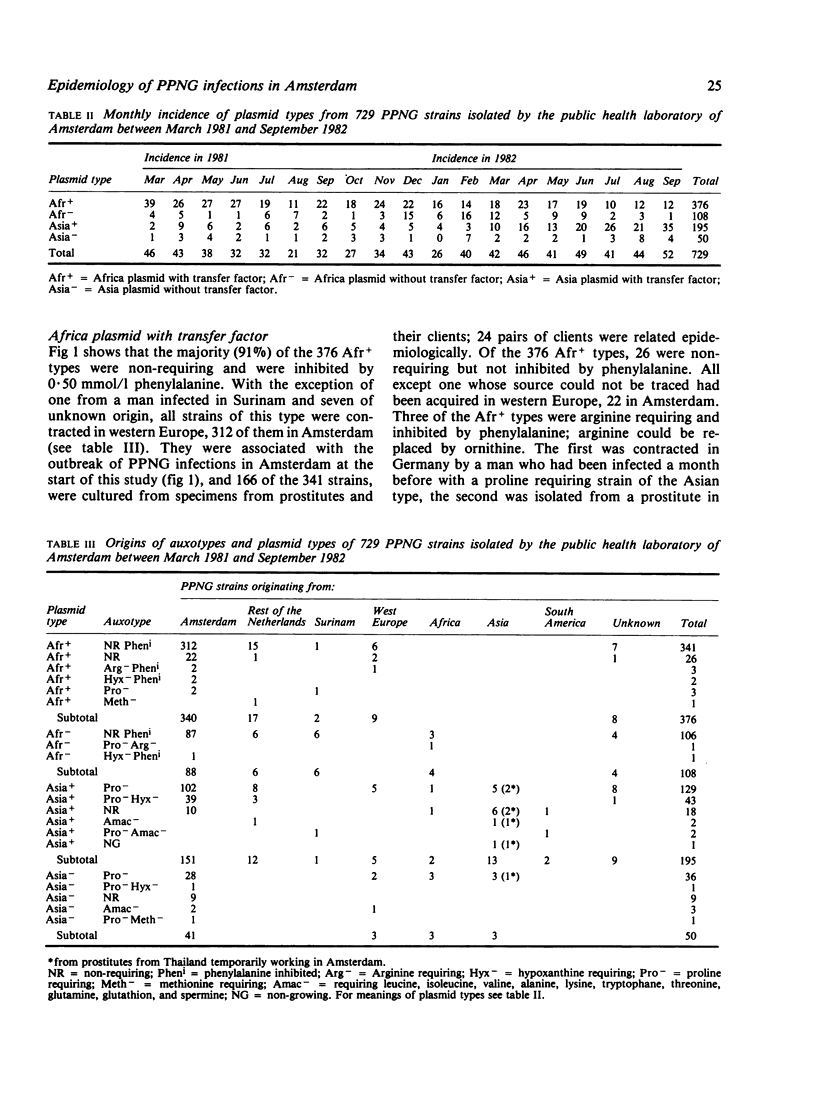
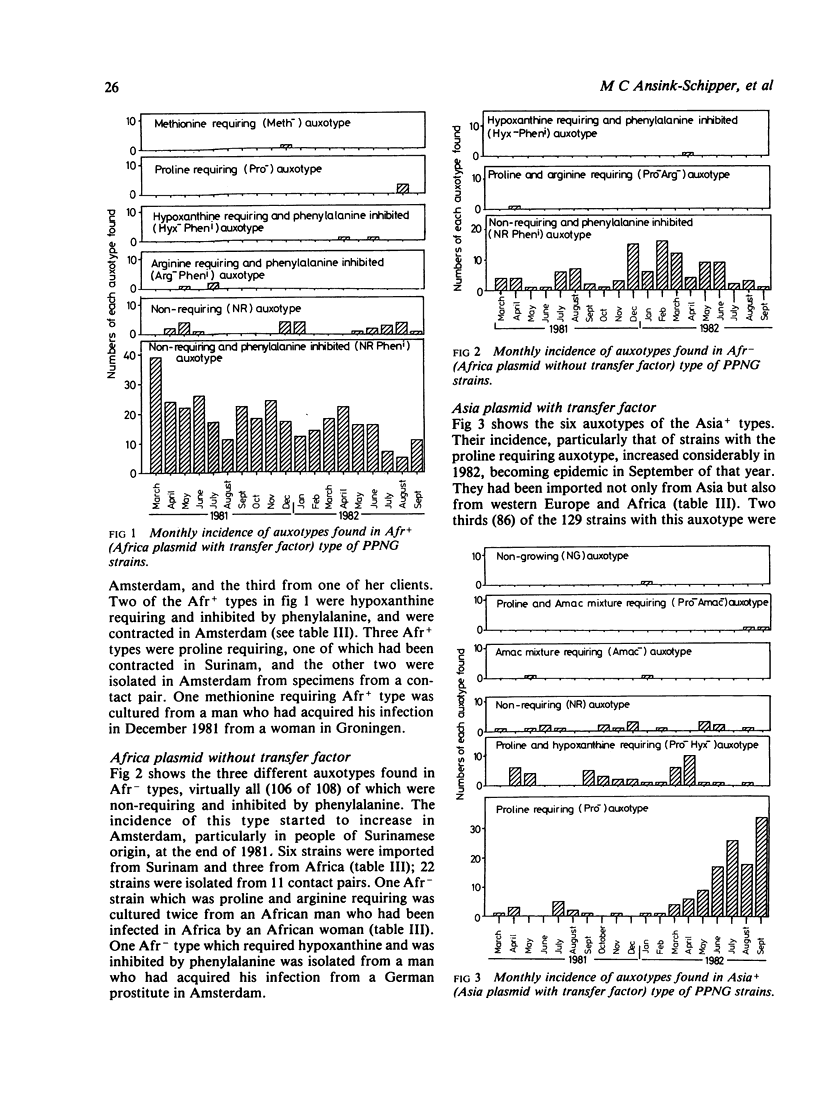
In January 1981 the incidence of penicillinase producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae (PPNG) strains in Amsterdam had increased to 18% of all new cases of gonorrhoea. Auxanographic typing in combination with plasmid determination of 729 PPNG strains showed that in 1981 the predominant and endemic types were those with the Africa plasmid and transfer factor which were non-requiring and inhibited by phenylalanine. In 1982 proline requiring strains with the Asia plasmid and transfer factor increased after being imported and spread by prostitution. Four different plasmid patterns and 12 auxotypes were distinguishable. Unusual auxotypes of both African and Asian plasmid types are frequently imported, some disappearing soon after their introduction into Holland but others providing an opportunity to trace sources and contacts. Prostitution and the biological properties of PPNG strains seem to play an important role in their spread. Only 2.6% of them were isolated from homosexual men. In areas where PPNG strains are prevalent, auxotyping is an important tool in their surveillance.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B., Odugbemi T., Johnson S. Penicillinase producing Neisseria Gonorrhoeae strains from Nigeria with Far Eastern type plasmid. Lancet. 1982 Mar 20;1(8273):676–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Nutritional profiles of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Neisseria lactamica in chemically defined media and the use of growth requirements for gonococcal typing. J Infect Dis. 1973 Aug;128(2):178–194. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho R. A., Jansen Schoonhoven F., Ansink-Schipper M. C., de Koning G. A., Tio D. De verspreiding van penicillinase vormende gonokokken in Amsterdam. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1982 Jan 30;126(5):221–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon J. R., Duck P., Thomas D. Y. Molecular and phenotypic characterization of penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae from Canadian sources. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jun;19(6):952–957. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.6.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon J. R., Pauzé M. Appearance in Canada of Neisseria gonorrhoeae strains with a 3.2 megadalton penicillinase-producing plasmid and a 24.5 megadalton transfer plasmid. Lancet. 1981 Sep 26;2(8248):700–700. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handsfield H. H., Sandström E. G., Knapp J. S., Perine P. L., Whittington W. L., Sayers D. E., Holmes K. K. Epidemiology of penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae infections: analysis by auxotyping and serogrouping. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 22;306(16):950–954. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204223061602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry A. T., Stewart I. O. Auxanographic grouping and typing of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Apr;25(4):512–521. doi: 10.1139/m79-075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe H. W., Biddle J. W., Johnson S. R., Wiesner P. J. Infections due to penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the United States: 1976-1980. J Infect Dis. 1981 Aug;144(2):191–197. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.2.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jephcott A. E., Egglestone S. I., Copley C. Further evidence of dissemination of ability to produce penicillinase amongst gonococci. Lancet. 1982 Jun 26;1(8287):1467–1468. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92475-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus T. J., Harris J. R., Ison C. A., Easmon C. S. Penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae. N Engl J Med. 1982 Dec 30;307(27):1706–1706. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198212303072712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayyar K. C., Noble R. C., Michel M. F., Stolz E. Gonorrhea in Rotterdam caused by penicillinase-producing gonococci. Br J Vener Dis. 1980 Aug;56(4):244–248. doi: 10.1136/sti.56.4.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D., van Klingeren B., Dessens-Kroon M., van Wijngaarden L. J. Emergence in the Netherlands of penicillinase-producing gonococci carrying "Africa" plasmid in combination with transfer plasmid. Lancet. 1981 Apr 25;1(8226):938–938. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91630-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D., van Klingeren B., Dessens-Kroon M., van Wijngaarden L. J. Penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the Netherlands: epidemiology and genetic and molecular characterization of their plasmids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):789–797. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Klingeren B., van Wijngaarden L. J., Dessens-Kroon M., van Embden J. D. Penicillinase-producing gonococci in the Netherlands in 1981. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Jan;11(1):15–20. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


