Key Points
Question
Does combination therapy of standard-dose nivolumab and ipilimumab improve clinical outcomes and justify additional toxicity compared with nivolumab monotherapy in advanced cancers other than metastatic melanoma?
Findings
In this meta-analysis of 8 clinical trials including 1727 patients, the addition of ipilimumab to standard-dose nivolumab was not associated with a clinically meaningful improvement in overall survival or progression-free survival over standard-dose nivolumab alone. The combination was associated with substantially higher treatment-related high-grade toxicities without commensurate clinical benefit.
Meaning
Combination therapy with nivolumab and ipilimumab may be unnecessary in many patient populations, and nivolumab or other anti–programmed death 1–directed therapy alone may deliver equivalent clinical outcomes with lower toxicity (clinical and financial) in many advanced cancers other than melanoma.
This meta-analysis investigates the efficacy and safety of nivolumab plus ipilimumab vs nivolumab alone in the treatment of advanced cancers other than melanoma.
Abstract
Importance
Although the combination of nivolumab plus ipilimumab has unquestionable benefit over nivolumab monotherapy in advanced melanoma, currently no summative analyses have compared the combination with nivolumab monotherapy for advanced cancers other than melanoma.
Objective
To examine whether the addition of ipilimumab to standard-dose nivolumab safely improves clinical outcomes in patients with advanced cancers other than melanoma.
Data Sources
Electronic databases (PubMed, EBSCO Information Services, Embase, and Cochrane Library) were systematically searched for studies of standard-dose nivolumab plus ipilimumab vs nivolumab alone in the treatment of advanced cancers other than melanoma published from database inception to October 31, 2022.
Study Selection
Eight studies (total patients, 1727; nivolumab plus ipilimumab group, 854; nivolumab monotherapy group, 873) met the selection criteria. Patients had squamous cell lung cancer, non–small cell lung cancer with programmed death ligand 1 level of 1% or higher, small cell lung cancer, pleural mesothelioma, urothelial carcinoma, esophagogastric carcinoma, sarcoma, or glioblastoma multiforme.
Data Extraction and Synthesis
For comparison of overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) outcomes, estimation of log(hazard ratios [HRs]) and SEs was initially performed for OS and PFS of each included study based on summary statistics extracted from individual Kaplan-Meier curves. Inverse-variance weighting was then used to compute pooled HRs (95% CIs). For comparison of dichotomous data (treatment-related grade 3 to 4 adverse events and discontinuations), odds ratios (ORs) were used, and the Mantel-Haenszel method was used to estimate pooled ORs (95% CIs).
Results
Treatment with nivolumab plus ipilimumab was not associated with improvement in OS over treatment with nivolumab alone (pooled HR, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.85-1.06; P = .36), with 4 of the 8 studies having numerically lower median OS with the combination. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab combination therapy was associated with marginal, but not clinically meaningful, improvement in PFS over nivolumab alone (pooled HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.79-0.98; P = .02). The combination was associated with substantially higher treatment-related grade 3 to 4 adverse events (pooled OR, 1.84; 95% CI, 1.47-2.31; P < .001) and treatment-related discontinuations (pooled OR, 1.96; 95% CI, 1.44-2.65; P < .001). This finding was recapitulated in meta-analyses of individual grade 3 to 4 adverse events of hepatotoxicity, gastrointestinal toxicity, pneumonitis, endocrine dysfunction, dermatitis, fatigue.
Conclusions and Relevance
In this meta-analysis of 8 advanced cancers other than melanoma, the differences detected in OS and PFS between nivolumab plus ipilimumab and nivolumab were not clinically meaningful (even though statistical significance was detected in PFS). Treatment-related higher-grade toxicity and discontinuations were substantially higher with the combination therapy. The data indicate that investigations of anti–programmed death 1 (PD1) plus anti–cytotoxic T-lymphocyte–associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) therapies in any nonmelanoma advanced cancer should be conducted along with anti-PD1 monotherapy to ensure that the net effect of the addition of anti-CTLA-4 to anti-PD1 can be clearly established for that cancer and setting and that unnecessary CTLA-4 inhibition with related toxic effects (both clinical and financial) can be avoided.
Introduction
Although the combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab has clearly demonstrated improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) over nivolumab alone in metastatic melanoma (particularly in programmed death ligand 1 [PD-L1]–negative and BRAF [OMIM 164757] mutation–positive melanoma),1,2 its comparative efficacy over nivolumab monotherapy in other advanced cancers has not been well established. Relatively few trials to date have directly compared nivolumab plus ipilimumab with nivolumab monotherapy, and currently no summative analyses, to our knowledge, have compared the combination with nivolumab monotherapy for advanced cancers other than melanoma. However, the combination is often assumed superior to nivolumab monotherapy across cancers, and multiple trials have investigated the combination against the standard of care in different cancers. We thus sought to perform a meta-analysis aimed at investigating the efficacy and safety of nivolumab plus ipilimumab vs nivolumab alone in advanced cancers other than melanoma. For this meta-analysis, we included studies in which ipilimumab was added to standard-dose nivolumab (3 mg/kg or 240 mg).
Methods
This meta-analysis conformed to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) reporting guidelines. PubMed, EBSCO Information Services, Embase, and Cochrane Library were systematically searched for studies of standard-dose nivolumab plus ipilimumab vs nivolumab alone for the treatment of advanced cancers other than melanoma published from database inception to October 31, 2022. Full details of the search strategy, eligibility and inclusion criteria, outcome measures, and data extraction are described in eAppendix 1 in Supplement 1. The search process is outlined in the PRISMA schema (eFigure 1 in Supplement 1) and described in eAppendix 1 Supplement 1.
For comparison of time-to-event OS and PFS outcomes, estimation of log(hazard ratios [HRs]) and SEs was initially performed for OS and PFS of each included study based on summary statistics extracted from individual Kaplan-Meier (K-M) curves (incorporating number at risk, estimated number of events, and number censored for each specified interval, ensuring that the K-M curves generated from these numbers matched the published K-M curves), as described by Tierney et al.3 Detailed calculations for each study have been provided (eAppendix 3 in Supplement 1). Inverse-variance weighting was then used to compute pooled HRs (95% CIs) using the estimated individual log(HR) and SE values.
For comparison of dichotomous data, odds ratios (ORs) were used; all results were reported with 95% CIs. The Mantel-Haenszel method was used to estimate pooled ORs (95% CIs). The I2 test was used to assess impact of study heterogeneity (see eAppendix 1 in Supplement 1 for further details). RevMan, version 5.4 (Cochrane Collaboration) was used for the meta-analyses.
Results
Search Results and Study Characteristics
Eight studies (total patients, 1727; nivolumab plus ipilimumab group, 854; nivolumab monotherapy group, 873) met the selection criteria. Patients had squamous cell lung cancer,4 non–small cell lung cancer with programmed death ligand 1 level of 1% or higher,5 small cell lung cancer,6 pleural mesothelioma,7 urothelial carcinoma,8 esophagogastric carcinoma,9 sarcoma,10 or glioblastoma multiforme (see eAppendix 2 in Supplement 1 for further details).11 A summary of the included trials and their characteristics is given in the Table.
Table. Characteristics of Trials Included in the Meta-Analysis.
| Source | Phase | Randomized | Open label | Rating | Disease | Total No. of patients (I/C)a | Interventionb | Control | Median age, y | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | C | |||||||||
| Gettinger et al,4 2021 | 3 | Yes | Yes | 1 | Metastatic squamous cell lung cancer | 252 (125/127) | Nivolumab, 3 mg/kg every 2 wk, plus ipilimumab, 1 mg/kg every 6 wk until progression | Nivolumab, 3 mg/kg every 2 wk | 67.5 | 68.1 |
| Hellmann et al,5 2019 | 3 | Yes | Yes | 1 | Metastatic or recurrent NSCLC with PD-L1 ≥ 1% | 792 (396/ 396) | Nivolumab, 3 mg/kg every 2 wk, plus ipilimumab, 1 mg/kg every 6 wk until progression | Nivolumab, 240 mg every 2 wk | 64 | 64 |
| Scherpereel et al,7 2019 | 2 | Yes | Yes | 2 | Relapsed pleural mesothelioma | 125 (62/63) | Nivolumab, 3 mg/kg every 2 wk, plus ipilimumab, 1 mg/kg every 6 wk until progression | Nivolumab, 3 mg/kg every 2 wk | 71.2 | 72.3 |
| Sharma et al,8 2019 | 1/2 | No | Yes | 2 | Metastatic urothelial carcinoma | 182 (104/78) | Nivolumab, 3 mg/kg every 3 wk, plus ipilimumab, 1 mg/kg every 3 wk, for 4 doses followed by nivolumab, 3 mg/kg for every 2-week maintenance | Nivolumab, 3 mg/kg every 2 wk | 63 | 65.5 |
| Janjigian et al,9 2018 | 1/2 | No | Yes | 2 | Metastatic esophagogastric carcinoma | 111 (52/59) | Nivolumab, 3 mg/kg every 3 wk, plus ipilimumab, 1 mg/kg every 3 wk, for 4 doses followed by nivolumab, 3 mg/kg for every 2-week maintenance | Nivolumab, 3 mg/kg every 2 wk | 58 | 60 |
| D’Angelo et al,10 2018 | 2 | Yes | Yes | 2 | Advanced sarcoma | 83 (41/42) | Nivolumab, 3 mg/kg every 3 wk, plus ipilimumab, 1 mg/kg every 3 wk, for 4 doses followed by nivolumab, 3 mg/kg for every 2-week maintenance | Nivolumab, 3 mg/kg every 2 wk | 57 | 56 |
| Omuro, et al,11 2018 | 1 | No | Yes | 2 | Glioblastoma multiforme | 30 (20/10) | Nivolumab, 3 mg/kg every 3 wk, plus ipilimumab, 1 mg/kg every 3 wk, for 4 doses followed by nivolumab, 3 mg/kg for every 2-week maintenance | Nivolumab, 3 mg/kg every 2 wk | 60 | 58.5 |
| Antonia, et al,6 2016 | 1/2 | No | Yes | 2 | Recurrent small cell lung cancer | 152 (54/98) | Nivolumab, 3 mg/kg every 2 wk, plus ipilimumab, 1 mg/kg for every 3 wk, for 4 doses followed by nivolumab, 3 mg/kg for every 2-week maintenance | Nivolumab, 3 mg/kg every 2 wk | 61 | 63 |
Abbreviations: I, intervention; C, control; NSCLC, non–small cell lung cancer; PD-L1 programmed death ligand 1.
Total patients includes patients in the ipilimumab and standard-dose nivolumab and standard-dose nivolumab arms and excludes other patients and arms.
Trials may have included other dosing arms but were excluded from this meta-analysis.
Efficacy
The efficacy of nivolumab and ipilimumab vs nivolumab was evaluated by focusing on OS and PFS, the most clinically relevant metrics. Treatment with nivolumab and ipilimumab was not associated with an improvement in OS (pooled HR, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.85-1.06; P = .36; I2 = 0%) (Figure 1A). Of note, 4 of the studies4,8,9,11 had numerically lower median OS with the combination.
Figure 1. Meta-Analysis of Overall Survival and Progression-Free Survival With Nivolumab and Ipilimumab vs Nivolumab Alone in Advanced Cancers Other Than Melanoma.
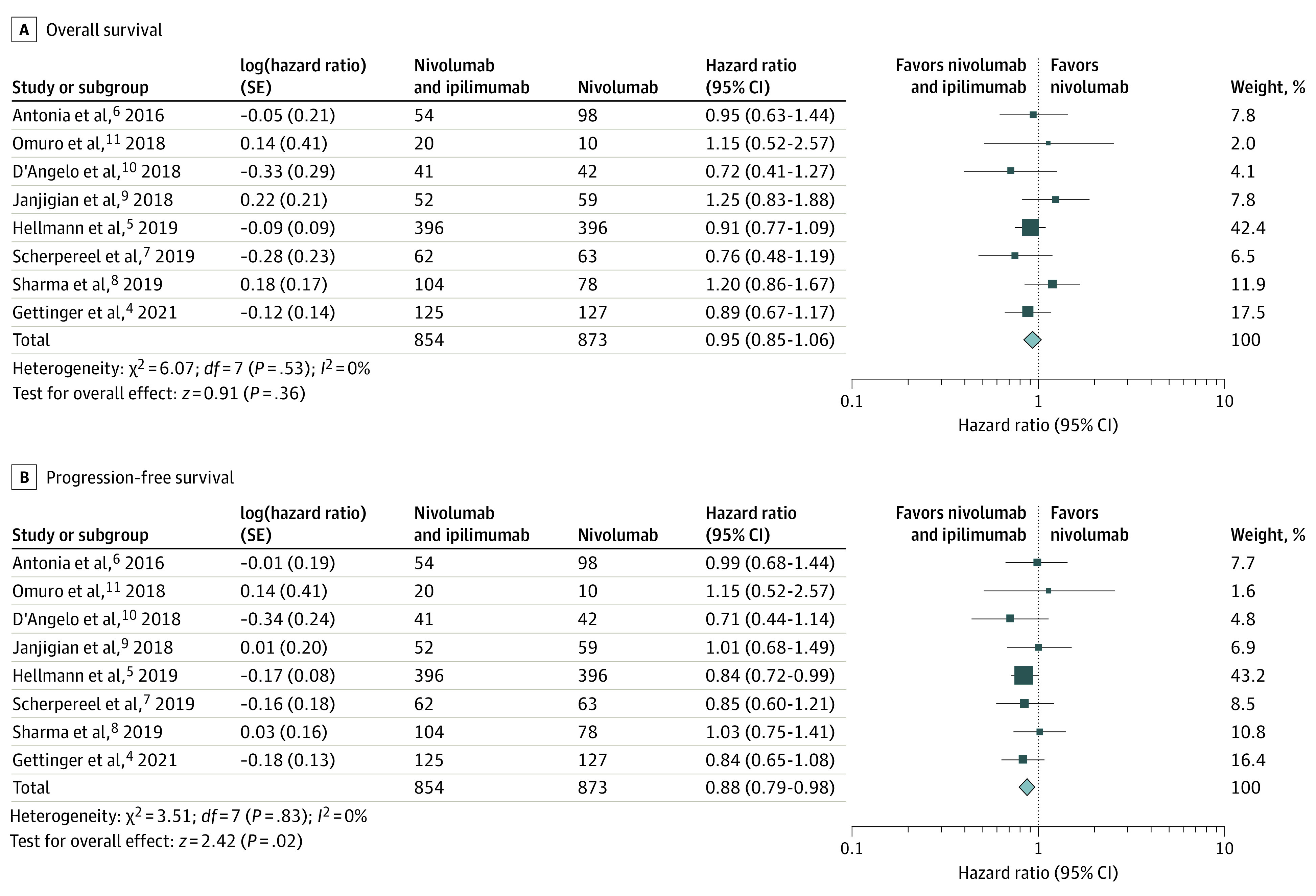
A, Forest plot and meta-analysis of overall survival with nivolumab and ipilimumab vs nivolumab alone in advanced cancers other than melanoma show no improvement in overall survival with the combination (pooled hazard ratio, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.85-1.06; P = .36; I2 = 0%). B, Forest plot and meta-analysis of progression-free survival with nivolumab and ipilimumab vs nivolumab alone in advanced cancers other than melanoma show marginal, but not clinically meaningful, improvement in progression-free survival with the combination (pooled hazard ratio, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.79-0.98; P = .02; I2 = 0%).
Nivolumab and ipilimumab combination therapy was associated with a marginal, but not clinically meaningful, improvement in PFS over nivolumab alone (pooled HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.79-0.98; P = .02; I2 = 0%) (Figure 1B). Of note, only 1 study5 had a statistically significant PFS benefit (HR, 0.84; 95% CI, 0.72-0.99), which was by far the largest study, with 792 patients, accounting for more than 40% of the weight in the meta-analysis. (A PFS HR of 0.88 [95% CI, 0.79-0.98] and an OS HR of 0.95 [95% CI, 0.85-1.06] falls well below what the American Society of Clinical Oncology considers a clinically meaningful incremental improvement for oncologic trial interventions, which is an OS HR of 0.8 or lower.12)
A sensitivity analysis was performed to determine the extent to which Hellmann et al5 influenced the OS and PFS meta-analysis (eFigure 2 in Supplement 1). The pooled HR without the study by Hellmann et al5 was 0.97 (95% CI, 0.84-1.13) for OS and 0.91 (95% CI, 0.79-1.04) for PFS (n = 936), revealing that without that study, the small PFS advantage dissipated across the other 936 patients in 7 studies.4,6,7,8,9,10,11 The sensitivity analysis did not affect study heterogeneity (I2 = 0%).
Safety
The pooled OR of grade 3 to 4 adverse events (AEs) for nivolumab and ipilimumab vs nivolumab and ipilimumab alone was 1.84 (95% CI, 1.47-2.31; P < .001; I2 = 0%) (Figure 2A). Across the 8 studies,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11 there were 272 grade 3 to 4 AEs in 854 patients who received nivolumab and ipilimumab (approximately 0.47 odds) and 173 grade 3 to 4 AEs in 873 patients who received nivolumab alone (approximately 0.25 odds). Similarly, treatment-related discontinuations (Figure 2B) with nivolumab and ipilimumab vs nivolumab alone had a pooled OR of 1.96 (95% CI, 1.45-2.66; P < .001; I2 = 2%). Across all studies, 150 of 854 patients who received nivolumab and ipilimumab experienced treatment-related discontinuation (approximately 0.21 odds) compared with 83 of 873 patients who received nivolumab alone (approximately 0.11 odds).
Figure 2. Meta-Analysis of Treatment-Related High-Grade Adverse Events and Discontinuations With Nivolumab and Ipilimumab vs Nivolumab Alone.
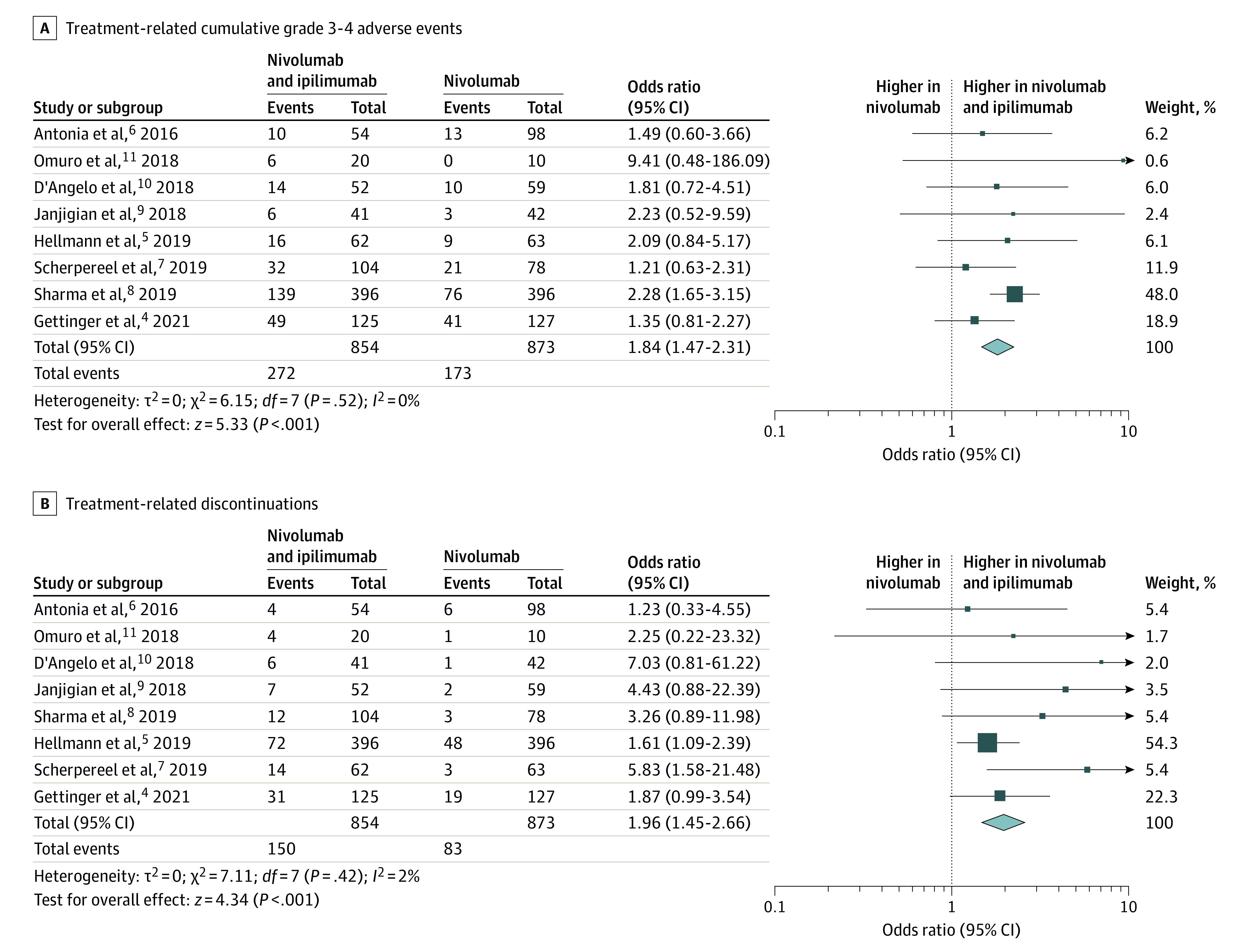
A, Forest plot and meta-analysis of cumulative grade 3 to 4 adverse events with nivolumab and ipilimumab vs nivolumab alone show substantial increase in severe adverse events with the combination (pooled odds ratio, 1.84; 95% CI, 1.47-2.31; P < .001; I2 = 0%). B, Forest plot and meta-analysis of treatment-related discontinuation with nivolumab and ipilimumab vs nivolumab alone show nearly 2 times greater odds of treatment-related discontinuation with the combination (pooled odds ratio, 1.96; 95% CI, 1.45-2.66; P < .001; I2 = 2%).
The following grade 3 to 4 AEs occurred in the 854 patients in the combination treatment group: hepatotoxicity (n = 83 [9.7%]), gastrointestinal toxicity (n = 34 [4.0%]) pneumonitis (n = 31 [3.6%]), endocrine dysfunction (n = 29 [3.4%]), dermatitis (n = 30 [3.2%]), and fatigue (n = 30 [3.2%]). These grade 3 to 4 AEs were substantially lower in the 873 patients in the nivolumab group (hepatotoxicity [n = 26 (3.0%)], fatigue [n = 15 (1.7%)], pneumonitis [n = 13 (1.5%)], gastrointestinal toxicity [n = 9 (1%)], dermatitis [n = 8 (0.9%)], and endocrine dysfunction [n = 2 (0.2%)]). The pooled ORs for nivolumab and ipilimumab vs nivolumab for the individual grade 3 to 4 AEs were as follows: hepatotoxicity, 2.94 (95% CI, 1.67-5.15; P < .001); gastrointestinal toxicity, 3.28 (95% CI, 1.65-6.49; P < .001); pneumonitis, 2.37 (95% CI, 1.24-4.54; P = .009); endocrine dysfunction, 7.95 (95% CI, 2.57-24.65; P < .001); fatigue, 1.91 (95% CI, 1.03-3.52; P = .04); and dermatitis, 2.52 (95% CI, 0.68-9.36; P = .17) (eFigures 3-8 in Supplement 1).
Discussion
In this meta-analysis of a wide spectrum of advanced cancers other than melanoma (small cell lung cancer, non–small cell lung cancer, squamous cell lung cancer, mesothelioma, urothelial carcinoma, esophagogastric carcinoma, sarcoma, and glioblastoma multiforme), the addition of ipilimumab to standard-dose nivolumab was not associated with a clinically meaningful improvement in OS or PFS over nivolumab monotherapy. Furthermore, the combination was associated with substantially higher treatment-related high-grade AEs and discontinuations.
Although 2 prior meta-analyses13,14 claimed that the combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab may be more effective than nivolumab alone for advanced cancers, these studies were heavily influenced by trials of advanced melanoma, accounting for more than 60% weight and driving up the pooled efficacy of nivolumab and ipilimumab compared with nivolumab. In addition, the meta-analyses13,14 reported a standard mean difference for survival outcomes, which is a much inferior statistical method for survival meta-analysis. Finally, additional trials investigating nivolumab and ipilimumab and nivolumab alone have since been reported, including 2 large randomized clinical trials in non–small cell lung cancer,4,5 included in our meta-analysis.
It is possible that certain immunogenic nonmelanoma cancers (such as renal cell carcinoma and triple-negative breast cancer) or specific subsets of populations (such as sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma or squamous cell lung cancer with high tumor mutational burden and low PD-L1) may have survival benefit with the combination over single-agent nivolumab, although this remains to be determined. In advanced Merkel cell carcinoma, a rare immunogenic cutaneous cancer, nivolumab and ipilimumab combination therapy has demonstrated substantial benefit (objective response rate, 31%) even after prior anti-PD1/anti–PD-L1 exposure and a 100% objective response rate in the immune checkpoint inhibitor–naive setting, establishing the superiority of the combination in treating this cancer.15 Future randomized investigations in immunogenic cancers and biomarker-driven studies may identify combination-responsive cancers and subsets.
Our data indicate that investigations of anti-PD1 plus anti–cytotoxic T-lymphocyte–associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) therapies in any nonmelanoma advanced cancer should be conducted along with anti-PD1 monotherapy to ensure that the net effect of the addition of anti-CTLA-4 to anti-PD1 can be clearly established for that cancer and setting and that unnecessary CTLA-4 inhibition with related toxic effects (clinical and financial) can be avoided. Furthermore, in cancers in which nivolumab and ipilimumab combination therapy has been approved without comparison with nivolumab, noninferiority trials should be considered.
Limitations
This study has some limitations. First, this meta-analysis includes several different tumor types, and there may be heterogeneity in the benefit of nivolumab and ipilimumab with relation to each tumor type. However, none of the trials individually had an OS benefit (with 4 of 8 having numerically lower median OS), and only 1 trial5 demonstrated a marginal PFS benefit for nivolumab and ipilimumab over nivolumab alone. Second, we did not include studies with a dosing regimen of 1 mg/kg of nivolumab and 3 mg/kg of ipilimumab to avoid further heterogeneity, and outcomes could possibly be different with this dosing regimen in certain disease contexts (as demonstrated in urothelial and esophagogastric carcinoma), although this regimen is known to be even more toxic than the more common regimen of 3 mg/kg of nivolumab and 1 mg/kg of ipilimumab, with substantially higher grade 3 to 4 event rate. Third, 1 study5 accounted for more than 40% of the analyses. However, sensitivity analysis without that study did not affect heterogeneity (I2 = 0) and revealed no benefit in OS or PFS for nivolumab and ipilimumab vs nivolumab across the other 936 patients in 7 studies.4,6,7,8,9,10,11
Conclusion
In this meta-analysis of 8 clinical trials4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11 of 1727 patients with advanced cancers other than melanoma, the addition of ipilimumab to standard-dose nivolumab was not associated with a clinically meaningful improvement in OS or PFS over standard-dose nivolumab alone. The combination was associated with substantially higher treatment-related high-grade AEs and discontinuations. These findings suggest that combination therapy with nivolumab and ipilimumab may be unnecessary in many patient populations and that nivolumab alone may deliver equivalent clinical outcomes with lower toxicity (clinical and financial) in many advanced cancers other than melanoma.
eAppendix 1. Supplemental Methods
eAppendix 2. Supplemental Results
eAppendix 3. PFS and OS HR Calculation Analysis of Individual Studies
eFigure 1. PRISMA Schema
eFigure 2. OS and PFS Meta-analysis Without Hellman et al 2019 (Sensitivity Analysis)
eFigure 3. Grade 3 to 4 Hepatotoxicity
eFigure 4. Grade 3 to 4 GI Toxicity
eFigure 5. Grade 3 to 4 Pneumonitis
eFigure 6. Grade 3 to 4 Endocrine Dysfunction
eFigure 7. Grade 3 to 4 Fatigue
eFigure 8. Grade 3 to 4 Dermatitis
Data Sharing Statement
References
- 1.Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, et al. Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(1):23-34. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1504030 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, et al. Five-year survival with combined nivolumab and ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(16):1535-1546. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1910836 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett S, Sydes MR. Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials. 2007;8:16. doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-8-16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gettinger SN, Redman MW, Bazhenova L, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab vs nivolumab for previously treated patients with stage IV squamous cell lung cancer: the Lung-MAP S1400I phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(9):1368-1377. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.2209 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hellmann MD, Paz-Ares L, Bernabe Caro R, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(21):2020-2031. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1910231 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Antonia SJ, López-Martin JA, Bendell J, et al. Nivolumab alone and nivolumab plus ipilimumab in recurrent small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 032): a multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(7):883-895. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30098-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Scherpereel A, Mazieres J, Greillier L, et al. ; French Cooperative Thoracic Intergroup . Nivolumab or nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with relapsed malignant pleural mesothelioma (IFCT-1501 MAPS2): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, non-comparative, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(2):239-253. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30765-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sharma P, Siefker-Radtke A, de Braud F, et al. Nivolumab alone and with ipilimumab in previously treated metastatic urothelial carcinoma: CheckMate 032 nivolumab 1 mg/kg plus ipilimumab 3 mg/kg expansion cohort results. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(19):1608-1616. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00538 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Janjigian YY, Bendell J, Calvo E, et al. CheckMate-032 study: efficacy and safety of nivolumab and nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with metastatic esophagogastric cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(28):2836-2844. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.76.6212 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.D’Angelo SP, Mahoney MR, Van Tine BA, et al. Nivolumab with or without ipilimumab treatment for metastatic sarcoma (Alliance A091401): two open-label, non-comparative, randomised, phase 2 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(3):416-426. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30006-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Omuro A, Vlahovic G, Lim M, et al. Nivolumab with or without ipilimumab in patients with recurrent glioblastoma: results from exploratory phase I cohorts of CheckMate 143. Neuro Oncol. 2018;20(5):674-686. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nox208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ellis LM, Bernstein DS, Voest EE, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology perspective: raising the bar for clinical trials by defining clinically meaningful outcomes. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(12):1277-1280. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.53.8009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen J, Li S, Yao Q, et al. The efficacy and safety of combined immune checkpoint inhibitors (nivolumab plus ipilimumab): a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol. 2020;18(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12957-020-01933-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yang Y, Jin G, Pang Y, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of nivolumab and nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:40 doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00040 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kim S, Wuthrick E, Blakaj D, et al. Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab with or without stereotactic body radiation therapy for advanced Merkel cell carcinoma: a randomised, open label, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2022;400(10357):1008-1019. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01659-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eAppendix 1. Supplemental Methods
eAppendix 2. Supplemental Results
eAppendix 3. PFS and OS HR Calculation Analysis of Individual Studies
eFigure 1. PRISMA Schema
eFigure 2. OS and PFS Meta-analysis Without Hellman et al 2019 (Sensitivity Analysis)
eFigure 3. Grade 3 to 4 Hepatotoxicity
eFigure 4. Grade 3 to 4 GI Toxicity
eFigure 5. Grade 3 to 4 Pneumonitis
eFigure 6. Grade 3 to 4 Endocrine Dysfunction
eFigure 7. Grade 3 to 4 Fatigue
eFigure 8. Grade 3 to 4 Dermatitis
Data Sharing Statement


