Abstract
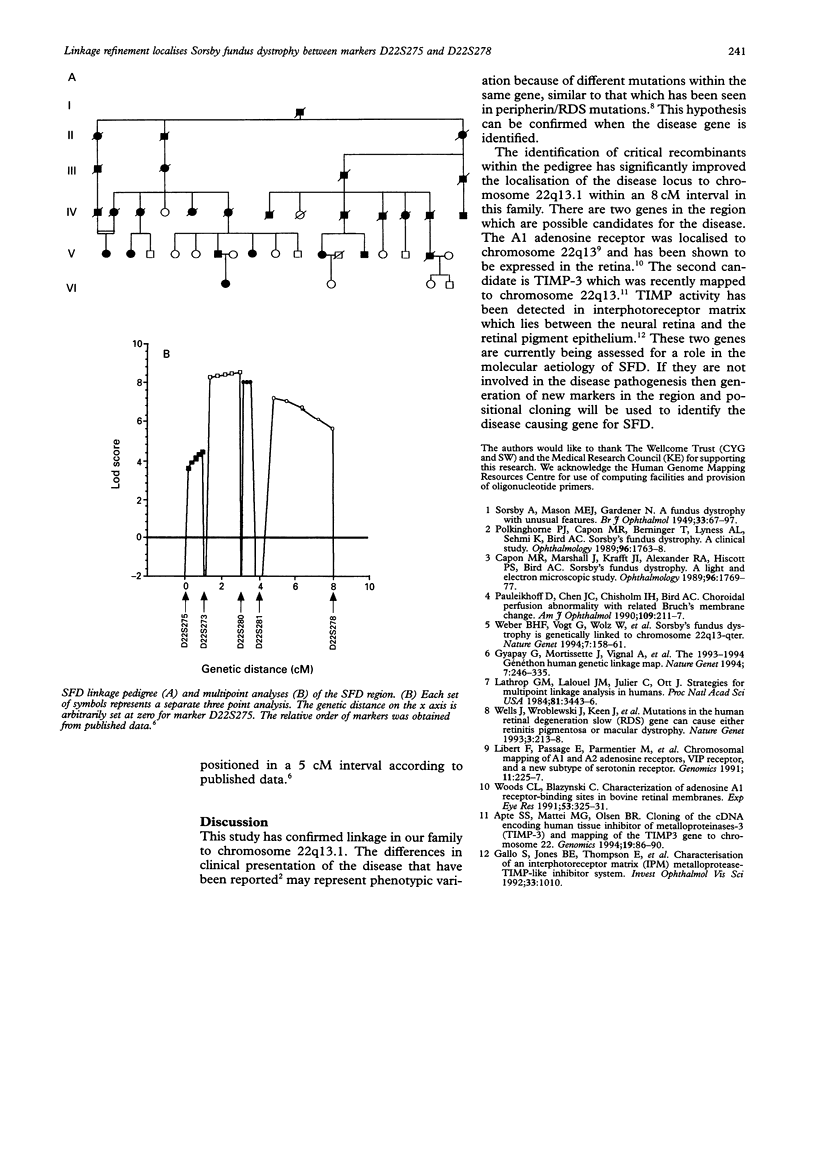
Sorsby fundus dystrophy is an autosomal dominant disorder which both clinically and histopathologically bears striking similarities to age related macular degeneration, one of the leading causes of blindness in the developed world. Recent studies have suggested a genetic localisation of the disease to chromosome 22q in a large genetic interval of approximately 25 cM. Independent genetic linkage analysis in a six generation British pedigree confirms linkage to the chromosome 22q region. A maximum two point lod score of 7.09 with no recombination was obtained with marker D22S280. Haplotype data positioned the disease between loci D22S275 and D22S278, thus significantly reducing the region on chromosome 22q where the gene is located.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apte S. S., Mattei M. G., Olsen B. R. Cloning of the cDNA encoding human tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 (TIMP-3) and mapping of the TIMP3 gene to chromosome 22. Genomics. 1994 Jan 1;19(1):86–90. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capon M. R., Marshall J., Krafft J. I., Alexander R. A., Hiscott P. S., Bird A. C. Sorsby's fundus dystrophy. A light and electron microscopic study. Ophthalmology. 1989 Dec;96(12):1769–1777. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(89)32664-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libert F., Passage E., Parmentier M., Simons M. J., Vassart G., Mattei M. G. Chromosomal mapping of A1 and A2 adenosine receptors, VIP receptor, and a new subtype of serotonin receptor. Genomics. 1991 Sep;11(1):225–227. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauleikhoff D., Chen J. C., Chisholm I. H., Bird A. C. Choroidal perfusion abnormality with age-related Bruch's membrane change. Am J Ophthalmol. 1990 Feb 15;109(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)75989-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polkinghorne P. J., Capon M. R., Berninger T., Lyness A. L., Sehmi K., Bird A. C. Sorsby's fundus dystrophy. A clinical study. Ophthalmology. 1989 Dec;96(12):1763–1768. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(89)32654-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SORSBY A., MASON M. E. J. A fundus dystrophy with unusual features. Br J Ophthalmol. 1949 Feb;33(2):67–97. doi: 10.1136/bjo.33.2.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber B. H., Vogt G., Wolz W., Ives E. J., Ewing C. C. Sorsby's fundus dystrophy is genetically linked to chromosome 22q13-qter. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2):158–161. doi: 10.1038/ng0694-158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J., Wroblewski J., Keen J., Inglehearn C., Jubb C., Eckstein A., Jay M., Arden G., Bhattacharya S., Fitzke F. Mutations in the human retinal degeneration slow (RDS) gene can cause either retinitis pigmentosa or macular dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1993 Mar;3(3):213–218. doi: 10.1038/ng0393-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods C. L., Blazynski C. Characterization of adenosine A1-receptor binding sites in bovine retinal membranes. Exp Eye Res. 1991 Sep;53(3):325–331. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(91)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


