Abstract
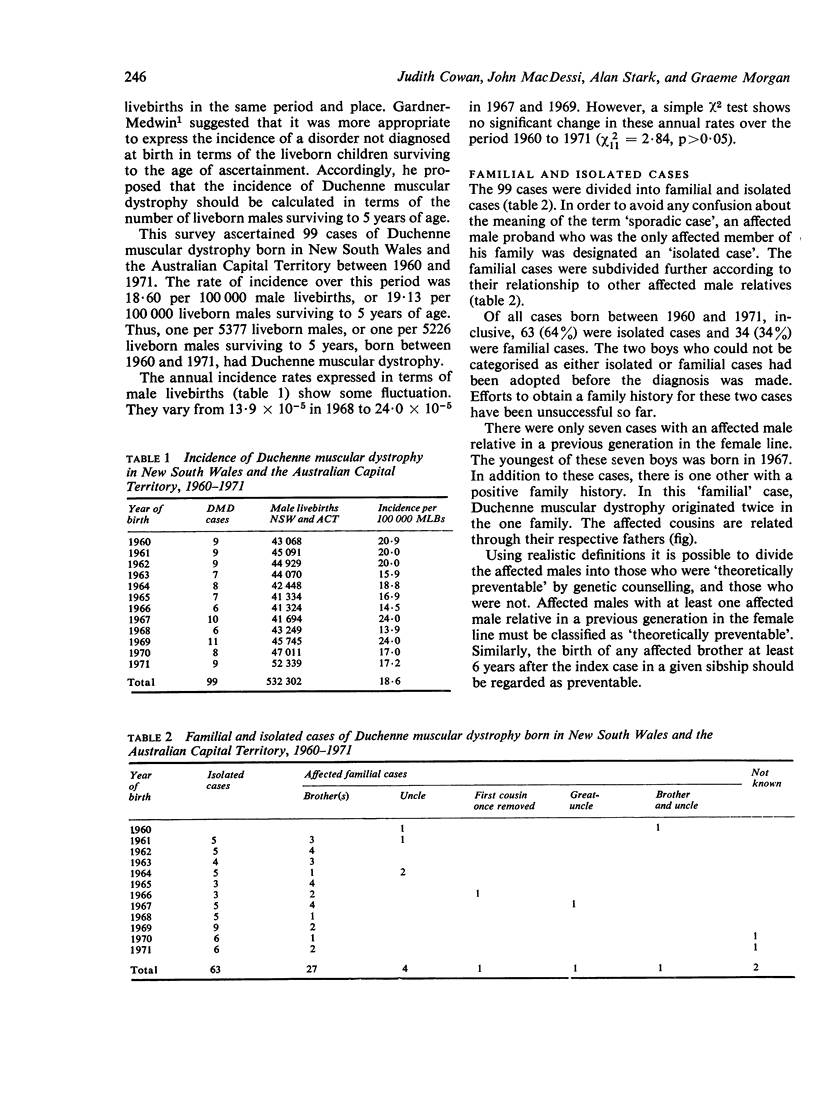
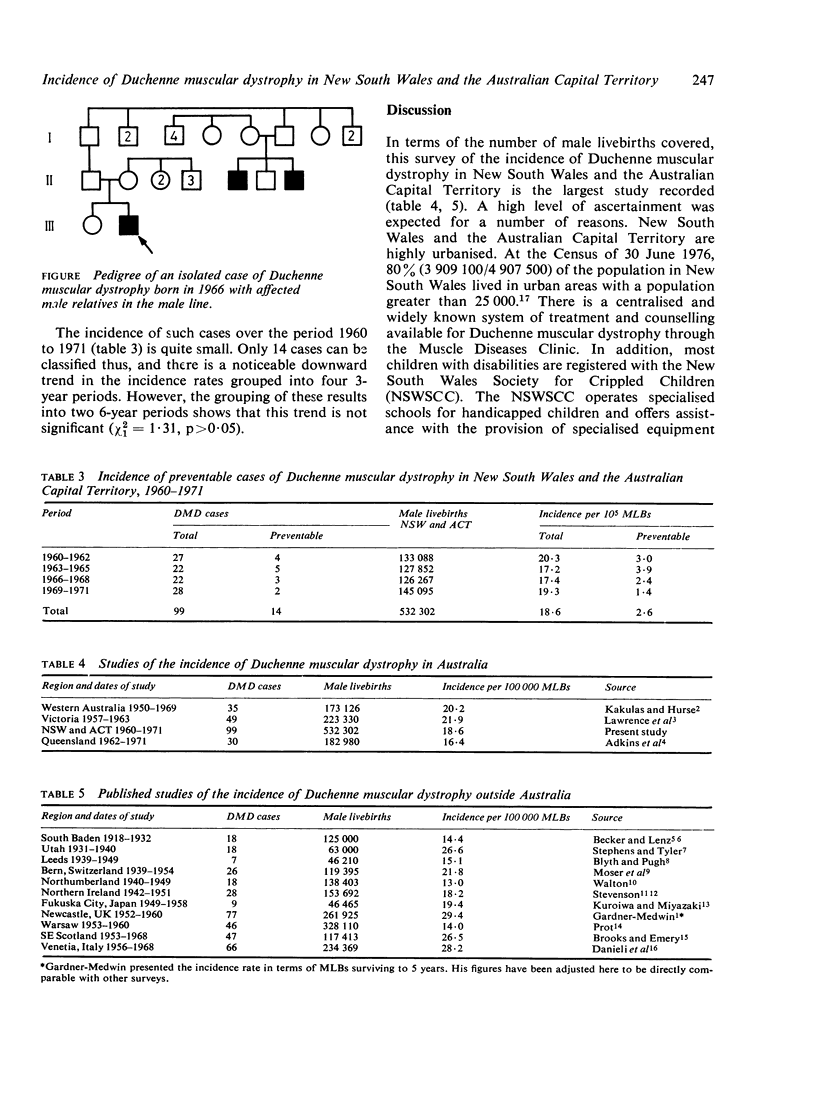
A survey was conducted during 1977 to 1978 to determine the incidence of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in New South Wales and the Australian Capital Territory. Ninety-nine cases born between 1960 and 1971 were ascertained representing an incidence rate of 18.6 per 100 000 liveborn males. Over 60% of the ascertained males were isolated cases, and only 7% of affected males had an affected males relative in a previous generation in the female line. Categorisation of ascertained cases as either "theoretically preventable" or not shows that genetic counselling alone in the present circumstances is insufficient to reduce the incidence rate significantly.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKER P. E., LENZ F. Zur Schätzung der Mutationsrate der Muskeldystrophien. Z Mensch Vererb Konstitutionsl. 1955;33(1):42–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLYTH H., PUGH R. J. Muscular dystrophy in childhood; the genetic aspect; a field study in the Leeds region of clinical types and their inheritance. Ann Hum Genet. 1959 Apr;23(2):127–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1958.tb01457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks A. P., Emery A. E. The incidence of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in the South East of Scotland. Clin Genet. 1977 Apr;11(4):290–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1977.tb01315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEESEMAN E. A., KILPATRICK S. J., STEVENSON A. C., SMITH C. A. The sex ratio of mutation rates of sex-linked recessive genes in man with particular reference to Duchenne type muscular dystrophy. Ann Hum Genet. 1958 May;22(3):235–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1958.tb01418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner-Medwin D. Mutation rate in Duchenne type of muscular dystrophy. J Med Genet. 1970 Dec;7(4):334–337. doi: 10.1136/jmg.7.4.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence E. F., Brown B., Hopkins I. J. Pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy of childhood: an epidemiological survey in Victoria. Aust N Z J Med. 1973 Apr;3(2):142–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1973.tb03967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSER H., WIESMANN U., RICHTERICH R., ROSSI E. PROGRESSIVE MUSKELDYSTROPHIE. VI. HAEUFIGKEIT, KLINIK UND GENETIK DER DUCHENNE-FORM. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1964 Nov 14;94:1610–1621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prot J. Genetic-epidemiological studies in progressive muscular dystrophy. J Med Genet. 1971 Mar;8(1):90–95. doi: 10.1136/jmg.8.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEPHENS F. E., TYLER F. H. Studies in disorders of muscle. V. The inheritance of childhood progressive muscular dystrophy in 33 kindreds. Am J Hum Genet. 1951 Jun;3(2):111–125. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEVENSON A. C. Muscular dystrophy in Northern Ireland, I. An account of the condition in fifty-one families. Ann Eugen. 1953 Jun;18(1):50–contd. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1952.tb02497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEVENSON A. C. Muscular dystrophy in Northern Ireland. IV. Some additional data. Ann Hum Genet. 1958 May;22(3):231–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1958.tb01417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALTON J. N., RACE R. R., PHILIP U. On the inheritance of muscular dystrophy; with a note on the blood groups, and a note on colour vision and linkage studies. Ann Hum Genet. 1955 Aug;20(1):1–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1955.tb01274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


