Abstract
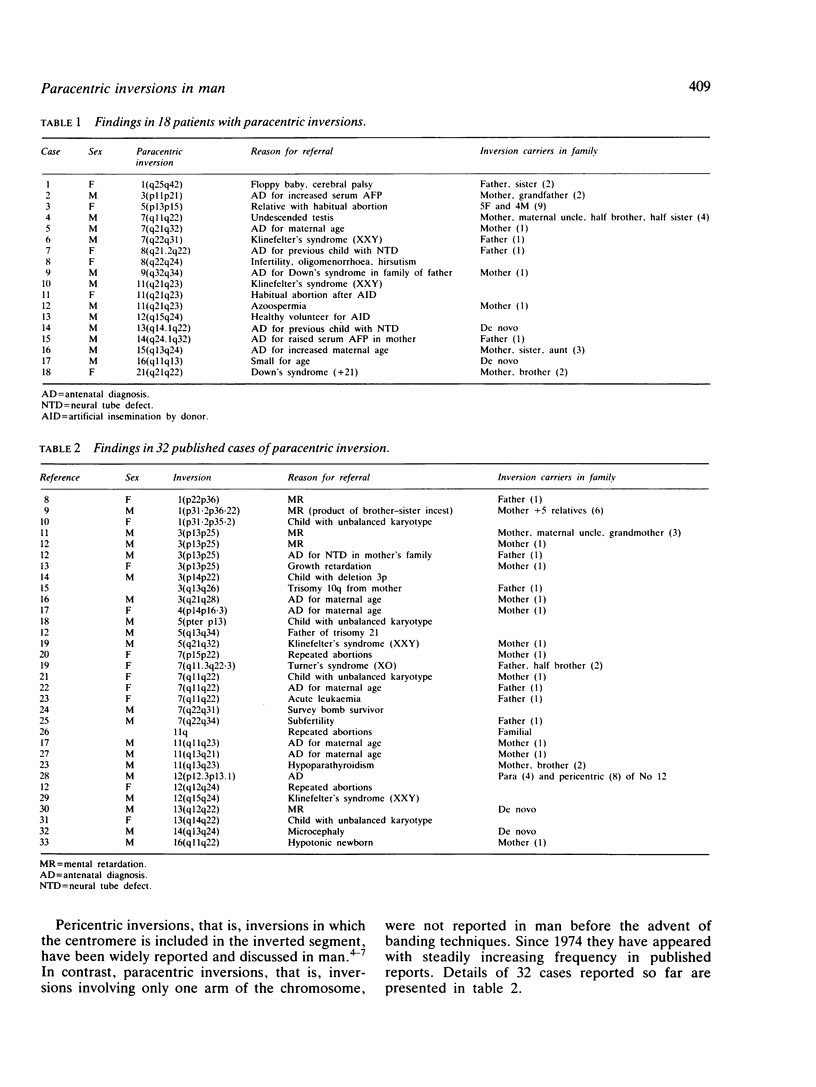
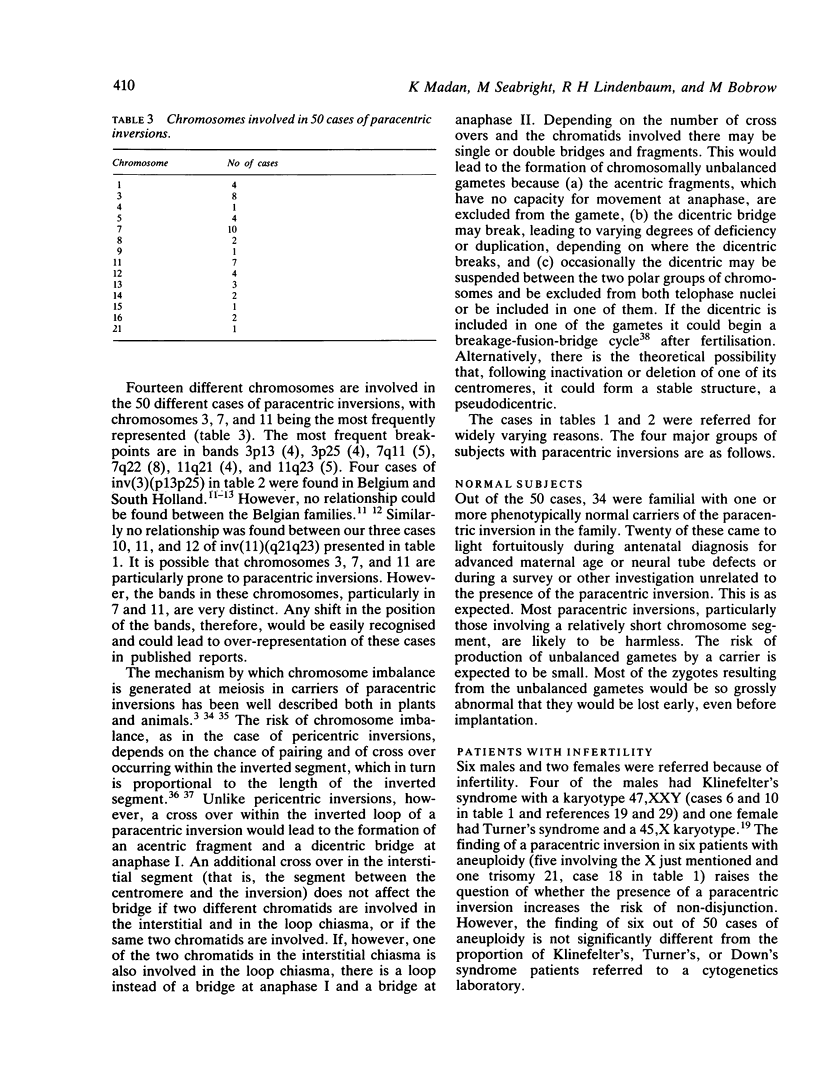
We have reviewed 50 cases of paracentric inversions. Of these 34 were familial with 62 phenotypically normal carrier relatives. Twenty of the 50 were discovered fortuitously. There were two reports of children with easily recognised unbalanced karyotypes resulting from a paracentric inversion in one of the parents. The vast majority of paracentric inversions are harmless. The risk of abnormal children for paracentric inversion heterozygotes is low but increases with the finding of recurrent abortions or abnormal children or both in other carriers in the family. We emphasise the need for caution in interpreting the results of antenatal diagnosis because of the variety of unexpected unbalanced chromosome types that can result from a paracentric inversion, and the difficulty in recognising, with confidence, minute differences (for the detection of which very high resolution banding is required) between apparently similar parental and fetal inversions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Canki N., Dutrillaux B. Two cases of familial paracentric inversion in man associated with sex chromosome anomaly. 47,XXY,inv(5)(q21q32) and 45,X,inv(7)(q11.3q22.3). Hum Genet. 1979 Apr 5;47(3):261–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00321018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson H L. The Selective Elimination of Inversion Dicentric Chromatids during Meiosis in the Eggs of Sciara Impatiens. Genetics. 1946 Jan;31(1):95–113. doi: 10.1093/genetics/31.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandall B. F., Lebherz T. B., Rubinstein L., Robertson R. D., Sample W. F., Sarti D., Howard J. Chromosome findings in 2,500 second trimester amniocenteses. Am J Med Genet. 1980;5(4):345–356. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320050405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deroover J., Fryns J. P., Haegeman J., Van Den Bergh H. Paracentric inversion in the short arm of chromosome 1. Hum Genet. 1979 Jun 19;49(2):117–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00277632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faed M. J., Robertson J., Lamont M. A., MacIntosh W., Grieve J., Baxby K., James G. B., Crowder A. M. A cytogenetic survey of men being investigated for subfertility. J Reprod Fertil. 1979 May;56(1):209–216. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0560209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., Van den Berghe H. Paracentric Inversion in man: personal experience and review of the literature. Hum Genet. 1980;54(3):413–416. doi: 10.1007/BF00291590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., van den Berghe H. Familial paracentric inversion of the short arm of chromosome 3. Ann Genet. 1979;22(3):163–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoegerman S. F. Chromosome 13 long arm interstitial deletion may result from maternal inverted insertion. Science. 1979 Sep 7;205(4410):1035–1036. doi: 10.1126/science.472726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoo J. J., Lorenz R., Fischer A., Fuhrmann W. Tiny interstitial duplication of proximal 7q in association with a maternal paracentric inversion. Hum Genet. 1982;62(2):113–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00282296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madan K., Bobrow M. Structural variation in chromosome No 9. Ann Genet. 1974 Jun;17(2):81–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClintock B. The Stability of Broken Ends of Chromosomes in Zea Mays. Genetics. 1941 Mar;26(2):234–282. doi: 10.1093/genetics/26.2.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orye E., Van Bever H. Paracentric inversions: two new familial cases, inv (7)(q22q11) and inv (11)(q23q13). J Med Genet. 1983 Jun;20(3):231–231. doi: 10.1136/jmg.20.3.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen H., Mikkelsen M., Holmgren G. Peri- and paracentric inversions in chromosome 12: prenatal diagnosis and family study. Prenat Diagn. 1981 Jan;1(1):35–42. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970010108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccardi V. M., Holmquist G. P. De novo 13q paracentric inversion in a boy with cleft palate and mental retardation. Hum Genet. 1979 Nov;52(2):211–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridler M. A., Sutton S. D. A case of a paracentric inversion inv(7)(q11q22). Prenatal detection and counselling. Prenat Diagn. 1981 Jan;1(1):81–84. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970010113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romain D. R., Columbano-Green L. M., Whyte S., Smythe R. H., Parfitt R. G., Gebbie O. B., Chapman C. J. Familial paracentric inversion of 1p. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Apr;14(4):629–634. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320140406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimba H., Ohtaki K., Tanabe K., Sofuni T. Paracentric inversion of a human chromosome 7. Hum Genet. 1976 Jan 28;31(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00270393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R. P. Klinefelter's syndrome with a 47,XXY, inv (12) (q15q24) karyotype. Clin Genet. 1981 Mar;19(3):188–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1981.tb00694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparkes R. S., Muller H., Klisak I. Retinoblastoma with 13q- chromosomal deletion associated with maternal paracentric inversion of 13q. Science. 1979 Mar 9;203(4384):1027–1029. doi: 10.1126/science.424728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetten G., Rock J. A. A paracentric chromosomal inversion associated with repeated early pregnancy wastage. Fertil Steril. 1983 Jul;40(1):124–126. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)47190-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturtevant A H, Beadle G W. The Relations of Inversions in the X Chromosome of Drosophila Melanogaster to Crossing over and Disjunction. Genetics. 1936 Sep;21(5):554–604. doi: 10.1093/genetics/21.5.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturtevant A H. Genetic Studies on DROSOPHILA SIMULANS. I. Introduction. Hybrids with DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Genetics. 1920 Sep;5(5):488–500. doi: 10.1093/genetics/5.5.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trunca C., Opitz J. M. Pericentric inversion of chromosome 14 and the risk of partial duplication of 14q (14q31 leads to 14qter). Am J Med Genet. 1977;1(2):217–228. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320010208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valcárcel E., Benítez J., Martínez P., Rey J. A., Sánchez Cascos A. Cytogenetic recombinants from a female carrying a paracentric inversion of the short arm of chromosome number 5. Hum Genet. 1983;63(1):78–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00285405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke D. L., Weiss L., Roberson J. R., Babu V. R. The frequency and mutation rate of balanced autosomal rearrangements in man estimated from prenatal genetic studies for advanced maternal age. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Mar;35(2):301–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vine D. T., Yarkoni S., Cohen M. M. Inversion homozygosity of chromosome no. 9 in a higly inbred kindred. Am J Hum Genet. 1976 May;28(3):203–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Chapelle A., Schröder J., Stenstrand K., Fellman J., Herva R., Saarni M., Anttolainen I., Tallila I., Tervilä L., Husa L. Pericentric inversions of human chromosomes 9 and 10. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Nov;26(6):746–766. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Solar C., Uchida I. A. Identification of chromosomal abnormalities by quinacrine-staining technique in patients with normal karyotypes by conventional analysis. J Pediatr. 1974 Apr;84(4):534–538. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80673-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


