Abstract
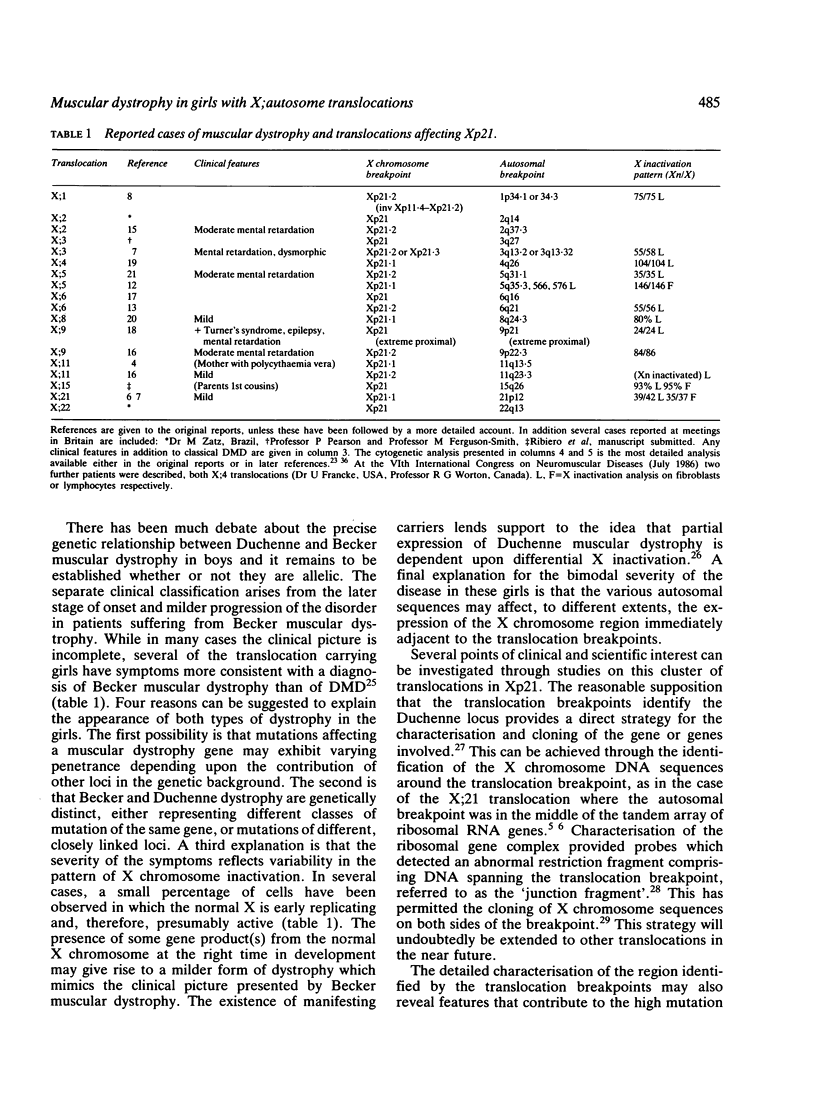
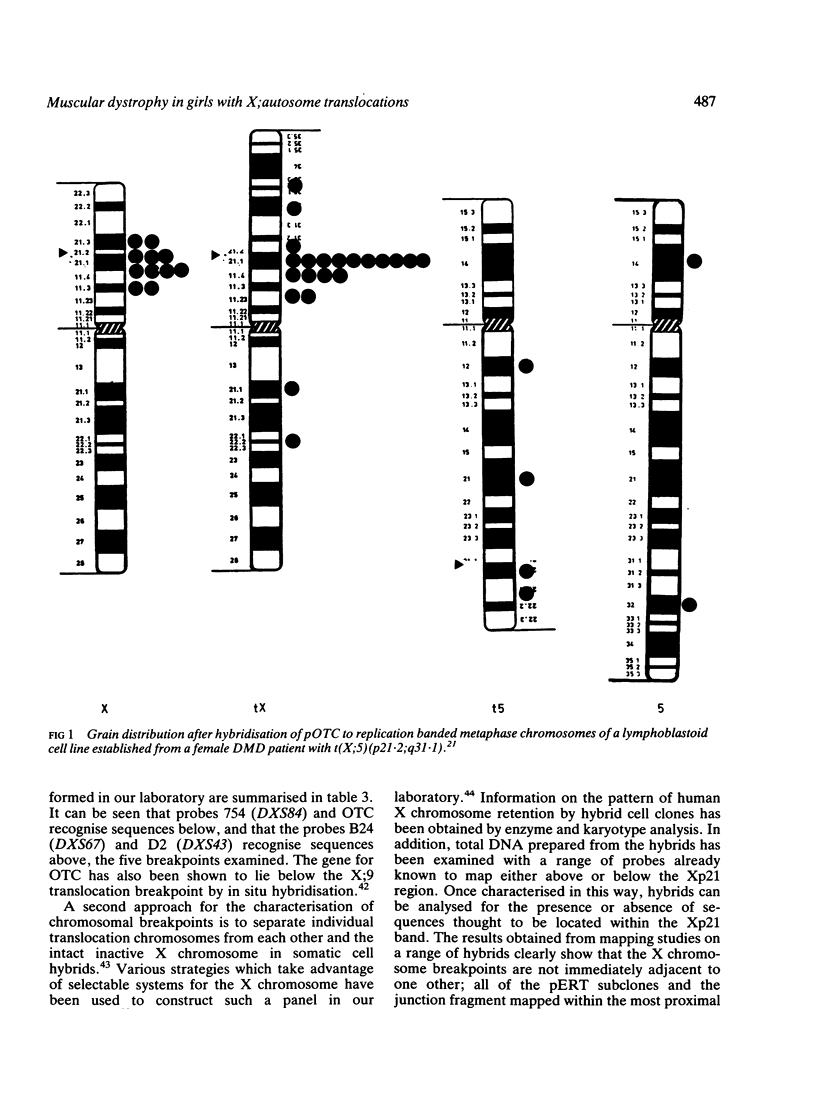
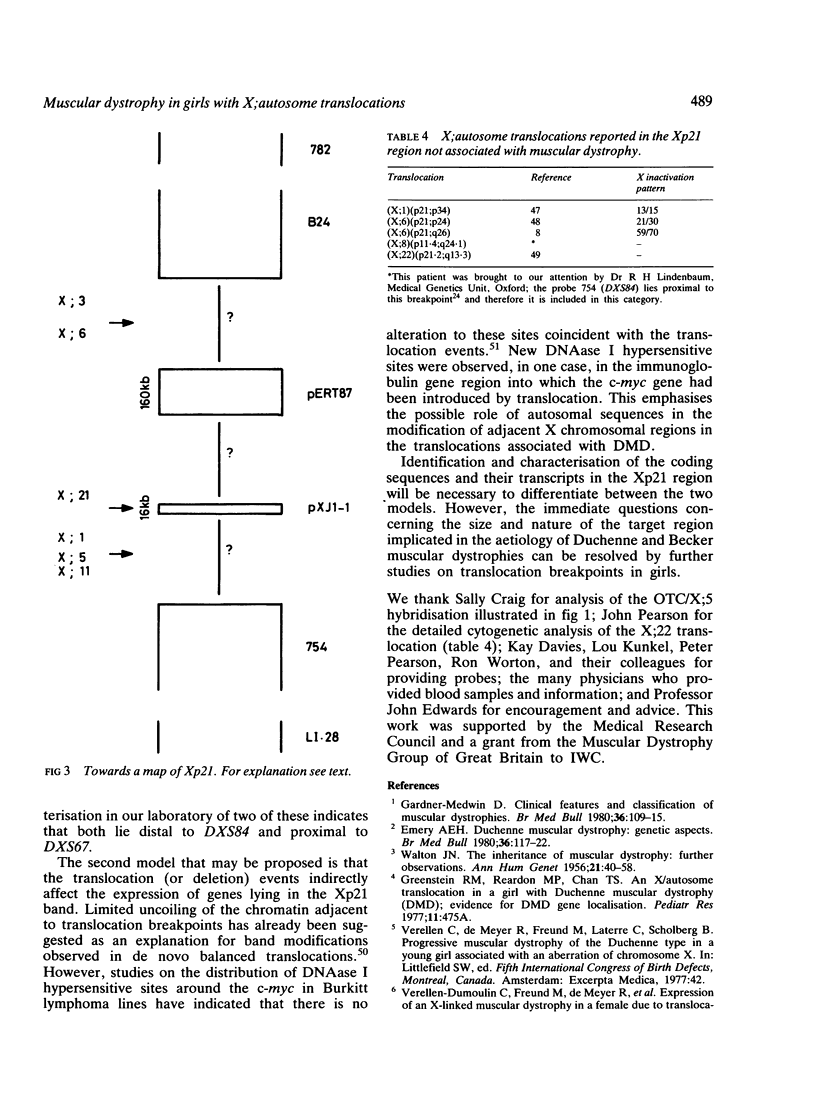
Twenty known cases of X;autosome translocations with breakpoints at Xp21 associated with Duchenne or Becker muscular dystrophy in girls are reviewed. The variable severity described for different persons may reflect differences in X inactivation or in the nature of the genomic target disrupted. High resolution cytogenetic studies on 12 cases indicate breakpoints on the X chromosome at Xp21.1 or Xp21.2. Translocation chromosomes from several of these cases have been isolated in human/mouse somatic cell hybrids. Molecular heterogeneity in the breakpoint positions has been established by probing DNA from these hybrids with a range of cloned sequences known to be located within, or closely linked to, the Duchenne region. The minimum separation between the most distal and the most proximal breakpoints is 176 kb suggesting that, if a single gene is involved, it must be large. Alternatively, the translocations may affect different genes, or confer alterations to regulatory sequences which operate at a distance.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger R., Bloomfield C. D., Sutherland G. R. Report of the Committee on Chromosome Rearrangements in Neoplasia and on Fragile Sites. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):490–535. doi: 10.1159/000132181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerglund Nielsen L., Nielsen I. M. Turner's syndrome and Duchenne muscular dystrophy in a girl with an X; autosome translocation. Ann Genet. 1984;27(3):173–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd Y., Buckle V. J. Cytogenetic heterogeneity of translocations associated with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Clin Genet. 1986 Feb;29(2):108–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb01232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz M. O., Le Beau M. M., Pitha P., Rowley J. D. Interferon and c-ets-1 genes in the translocation (9;11)(p22;q23) in human acute monocytic leukemia. Science. 1986 Jan 17;231(4735):265–267. doi: 10.1126/science.3455787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disteche C. M., Eicher E. M., Latt S. A. Late replication in an X-autosome translocation in the mouse: correlation with genetic inactivation and evidence for selective effects during embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5234–5238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubowitz V. X;autosome translocations in females with Duchenne or Becker muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):291–292. doi: 10.1038/322291b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson P. J., Rabbitts T. H. Chromatin structure around the c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphomas with upstream and downstream translocation points. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1984–1988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel B. S., Zackai E. H., Tucker S. H. Further evidence for Xp21 location of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) locus: X;9 translocation in a female with DMD. J Med Genet. 1983 Dec;20(6):461–463. doi: 10.1136/jmg.20.6.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery A. E. Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Genetic aspects, carrier detection and antenatal diagnosis. Br Med Bull. 1980 May;36(2):117–122. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Ochs H. D., de Martinville B., Giacalone J., Lindgren V., Distèche C., Pagon R. A., Hofker M. H., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Minor Xp21 chromosome deletion in a male associated with expression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa, and McLeod syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Mar;37(2):250–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner-Medwin D. Clinical features and classification of the muscular dystrophies. Br Med Bull. 1980 May;36(2):109–115. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaál M., László J. X inactivation pattern in an unbalanced X-autosome translocation with gonadal dysgenesis. Hum Hered. 1977;27(6):396–402. doi: 10.1159/000152900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitschier J., Wood W. I., Goralka T. M., Wion K. L., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Vehar G. A., Capon D. J., Lawn R. M. Characterization of the human factor VIII gene. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):326–330. doi: 10.1038/312326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. N., Davies K. E., Ropers H. H. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of the X and Y Chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):296–352. doi: 10.1159/000132178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagemeijer A., Hoovers J., Smit E. M., Bootsma D. Replication pattern of the X chromosomes in three X/autosomal translocations. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1977;18(6):333–348. doi: 10.1159/000130780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht F., Hecht B. K. Fragile sites and chromosome breakpoints in constitutional rearrangements II. Spontaneous abortions, stillbirths and newborns. Clin Genet. 1984 Sep;26(3):174–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb04364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Hunt P. A., Mayer M., Bart R. D. Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in a female with an X/autosome translocation: further evidence that the DMD locus is at Xp21. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Jul;33(4):513–518. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean V. M., Macleod H. L., Thompson M. W., Ray P. N., Verellen-Dumoulin C., Worton R. G. Paternal inheritance of translocation chromosomes in a t(X;21) patient with X linked muscular dystrophy. J Med Genet. 1986 Dec;23(6):491–493. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Hejtmancik J. F., Caskey C. T., Speer A., Monaco A. P., Middlesworth W., Colletti C. A., Bertelson C., Müller U., Bresnan M. Analysis of deletions in DNA from patients with Becker and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):73–77. doi: 10.1038/322073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Middlesworth W., Ochs H. D., Latt S. A. Specific cloning of DNA fragments absent from the DNA of a male patient with an X chromosome deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4778–4782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent C., Biemont M. C., Dutrillaux B. Sur quatre nouveax cas de translocation du chromosome X chez l'homme. Humangenetik. 1975;26(1):35–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00280283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenbaum R. H., Clarke G., Patel C., Moncrieff M., Hughes J. T. Muscular dystrophy in an X; 1 translocation female suggests that Duchenne locus is on X chromosome short arm. J Med Genet. 1979 Oct;16(5):389–392. doi: 10.1136/jmg.16.5.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren V., de Martinville B., Horwich A. L., Rosenberg L. E., Francke U. Human ornithine transcarbamylase locus mapped to band Xp21.1 near the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Science. 1984 Nov 9;226(4675):698–700. doi: 10.1126/science.6494904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madan K. Balanced structural changes involving the human X: effect on sexual phenotype. Hum Genet. 1983;63(3):216–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00284652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Ayme S., Giraud F. X-autosome translocations: cytogenetic characteristics and their consequences. Hum Genet. 1982;61(4):295–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00276593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Vidal I., Giraud F. Structural anomalies of the X chromosome and inactivation center. Hum Genet. 1981;56(3):401–408. doi: 10.1007/BF00274702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Bertelson C. J., Middlesworth W., Colletti C. A., Aldridge J., Fischbeck K. H., Bartlett R., Pericak-Vance M. A., Roses A. D., Kunkel L. M. Detection of deletions spanning the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus using a tightly linked DNA segment. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):842–845. doi: 10.1038/316842a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H., Emery A. E. The manifesting carrier in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Clin Genet. 1974;5(4):271–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1974.tb01694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narazaki O., Hanai T., Ueki Y., Mitsudome A. [Duchenne muscular dystrophy in a female with an X-autosome translocation]. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1985 Apr;25(4):432–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin N. C., Hughes A. E., Calwell M., Lim J. H. Duchenne muscular dystrophy in a female with a translocation involving Xp21. J Med Genet. 1986 Apr;23(2):171–173. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raimondi S. C., Luthardt F. W., Summitt R. L., Martens P. R. High-resolution chromosome analysis of phenotypically abnormal patients with apparently balanced structural rearrangements. Hum Genet. 1983;63(4):310–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00274751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. N., Belfall B., Duff C., Logan C., Kean V., Thompson M. W., Sylvester J. E., Gorski J. L., Schmickel R. D., Worton R. G. Cloning of the breakpoint of an X;21 translocation associated with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):672–675. doi: 10.1038/318672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito F., Tonomura A., Kimura S., Misugi N., Sugita H. High-resolution banding study of an X/4 translocation in a female with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet. 1985;71(4):370–371. doi: 10.1007/BF00388468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spowart G., Buckton K. E., Skinner R., Emery A. E. X chromosome in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Lancet. 1982 May 29;1(8283):1251–1251. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92380-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALTON J. N. The inheritance of muscular dystrophy: further observations. Ann Hum Genet. 1956 Jul;21(1):40–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1971.tb00264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worton R. G., Duff C., Sylvester J. E., Schmickel R. D., Willard H. F. Duchenne muscular dystrophy involving translocation of the dmd gene next to ribosomal RNA genes. Science. 1984 Jun 29;224(4656):1447–1449. doi: 10.1126/science.6729462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J., Soreng A. L. Constitutive fragile sites and cancer. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1199–1204. doi: 10.1126/science.6239375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel B. U., Naylor S. L., Sakaguchi A. Y., Bell G. I., Shows T. B. High-resolution chromosomal localization of human genes for amylase, proopiomelanocortin, somatostatin, and a DNA fragment (D3S1) by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6932–6936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz M., Vianna-Morgante A. M., Campos P., Diament A. J. Translocation (X;6) in a female with Duchenne muscular dystrophy: implications for the localisation of the DMD locus. J Med Genet. 1981 Dec;18(6):442–447. doi: 10.1136/jmg.18.6.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]