Abstract
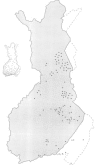
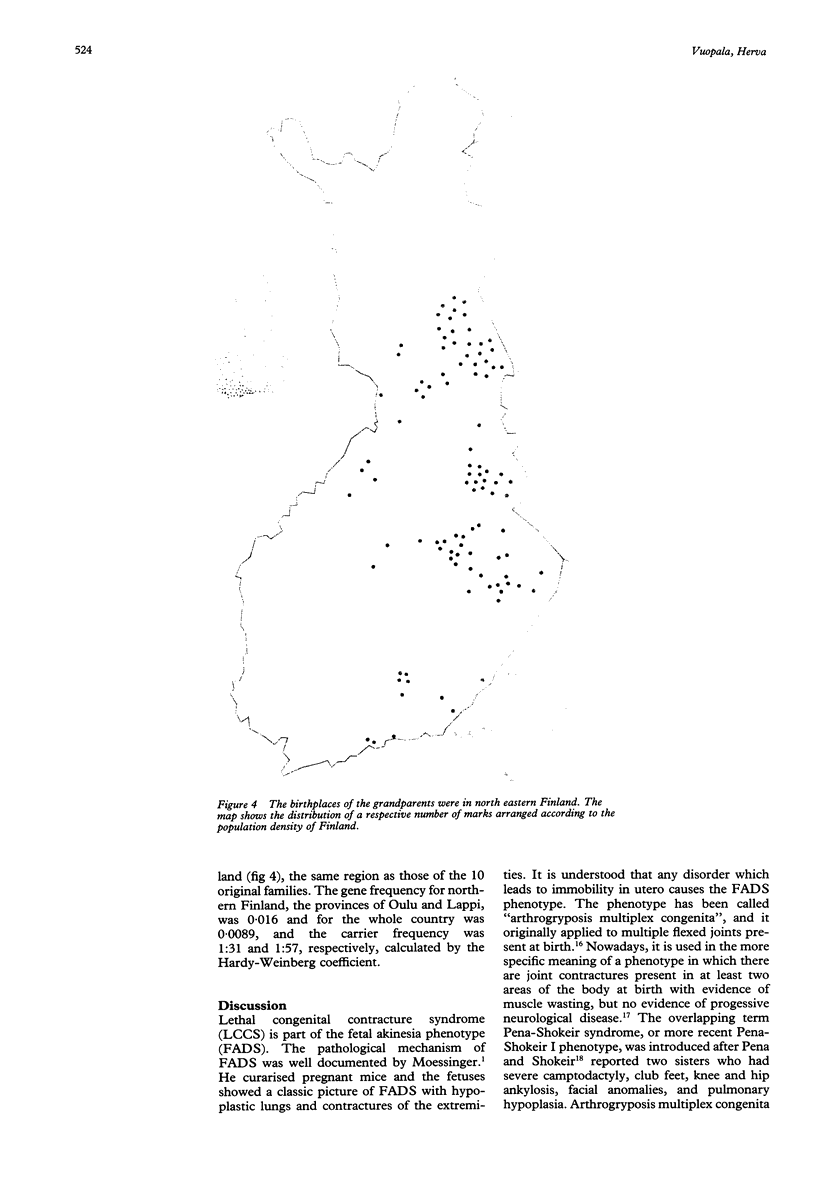
In a national morphology based study of lethal arthrogryposis between 1979 and 1992, 40 fetuses and infants with lethal congenital contracture syndrome (LCCS, McKusick 253310) were found in Finland. The incidence of LCCS in Finland was 1:19,000 births. There were 20 affected males and 20 affected females in 26 families. In 16 cases the pregnancy was terminated after the prenatal diagnosis of total akinesia and fetal hydrops on ultrasound. There were 19 stillborn infants and five were born showing signs of life, but died within one hour. The segregation analyses yielded 0.45 affected by the "singles" method and 0.34 by the "sib" method. The birthplaces of the grandparents were located in the sparsely populated north east of Finland. This finding supports the existence of an autosomal recessive LCCS gene in Finland, particularly in the north eastern part.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Askenazi S. S., Perlman M. Pulmonary hypoplasia: lung weight and radial alveolar count as criteria of diagnosis. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Aug;54(8):614–618. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.8.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri F., Santoro L., Crisci C., Massini R., Russo E., Campanella G. Is the sensory neuropathy in ataxia-telangiectasia distinguishable from that in Friedreich's ataxia? Morphometric and ultrastructural study of the sural nerve in a case of Louis Bar syndrome. Acta Neuropathol. 1986;69(3-4):213–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00688296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkemeier L. R., Ozçelik T., Francke U., Rosenthal A. Human chromosome 19 contains the neurotrophin-5 gene locus and three related genes that may encode novel acidic neurotrophins. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1992 May;18(3):233–245. doi: 10.1007/BF01233860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisceglia M., Zelante L., Bosman C., Cera R., Dallapiccola B. Pathologic features in two siblings with the Pena-Shokeir I syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 1987 May;146(3):283–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00716474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. H., Kaiser K. K. Three "myosin adenosine triphosphatase" systems: the nature of their pH lability and sulfhydryl dependence. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 Sep;18(9):670–672. doi: 10.1177/18.9.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzustowicz L. M., Lehner T., Castilla L. H., Penchaszadeh G. K., Wilhelmsen K. C., Daniels R., Davies K. E., Leppert M., Ziter F., Wood D. Genetic mapping of chronic childhood-onset spinal muscular atrophy to chromosome 5q11.2-13.3. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):540–541. doi: 10.1038/344540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H., Blumberg B., Immken L., Lachman R., Rightmire D., Fowler M., Bachman R., Beemer F. A. The Pena-Shokeir syndrome: report of five cases and further delineation of the syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Oct;16(2):213–224. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmick J. E., Berry K., MacLeod P. M., Hardwick D. F. Syndrome of ankylosis, facial anomalies, and pulmonary hypoplasia: a pathologic analysis of one infant. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1977;13(3D):133–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dracopoli N. C., Rose E., Whitfield G. K., Guidon P. T., Jr, Bale S. J., Chance P. A., Kourides I. A., Housman D. E. Two thyroid hormone regulated genes, the beta-subunits of nerve growth factor (NGFB) and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSHB), are located less than 310 kb apart in both human and mouse genomes. Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eubanks J. H., Puranam R. S., Kleckner N. W., Bettler B., Heinemann S. F., McNamara J. O. The gene encoding the glutamate receptor subunit GluR5 is located on human chromosome 21q21.1-22.1 in the vicinity of the gene for familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):178–182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. L., Johnstone W. T., Fisher W. H., Jr, Goldkamp O. G. Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita: a clinical investigation. J Pediatr. 1970 Feb;76(2):255–261. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80171-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forger N. G., Breedlove S. M. Motoneuronal death during human fetal development. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Oct 1;264(1):118–122. doi: 10.1002/cne.902640109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garson J. A., van den Berghe J. A., Kemshead J. T. Novel non-isotopic in situ hybridization technique detects small (1 Kb) unique sequences in routinely G-banded human chromosomes: fine mapping of N-myc and beta-NGF genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4761–4770. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannini M., Romo A. J., Evans G. A. Chromosomal localization of the human ciliary neurotrophic factor gene (CNTF) to 11q12 by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1993;63(1):62–63. doi: 10.1159/000133504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyr T., Katz M., Altermatt H. J., Braga S., Duerig P., Koenig C., Schneider H. Lethal Pena-Shokeir 1 syndrome in three male siblings. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 1992;251(3):149–154. doi: 10.1007/BF02718378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman G., Willemse J., van Ketel B. A., Verdonck A. F. The pathogenesis of fetal hypokinesia. A neurological study of 75 cases of congenital contractures with emphasis on cerebral lesions. Neuropediatrics. 1987 Feb;18(1):22–33. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1052430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G. Genetic aspects of arthrogryposis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985 Apr;(194):44–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson I. M., Seawright A., van Heyningen V. The human BDNF gene maps between FSHB and HVBS1 at the boundary of 11p13-p14. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1331–1333. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I., Fidziańska A., Niebrój-Dobosz I., Strugalska M. H. Is Kugelberg-Welander spinal muscular atrophy a fetal defect? Muscle Nerve. 1980 Sep-Oct;3(5):389–402. doi: 10.1002/mus.880030503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemminki K., Mutanen P., Saloniemi I., Niemi M. L., Vainio H. Spontaneous abortions in hospital staff engaged in sterilising instruments with chemical agents. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Nov 20;285(6353):1461–1463. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6353.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herva R., Conradi N. G., Kalimo H., Leisti J., Sourander P. A syndrome of multiple congenital contractures: neuropathological analysis on five fetal cases. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Jan;29(1):67–76. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320290109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herva R., Leisti J., Kirkinen P., Seppänen U. A lethal autosomal recessive syndrome of multiple congenital contractures. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Mar;20(3):431–439. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320200303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huebner K., Isobe M., Chao M., Bothwell M., Ross A. H., Finan J., Hoxie J. A., Sehgal A., Buck C. R., Lanahan A. The nerve growth factor receptor gene is at human chromosome region 17q12-17q22, distal to the chromosome 17 breakpoint in acute leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1403–1407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura M., Yamanaka N., Nakamura F., Oyanagi K. Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita: an autopsy case of a fatal form. Hum Pathol. 1981 Aug;12(8):699–704. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(81)80171-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Ibáez C. F., Nye S. H., McClain J., Jones P. F., Gies D. R., Belluscio L., Le Beau M. M., Espinosa R., 3rd, Squinto S. P. Mammalian neurotrophin-4: structure, chromosomal localization, tissue distribution, and receptor specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3060–3064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh K., Yokoyama N., Ishihara A., Kawai S., Takada S., Nishino M., Lee Y., Negishi H., Itoh H. Two cases of fetal akinesia/hypokinesia sequence. Pediatr Pathol. 1991 May-Jun;11(3):467–477. doi: 10.3109/15513819109064782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkinen P., Herva R., Leisti J. Early prenatal diagnosis of a lethal syndrome of multiple congenital contractures. Prenat Diagn. 1987 Mar;7(3):189–196. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970070306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkinen P., Herva R., Leisti J. Early prenatal diagnosis of a lethal syndrome of multiple congenital contractures. Prenat Diagn. 1987 Mar;7(3):189–196. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970070306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen O., Hirvensalo M. Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita. Ann Paediatr Fenn. 1966;12(2):133–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi E., Montone K. T., Rorke L. B., Kliman H. J. Fetal akinesia deformation sequence (Pena-Shokeir phenotype) associated with acquired intrauterine brain damage. Neurology. 1991 Sep;41(9):1467–1468. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.9.1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. C., Mantel N. A simple method of estimating the segregation ratio under complete ascertainment. Am J Hum Genet. 1968 Jan;20(1):61–81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mailhes J. B., Lancaster K., Bourgeois M. J., Sanusi I. D. 'Pena-Shokeir syndrome' in a newborn male infant. Am J Dis Child. 1977 Dec;131(12):1419–1420. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1977.02120250101035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisonpierre P. C., Le Beau M. M., Espinosa R., 3rd, Ip N. Y., Belluscio L., de la Monte S. M., Squinto S., Furth M. E., Yancopoulos G. D. Human and rat brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3: gene structures, distributions, and chromosomal localizations. Genomics. 1991 Jul;10(3):558–568. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90436-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mease A. D., Yeatman G. W., Pettett G., Merenstein G. B. A syndrome of ankylosis, facial anomalies and pulmonary hypoplasia secondary to fetal neuromuscular dysfunction. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1976;12(5):193–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melki J., Abdelhak S., Sheth P., Bachelot M. F., Burlet P., Marcadet A., Aicardi J., Barois A., Carriere J. P., Fardeau M. Gene for chronic proximal spinal muscular atrophies maps to chromosome 5q. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):767–768. doi: 10.1038/344767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moerman P., Fryns J. P., Goddeeris P., Lauweryns J. M. Multiple ankyloses, facial anomalies, and pulmonary hypoplasia associated with severe antenatal spinal muscular atrophy. J Pediatr. 1983 Aug;103(2):238–241. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80352-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moessinger A. C. Fetal akinesia deformation sequence: an animal model. Pediatrics. 1983 Dec;72(6):857–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabavi N., Freeman G. J., Gault A., Godfrey D., Nadler L. M., Glimcher L. H. Signalling through the MHC class II cytoplasmic domain is required for antigen presentation and induces B7 expression. Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):266–268. doi: 10.1038/360266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim R. W., Yin Q. W., Prevette D., Yan Q. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor rescues developing avian motoneurons from cell death. Nature. 1992 Dec 24;360(6406):755–757. doi: 10.1038/360755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozçelik T., Rosenthal A., Francke U. Chromosomal mapping of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 genes in man and mouse. Genomics. 1991 Jul;10(3):569–575. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90437-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pena S. D., Shokeir M. H. Syndrome of camptodactyly, multiple ankyloses, facial anomalies, and pulmonary hypoplasia: a lethal condition. J Pediatr. 1974 Sep;85(3):373–375. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pihkala J., Hakala T., Voutilainen P., Raivio K. Uudet suomalaiset sikiön kasvukäyrät. Duodecim. 1989;105(18):1540–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punnett H. H., Kistenmacher M. L., Valdes-Dapena M., Ellison R. T., Jr Syndrome of ankylosis, facial anomalies, and pulmonary hypoplasia. J Pediatr. 1974 Sep;85(3):375–377. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80120-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettig W. J., Thomson T. M., Spengler B. A., Biedler J. L., Old L. J. Assignment of human nerve growth factor receptor gene to chromosome 17 and regulation of receptor expression in somatic cell hybrids. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Sep;12(5):441–447. doi: 10.1007/BF01539915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sendtner M., Kreutzberg G. W., Thoenen H. Ciliary neurotrophic factor prevents the degeneration of motor neurons after axotomy. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):440–441. doi: 10.1038/345440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenker L., Reed K., Anderson C., Hauck L., Spark R. Syndrome of camptodactyly, ankyloses, facial anomalies, and pulmonary hypoplasia (Pena-Shokeir syndrome): obstetric and ultrasound aspects. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Jun 1;152(3):303–307. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(85)80216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares V. M., Brzustowicz L. M., Kleyn P. W., Knowles J. A., Palmer D. A., Asokan S., Penchaszadeh G. K., Munsat T. L., Gilliam T. C. Refinement of the spinal muscular atrophy locus to the interval between D5S435 and MAP1B. Genomics. 1993 Feb;15(2):365–371. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verloes A., Dodinval P., Retz M. C., Schaaps J. P., Koulischer L. A hydropic fetus with translucent ribs, arthrogryposis multiplex congenita and congenital myopathy: etiological heterogeneity of A.M.C., Toriello-Bauserman type? Genet Couns. 1991;2(1):63–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. S., Holmes L. B. The syndrome of multiple ankyloses and facial anomalies. A neuropathologic analysis. Acta Neuropathol. 1980;50(3):175–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00688750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth B., Voosen B., Röhrig D., Knapp M., Piechaczek B., Rudnik-Schöneborn S., Zerres K. Fine mapping and narrowing of the genetic interval of the spinal muscular atrophy region by linkage studies. Genomics. 1993 Jan;15(1):113–118. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. C., Fain P. R., Barker D. F., Chao M. V. A moderately frequent HindIII polymorphism at the human NGFR locus (17q12----17q22). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):825–825. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan Q., Elliott J., Snider W. D. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor rescues spinal motor neurons from axotomy-induced cell death. Nature. 1992 Dec 24;360(6406):753–755. doi: 10.1038/360753a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]