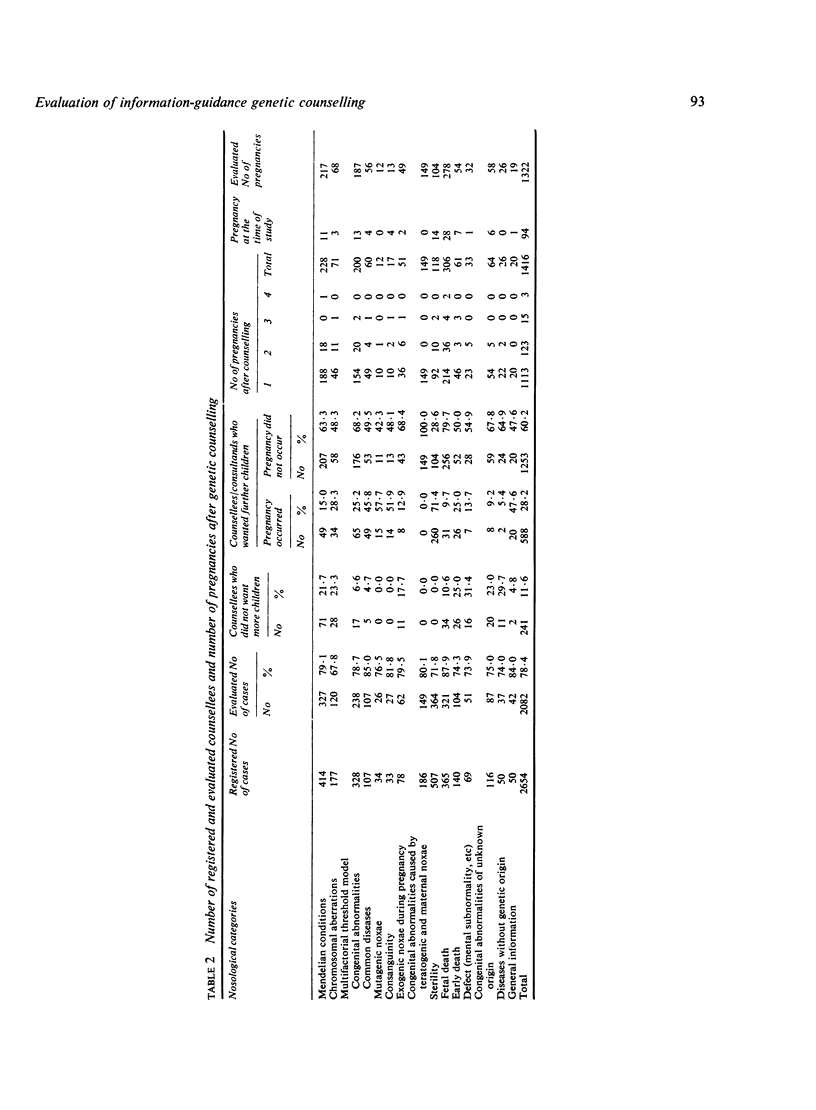
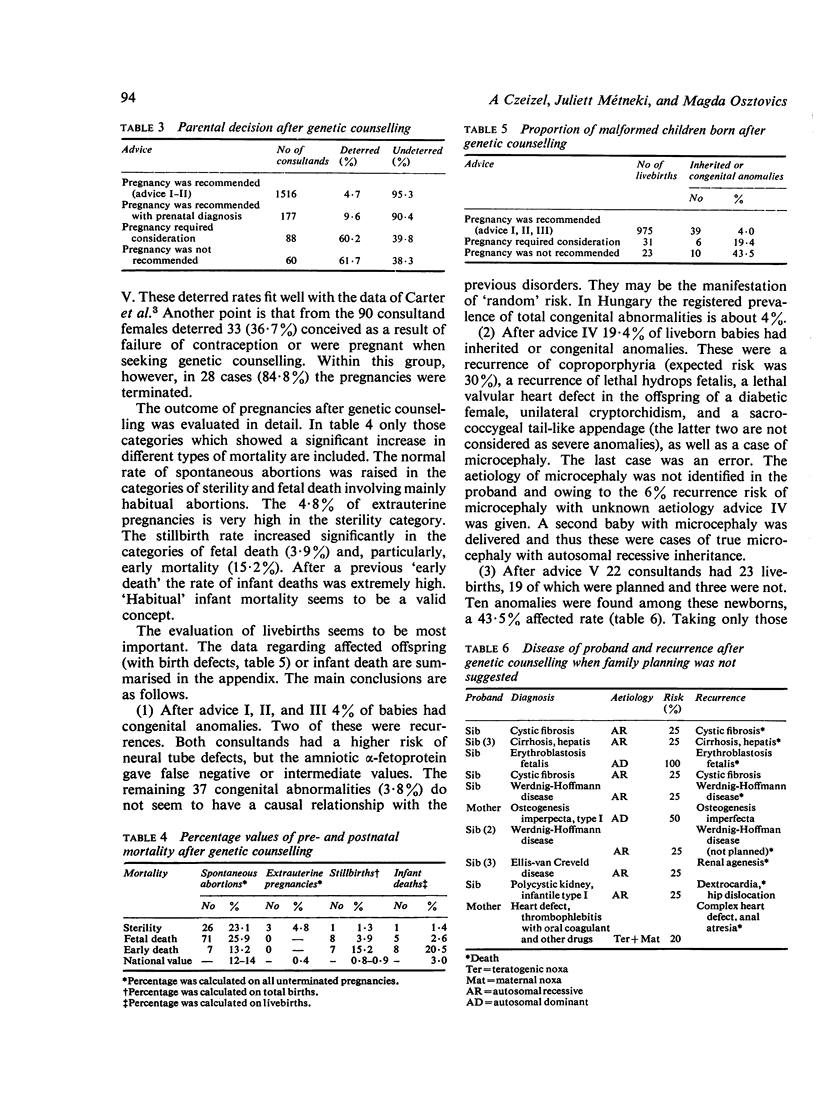
Abstract
The impact of information-guidance type of genetic counseling was evaluated for the family planning of 2082 consultands. The understanding of the risks, parental decision, and the number of induced and spontaneous abortions were evaluated by the use of questionnaires. The stillbirths, livebirths, infant deaths, and babies with inherited or congenital anomalies were checked by experts. When pregnancy was recommended the rate deterred was 4.7% while this rate was 61.7% and 60.7% when pregnancy was not recommended or pregnancy required consideration. When pregnancy was not recommended, 43.5% of offspring had congenital anomalies, while this value fitted with random risk (4%) in offspring born after recommended pregnancies.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carter C. O., Roberts J. A., Evans K. A., Buck A. R. Genetic clinic. A follow-up. Lancet. 1971 Feb 6;1(7693):281–285. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers-Kiebooms G., van den Berghe H. Impact of genetic counseling: a review of published follow-up studies. Clin Genet. 1979 Jun;15(6):465–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1979.tb00827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


