Abstract
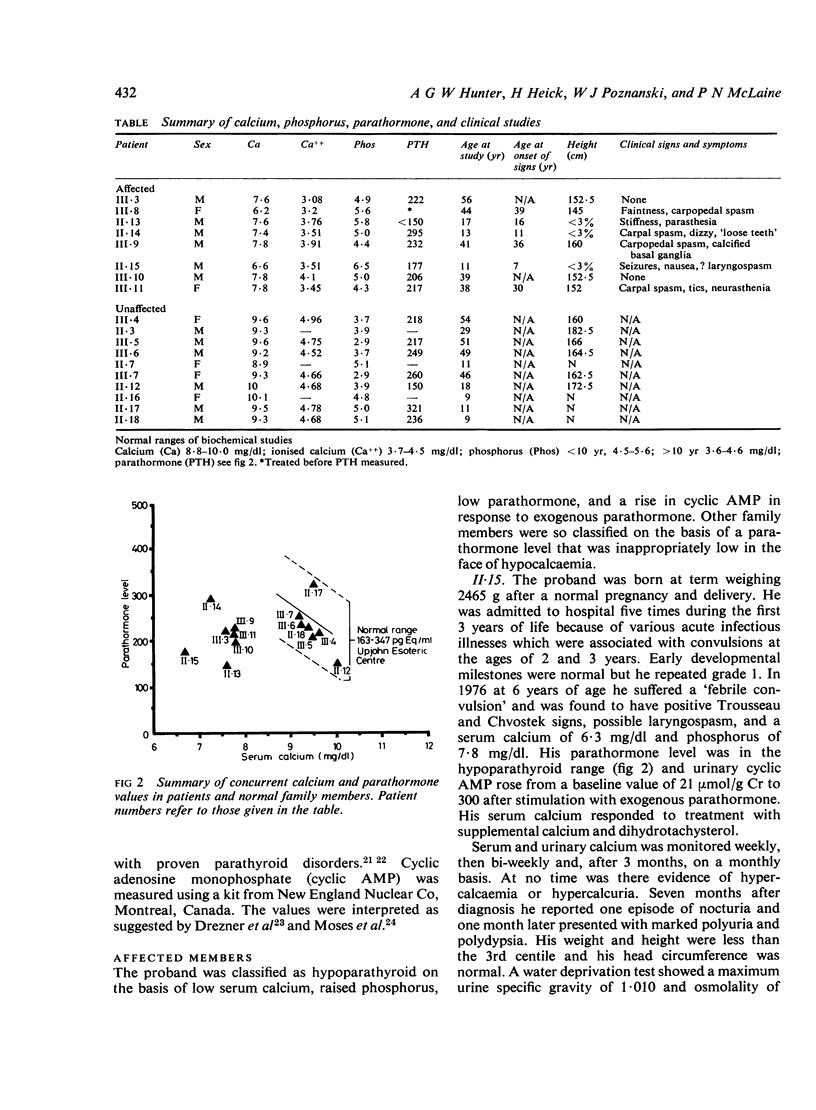
In this paper we report an extended family with well documented autosomal dominant hypoparathyroidism which was ascertained through a proband with coincident nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Clinical findings were limited to a slight decrease in overall stature and to clinical signs of hypocalcaemia. Intelligence was normal and two patients were asymptomatic. Published reports have established that autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, and sex linked recessive familial isolated hypoparathyroidism exist. However, in almost half the reported families an X linked dominant aetiology cannot be excluded and, at present, clinical criteria provide only minimal aid in distinguishing between the different genetic types. There remains a need for detailed documentation of further families were the pattern of inheritance is clear.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENSON P. F., PARSONS V. HEREDITARY HYPOPARATHYROIDISM PRESENTING WITH OEDEMA IN THE NEONATAL PERIOD. Q J Med. 1964 Apr;33:197–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barakat A. Y., D'Albora J. B., Martin M. M., Jose P. A. Familial nephrosis, nerve deafness, and hypoparathyroidism. J Pediatr. 1977 Jul;91(1):61–64. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80445-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr D. G., Prader A., Esper U., Rampini S., Marrian V. J., Forfar J. O. Chronic hypoparathyroidism in two generations. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1971 Dec;26(5):507–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barwich D. Familiär vorkommender Hypoparathyreoidismus. Med Klin. 1974 Dec 6;69(49):2029–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair A. J., Jr, Hawker C. D., Utiger R. D. Ectopic hyperparathyroidism in a patient with metastatic hypernephroma. Metabolism. 1973 Feb;22(2):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90265-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronsky D., Kiamko R. T., Waldstein S. S. Familial idiopathic hypoparathyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Jan;28(1):61–65. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-1-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPTAL J., JEAN R., BONNET H., GUILLAUMOT R., MOREL G. [Familial hypoparathyroidism. Clinical, biological and therapeutic study]. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1960 Jul-Aug;17:866–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN R., REYNOLDS J. L., CUMMINGS H. R., BASSETT S. H. Familial hypoparathyroidism; report of a case. J Am Med Assoc. 1952 Nov 15;150(11):1104–1106. doi: 10.1001/jama.1952.63680110002013a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlóczy F., Molnár M., Bizsik G., Nádor V., Szathmáry S. Zur Frage der Familiarität des Hypoparathyreoidismus. Acta Paediatr Acad Sci Hung. 1966;8(1):83–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorodischer R., Aceto T., Jr, Terplan K. Congenital familial hypoparathyroidism. Management of an infant, genetics, pathogenesis of hypoparathyroidism, and fetal undermineralization. Am J Dis Child. 1970 Jan;119(1):74–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSTED C., BRANDT S. Electroencephalographic changes in siblings with hypocalcemia due to hypoparathyroidism. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1953 Feb;5(1):101–104. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(53)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawker C. D. Parathyroid hormone: radioimmunoassay and clinical interpretation. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1975 Sep-Oct;5(5):383–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota Y., Cohen E. M., Bing O. H. Lactate dehydrogenase and isoenzyme changes in rats with experimental thiamine deficiency. Metabolism. 1976 Jan;25(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90153-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse K., Offermann G. Zur Klinik und Behandlung des familiären idiopathischen Hypoparathyreoidismus. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1977 May;125(5):489–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. M., Breslau N., Coulson R. Renal responses to PTH in patients with hormone-resistant (pseudo) hypoparathyroidism. Am J Med. 1976 Aug;61(2):184–189. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niklasson E. Familial early hypoparathyroidism associated with hypomagnesaemia. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1970 Nov;59(6):715–719. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1970.tb17712.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusynowitz M. L., Frame B., Kolb F. O. The spectrum of the hypoparathyroid states: A classification based on physiologic principles. Medicine (Baltimore) 1976 Mar;55(2):105–119. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197603000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEDEN V. H. True idiopathic hypoparathyroidism as a sexlinked recessive trait. Am J Hum Genet. 1960 Sep;12:323–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter P. L., Chutorian A. M. Familial hypoparathyroidism. Case reports and a eview of the literature. Neurology. 1968 Jan;18(1 Pt 1):75–80. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.1_part_1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYBI H., KEELE D. Hypoparathyroidism: a review of the literature and report of two cases in sisters, one with steatorrhea and intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1962 Sep;88:432–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


