Abstract
Techniques have been reported in which fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) and cosmid probes are used to detect trisomy 21 (and other abnormalities involving chromosomes X, Y, 13, and 18) on uncultured amniocytes. However the detection rate of trisomy 21 is lower than for the other anomalies owing to a larger number of uninformative results and false negatives. We report the simultaneous use of two differentially labelled cosmid contigs to improve the detection rate of trisomy 21 on uncultured amniocyte samples thus allowing the prenatal diagnosis of Down's syndrome even if only few labelled nuclei are available.
Full text
PDF




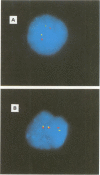
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adinolfi M., Davies A., Sharif S., Soothill P., Rodeck C. Detection of trisomy 18 and Y-derived sequences in fetal nucleated cells obtained by transcervical flushing. Lancet. 1993 Aug 14;342(8868):403–404. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92816-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adinolfi M. On a non-invasive approach to prenatal diagnosis based on the detection of fetal nucleated cells in maternal blood samples. Prenat Diagn. 1991 Oct;11(10):799–804. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970111008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anand R., Villasante A., Tyler-Smith C. Construction of yeast artificial chromosome libraries with large inserts using fractionation by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3425–3433. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch O., Schwinger E. A simplified protocol for fluorescence in situ hybridization with repetitive DNA probes and its use in clinical cytogenetics. Clin Genet. 1991 Jul;40(1):47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1991.tb03067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J., Chan V. T., Jonasson J. A., Fleming K. A., Taylor S., McGee J. O. Sensitive system for visualising biotinylated DNA probes hybridised in situ: rapid sex determination of intact cells. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Oct;38(10):1085–1092. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.10.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devilee P., Cremer T., Slagboom P., Bakker E., Scholl H. P., Hager H. D., Stevenson A. F., Cornelisse C. J., Pearson P. L. Two subsets of human alphoid repetitive DNA show distinct preferential localization in the pericentric regions of chromosomes 13, 18, and 21. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;41(4):193–201. doi: 10.1159/000132229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnirke A., Barnes T. S., Patterson D., Schild D., Featherstone T., Olson M. V. Cloning and in vivo expression of the human GART gene using yeast artificial chromosomes. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1629–1634. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07685.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. Glycoproteins that distinguish different cell types found in amniotic fluid. Hum Genet. 1982;62(3):188–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00333516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J., Coffey A. J., Giannelli F., Bentley D. R. Vertical integration of cosmid and YAC resources for interval mapping on the X-chromosome. Genomics. 1993 Feb;15(2):297–304. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien C., Bazin A., Guyot B., Forestier F., Daffos F. Rapid prenatal diagnosis of Down's syndrome with in-situ hybridisation of fluorescent DNA probes. Lancet. 1986 Oct 11;2(8511):863–864. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92900-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinger K., Landes G., Shook D., Harvey R., Lopez L., Locke P., Lerner T., Osathanondh R., Leverone B., Houseal T. Rapid detection of chromosome aneuploidies in uncultured amniocytes by using fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jul;51(1):55–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott V., Rees D. J., Cheng Z., Brownlee G. G. Randomly picked cosmid clones overlap the pyrB and oriC gap in the physical map of the E. coli chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2601–2612. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo W. L., Tenjin H., Segraves R., Pinkel D., Golbus M. S., Gray J. Detection of aneuploidy involving chromosomes 13, 18, or 21, by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to interphase and metaphase amniocytes. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jul;49(1):112–119. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Cremer T., Tang C. J., Watkins P. C., Manuelidis L., Ward D. C. Rapid detection of human chromosome 21 aberrations by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9664–9668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A. O. Characteristics of amniotic fluid cells in vitro and attempts to improve culture techniques. Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 1980 Apr;7(1):143–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Landegent J., Collins C., Fuscoe J., Segraves R., Lucas J., Gray J. Fluorescence in situ hybridization with human chromosome-specific libraries: detection of trisomy 21 and translocations of chromosome 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9138–9142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhine S. A., Palmer C. G., Thompson J. F. A simple alternative to amniocentesis for first trimester prenatal diagnosis. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1977;13(3D):231–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ried T., Landes G., Dackowski W., Klinger K., Ward D. C. Multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization for the simultaneous detection of probe sets for chromosomes 13, 18, 21, X and Y in uncultured amniotic fluid cells. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Aug;1(5):307–313. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.5.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. Transplacental passage of blood cells. J Med Genet. 1975 Sep;12(3):230–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M., Anand R., Brown W. R., Fletcher D. S. A model for the separation of large DNA molecules by crossed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):5925–5943. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.5925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward B. E., Gersen S. L., Carelli M. P., McGuire N. M., Dackowski W. R., Weinstein M., Sandlin C., Warren R., Klinger K. W. Rapid prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal aneuploidies by fluorescence in situ hybridization: clinical experience with 4,500 specimens. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 May;52(5):854–865. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Y. L., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Warner J. P., Ferguson-Smith M. E., Sargent C. A., Carter N. P. Analysis of chromosome 21 copy number in uncultured amniocytes by fluorescence in situ hybridization using a cosmid contig. Prenat Diagn. 1992 Nov;12(11):931–943. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970121113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]