Abstract
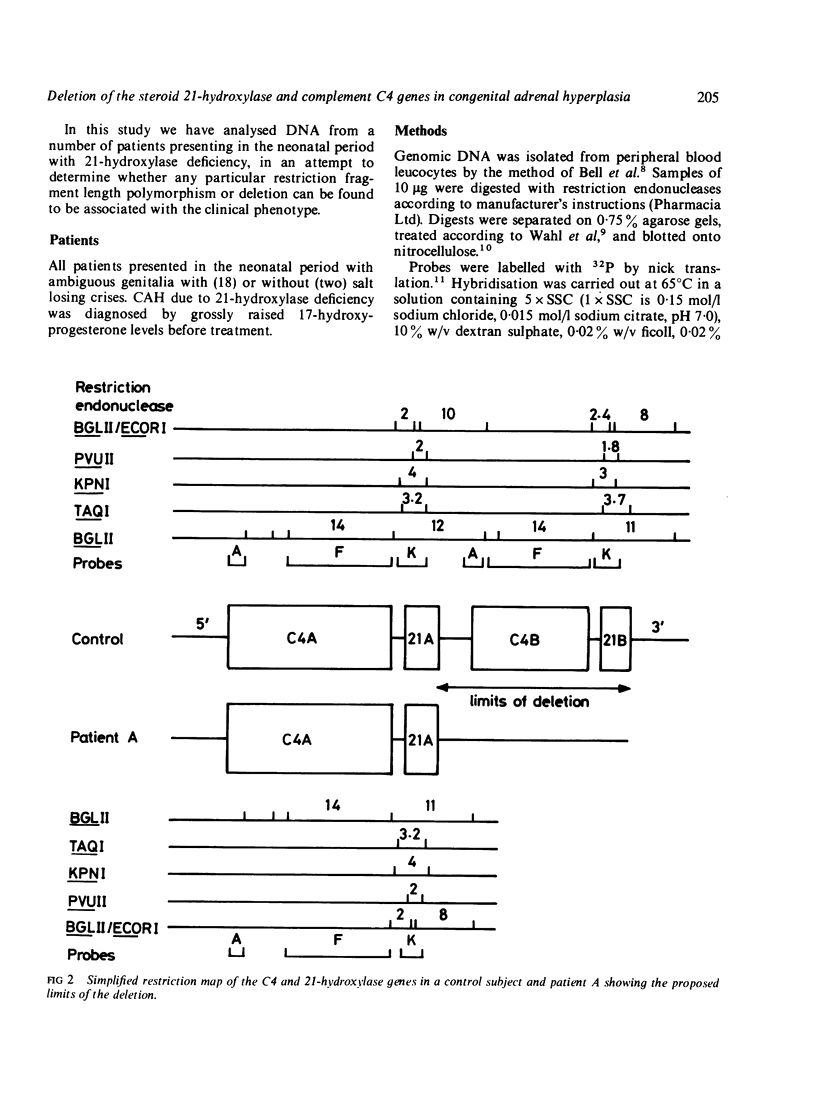
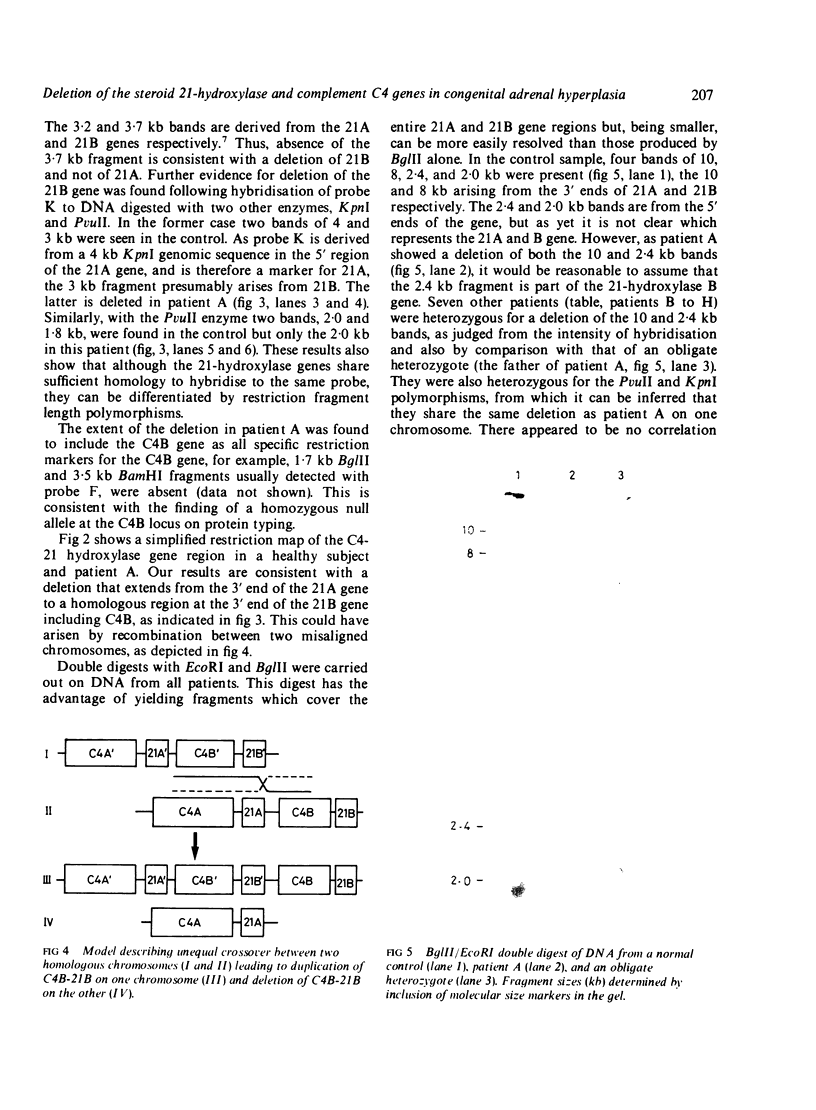
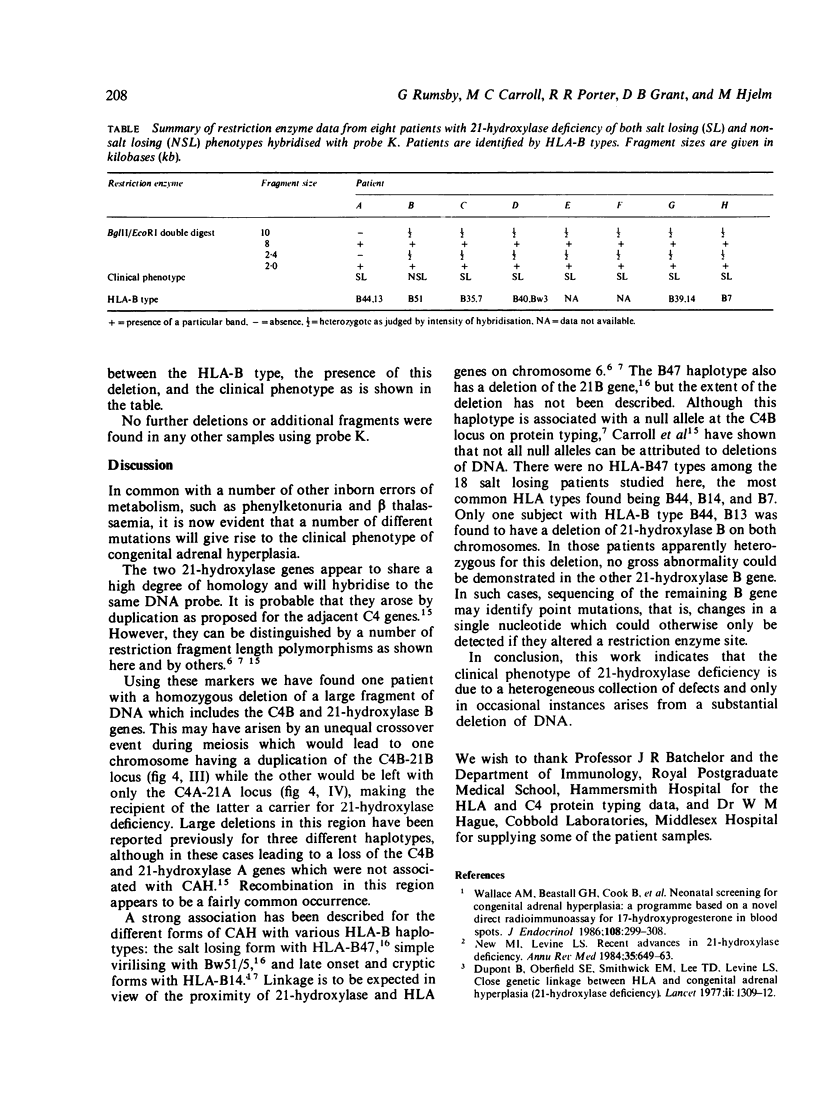
DNA was analysed from 20 patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to cytochrome P-450 steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Using probes recognising sequences in both the 21-hydroxylase gene and the adjacent fourth component of complement (C4), one patient was found to have a homozygous deletion of DNA which encompassed the C4B and 21-hydroxylase B genes. Evidence is presented for this deletion arising by recombination between homologous regions of 21-hydroxylase A and B. Seven patients appeared to be heterozygous for the same deletion, but no detectable alteration in the 21-hydroxylase gene could be demonstrated in others.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belt K. T., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. The structural basis of the multiple forms of human complement component C4. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):907–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Campbell R. D., Bentley D. R., Porter R. R. A molecular map of the human major histocompatibility complex class III region linking complement genes C4, C2 and factor B. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):237–241. doi: 10.1038/307237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Campbell R. D., Porter R. R. Mapping of steroid 21-hydroxylase genes adjacent to complement component C4 genes in HLA, the major histocompatibility complex in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):521–525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Palsdottir A., Belt K. T., Porter R. R. Deletion of complement C4 and steroid 21-hydroxylase genes in the HLA class III region. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2547–2552. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03969.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont B., Oberfield S. E., Smithwick E. M., Lee T. D., Levine L. S. Close genetic linkage between HLA and congenital adrenal hyperplasia (21-hydroxylase deficiency). Lancet. 1977 Dec 24;2(8052-8053):1309–1312. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90362-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- New M. I., Levine L. S. Recent advances in 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Annu Rev Med. 1984;35:649–663. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.35.020184.003245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palsdottir A., Cross S. J., Edwards J. H., Carroll M. C. Correlation between a DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism and C4A6 protein. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):615–616. doi: 10.1038/306615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M. S., Levine L. S., O'Neill G. J., Pang S., Lorenzen F., Kohn B., Rondanini G. F., Chiumello G., New M. I., Dupont B. HLA linkage and B14, DR1, BfS haplotype association with the genes for late onset and cryptic 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Jul;33(4):540–550. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace A. M., Beastall G. H., Cook B., Currie A. J., Ross A. M., Kennedy R., Girdwood R. W. Neonatal screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia: a programme based on a novel direct radioimmunoassay for 17-hydroxyprogesterone in blood spots. J Endocrinol. 1986 Feb;108(2):299–308. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1080299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Grossberger D., Onufer B. J., Chaplin D. D., New M. I., Dupont B., Strominger J. L. Two genes encoding steroid 21-hydroxylase are located near the genes encoding the fourth component of complement in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. HLA-linked congenital adrenal hyperplasia results from a defective gene encoding a cytochrome P-450 specific for steroid 21-hydroxylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7505–7509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]