Abstract
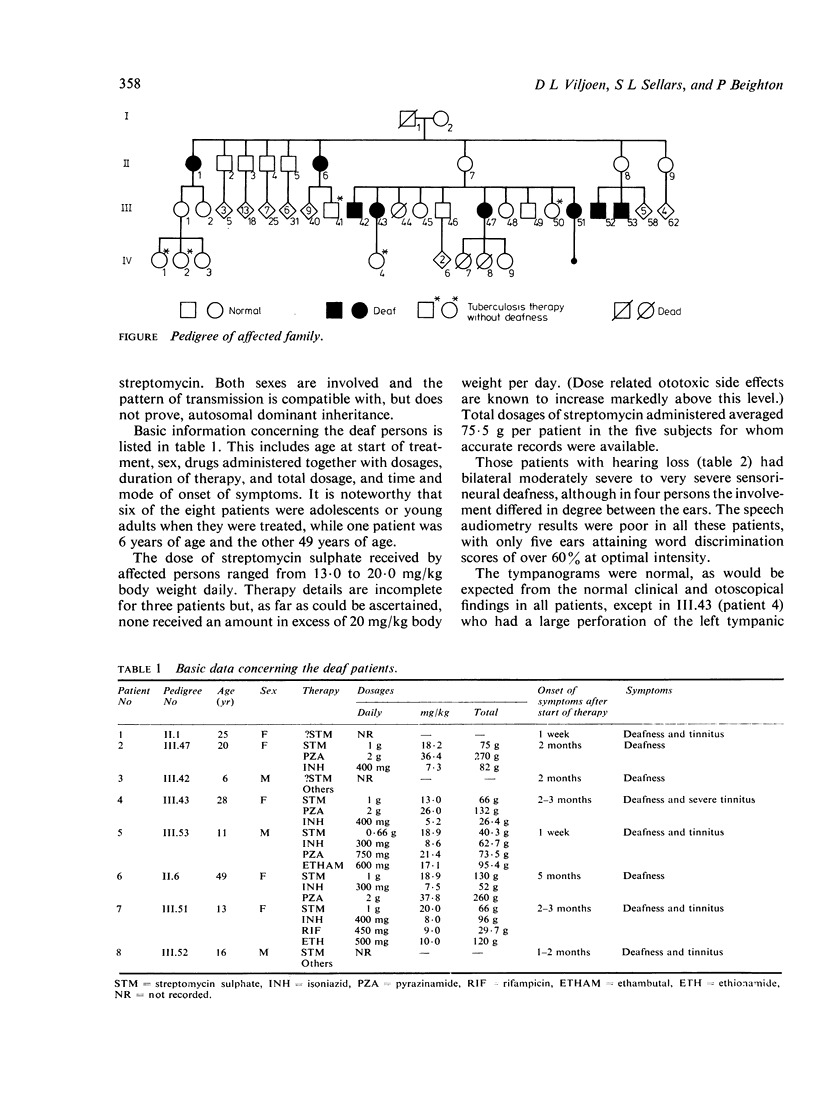
Eight members of a large kindred of mixed ancestry from a remote rural area of South Africa were investigated for deafness. In each, severe permanent perceptive hearing loss had developed during antituberculous therapy with streptomycin sulphate in conventional doses. Although unproven by the data available in this study, the familial aggregation and pattern of distribution of sensitivity to streptomycin suggested autosomal dominant inheritance.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballantyne J. Iatrogenic deafness. J Laryngol Otol. 1970 Oct;84(10):967–1000. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100072790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald P. R., Sellars S. L. Streptomycin ototoxicity in the unborn child. S Afr Med J. 1981 Aug 22;60(8):316–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsonbaugh R. E., Drexler H. G., Light I. J., Sutherland J. M. Familial occurrence of drug-induced hearing loss. Am J Dis Child. 1974 Feb;127(2):245–247. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1974.02110210095014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRAZIC M., SALAJ B., SUBOTIC R. FAMILIAL SENSITIVITY TO STREPTOMYCIN. J Laryngol Otol. 1964 Nov;78:1037–1043. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100063131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spoendlin H. Zur Ototoxizität des Streptomyzins. Pract Otorhinolaryngol (Basel) 1966;28(5):305–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


