Abstract
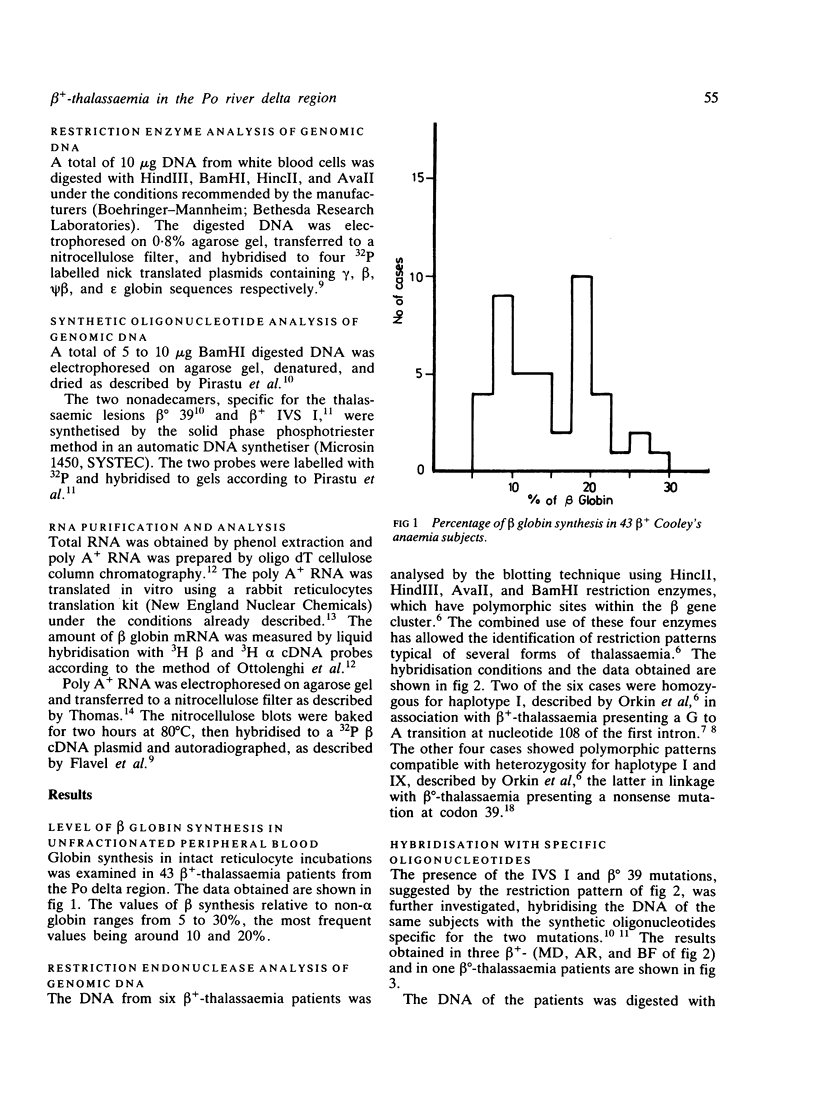
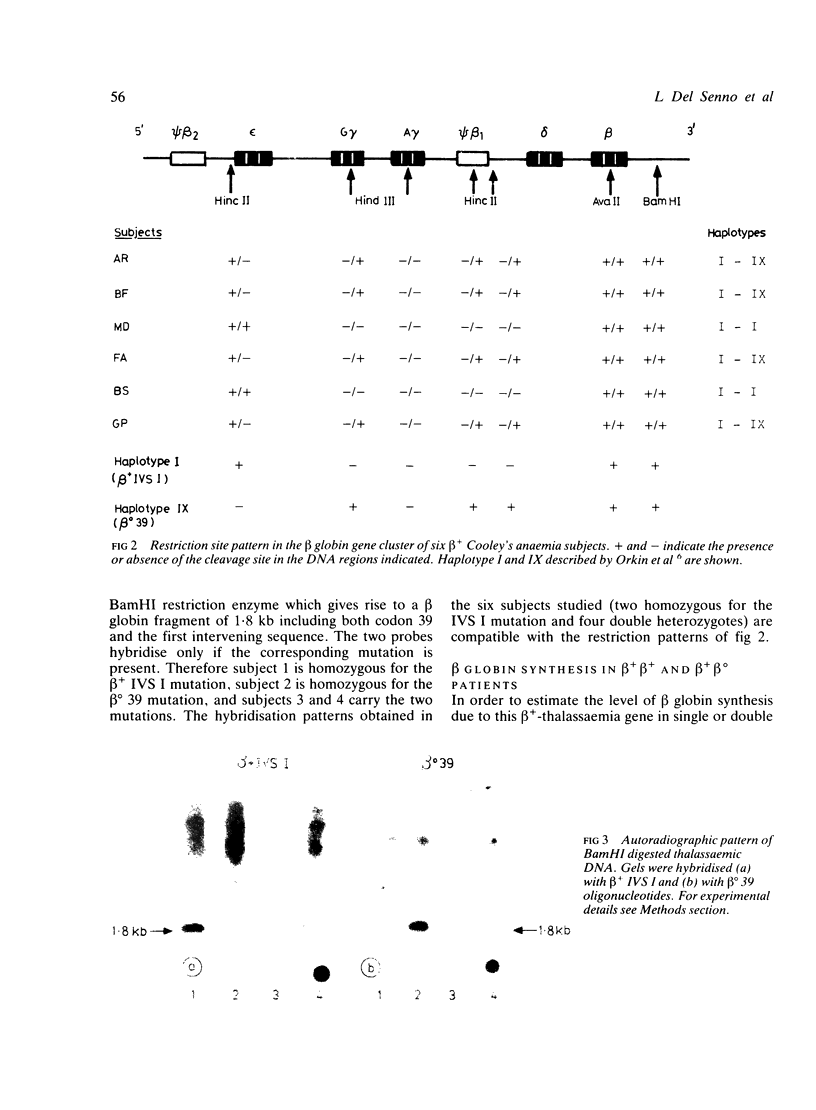
Six beta(+)-thalassaemic patients from the Po river delta region have been studied. Using synthetic oligonucleotides as specific hybridisation probes, the beta(+) IVS I mutation (G----A at position 108) was demonstrated. This lesion and the enzyme polymorphism pattern in the subjects examined are the same as have been described for other Mediterranean beta(+)-thalassaemias. Antenatal diagnosis through DNA analysis of beta(+)-thalassaemia is therefore possible. The production of beta globin in a beta(+), homozygote and in a beta (+), beta(0) 39 (nonsense mutation at codon 39) double heterozygote is approximately 20% and 10% respectively of total non-alpha globin synthesis. Despite some overlapping of the results, similar beta globin synthesis levels have been obtained in 43 beta(+)-thalassaemia patients. This suggests that in the Po river delta region the most common thalassaemic genes are beta(0) 39 and beta(+) IVS I.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonarakis S. E., Boehm C. D., Giardina P. J., Kazazian H. H., Jr Nonrandom association of polymorphic restriction sites in the beta-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):137–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargellesi A., Pontremoli S., Conconi F. Absence of beta-globin synthesis and excess of alpha-globin synthesis in homozygous beta-thalassemia. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):73–79. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz E. J., Forget B. G., Hillman D. G., Cohen-Solal M., Pritchard J., Cavallesco C., Prensky W., Housman D. Variability in the amount of beta-globin mRNA in beta0 thalassemia. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):299–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Moschonas N., Flavell R. A. Beta + thalassemia: aberrant splicing results from a single point mutation in an intron. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):289–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90412-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. B., Naughton M. A., Weatherball D. J. Abnormal human haemoglobins. Separation and characterization of the alpha and beta chains by chromatography, and the determination of two new variants, hb Chesapeak and hb J (Bangkok). J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(1):91–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conconi F., Bernardi F., Buzzoni D., Casoni I., del Senno L., Marchetti G., Perrotta C. M. beta-Globin messenger RNA in Ferrara beta 0 thalassemia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;344:120–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb33655.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell R. A., Kooter J. M., De Boer E., Little P. F., Williamson R. Analysis of the beta-delta-globin gene loci in normal and Hb Lepore DNA: direct determination of gene linkage and intergene distance. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):25–41. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumaki Y., Ghosh P. K., Benz E. J., Jr, Reddy V. B., Lebowitz P., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. Abnormally spliced messenger RNA in erythroid cells from patients with beta+ thalassemia and monkey cells expressing a cloned beta+-thalassemic gene. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housman D., Forget B. G., Skoultchi A., Benz E. J., Jr Quantitative deficiency of chain-specific globin messenger ribonucleic acids in the thalassemia syndromes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1809–1813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor J. A., Turner P. H., Nienhuis A. W. Beta Thalassemia: mutations which affect processing of the beta-Globin mRNA precursor. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Antonarakis S. E., Goff S. C., Boehm C. D., Sexton J. P., Waber P. G., Giardina P. J. Linkage of beta-thalassaemia mutations and beta-globin gene polymorphisms with DNA polymorphisms in human beta-globin gene cluster. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):627–631. doi: 10.1038/296627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Markham A. F., Kazazian H. H., Jr Direct detection of the common Mediterranean beta-thalassemia gene with synthetic DNA probes. An alternative approach for prenatal diagnosis. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):775–779. doi: 10.1172/JCI110826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottolenghi S., Comi P., Giglioni B., Williamson R., Vullo G., Conconi F. Direct demonstration of beta-globin mRNA in homozygous Ferrara betaO-thalassaemia patients. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):231–234. doi: 10.1038/266231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirastu M., Kan Y. W., Cao A., Conner B. J., Teplitz R. L., Wallace R. B. Prenatal diagnosis of beta-thalassemia. Detection of a single nucleotide mutation in DNA. N Engl J Med. 1983 Aug 4;309(5):284–287. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198308043090506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirastu M., del Senno L., Conconi F., Vullo C., Kan Y. W. Ferrara beta 0 thalassaemia caused by the beta 39 nonsense mutation. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):76–76. doi: 10.1038/307076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spritz R. A., Jagadeeswaran P., Choudary P. V., Biro P. A., Elder J. T., deRiel J. K., Manley J. L., Gefter M. L., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. Base substitution in an intervening sequence of a beta+-thalassemic human globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2455–2459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trecartin R. F., Liebhaber S. A., Chang J. C., Lee K. Y., Kan Y. W., Furbetta M., Angius A., Cao A. beta zero thalassemia in Sardinia is caused by a nonsense mutation. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):1012–1017. doi: 10.1172/JCI110323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vullo C. Thalassemia in Ferrara. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1982;18(7):199–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway D., Williamson R. An intron nucleotide sequence variant in a cloned beta +-thalassaemia globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1777–1788. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Senno L., Bernardi F., Buzzoni D., Marchetti G., Perrotta C., Conconi F. Molecular characteristics of a non-deletion alpha-thalassaemia of the Po River Delta. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):127–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Senno L., Bernardi F., Marchetti G., Perrotta C., Conconi F., Vullo C., Salsini G., Cristofori G., Cappellozza G., Bellinello F. Organization of alpha-globin genes and mRNA translation in subjects carrying haemoglobin Hasharon (alpha 47 Asp replaced by His) from the Ferrara Region (Northern Italy). Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(1):125–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Senno L., Bernardi F., Marchetti G., Perrotta C., Conconi F., Vullo C., Salsini G., Cristofori G., Cappellozza G., Bellinello F. Organization of alpha-globin genes and mRNA translation in subjects carrying haemoglobin Hasharon (alpha 47 Asp replaced by His) from the Ferrara Region (Northern Italy). Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(1):125–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]