Abstract
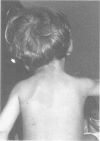
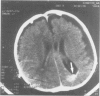
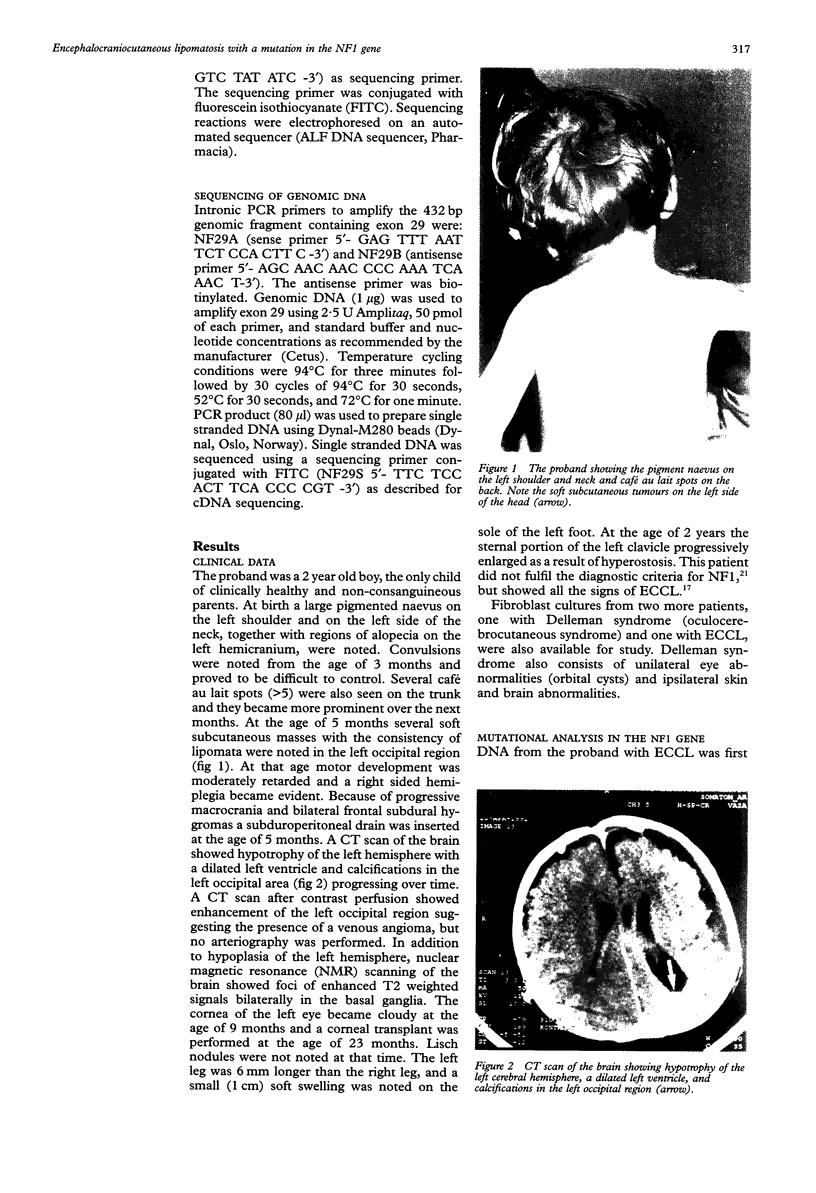
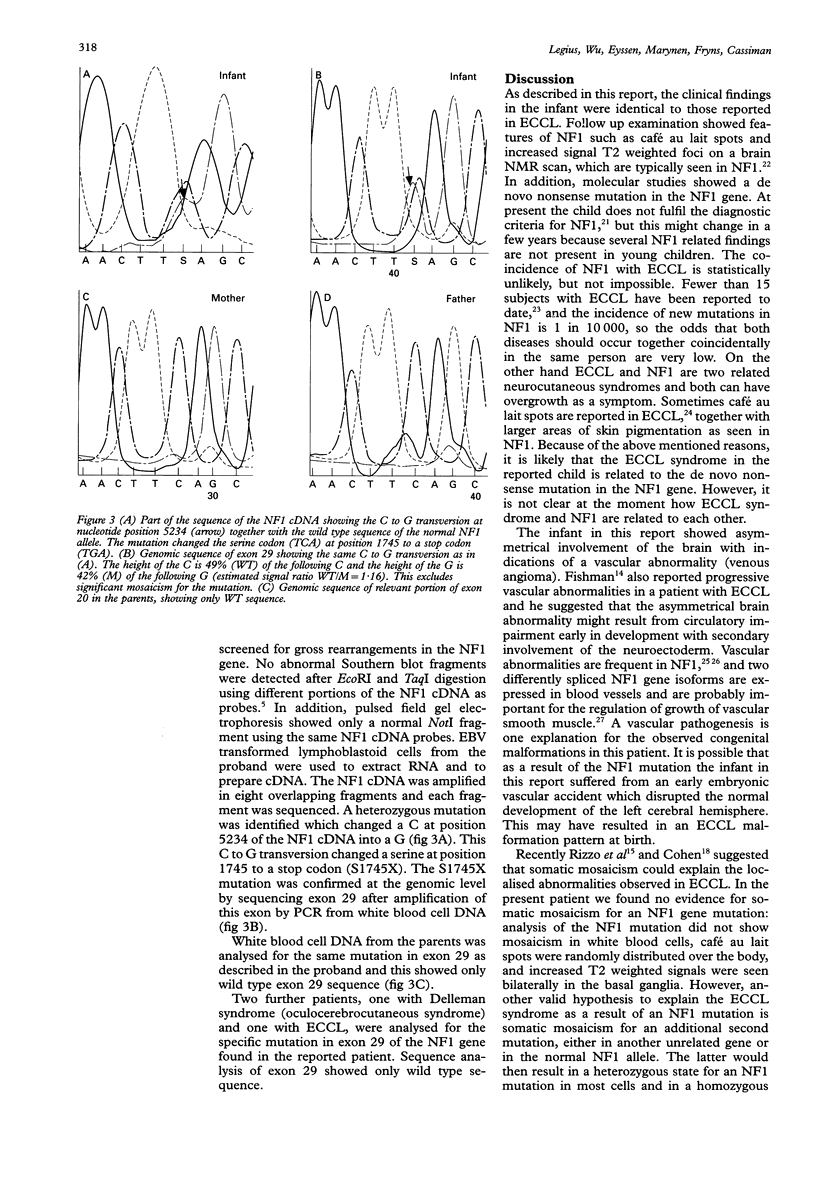
Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis (ECCL) is a congenital hamartomatous disorder characterised by unilateral skin lesions, lipomas, and ipsilateral ophthamological and cerebral malformations. The disorder is thought to represent a localised form of Proteus syndrome. In this report, a child is described with ECCL and a de novo nonsense mutation in exon 29 (S1745X) of the neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) gene. Although it is possible that both ECCL and NF1 occur coincidentally in this patient, we favour the hypothesis that in exceptional cases a mutation in the NF1 gene might give rise to severe congenital malformations such as ECCL. Possible pathogenetic mechanisms for these malformations are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlgren-Beckendorf J. A., Maggio W. W., Chen F., Kent T. A. Neurofibromatosis 1 mRNA expression in blood vessels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Dec 15;197(2):1019–1024. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mefty O., Fox J. L., Sakati N., Bashir R., Probst F. The multiple manifestations of the encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis syndrome. Childs Nerv Syst. 1987;3(2):132–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00271143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballester R., Marchuk D., Boguski M., Saulino A., Letcher R., Wigler M., Collins F. The NF1 locus encodes a protein functionally related to mammalian GAP and yeast IRA proteins. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):851–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawthon R. M., Weiss R., Xu G. F., Viskochil D., Culver M., Stevens J., Robertson M., Dunn D., Gesteland R., O'Connell P. A major segment of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene: cDNA sequence, genomic structure, and point mutations. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90253-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. M., Jr Proteus syndrome: clinical evidence for somatic mosaicism and selective review. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Oct 1;47(5):645–652. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320470514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. M., Jr Understanding Proteus syndrome, unmasking the elephant man, and stemming elephant fever. Neurofibromatosis. 1988;1(5-6):260–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMario F. J., Jr, Ramsby G., Greenstein R., Langshur S., Dunham B. Neurofibromatosis type 1: magnetic resonance imaging findings. J Child Neurol. 1993 Jan;8(1):32–39. doi: 10.1177/088307389300800105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman M. A. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis. J Child Neurol. 1987 Jul;2(3):186–193. doi: 10.1177/088307388700200303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene J. F., Jr, Fitzwater J. E., Burgess J. Arterial lesions associated with neurofibromatosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Oct;62(4):481–487. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/62.4.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimalt R., Ermacora E., Mistura L., Russo G., Tadini G. L., Triulzi F., Cavicchini S., Rondanini G. F., Caputo R. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis: case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 1993 Jun;10(2):164–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.1993.tb00047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberland C., Perou M. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis. A new example of ectomesodermal dysgenesis. Arch Neurol. 1970 Feb;22(2):144–155. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480200050005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotamisligil G. S. Proteus syndrome and neurofibromatosis. Neurofibromatosis. 1989;2(5-6):339–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson A. G., Jr Genetics of human cancer. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:231–251. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legius E., Marchuk D. A., Collins F. S., Glover T. W. Somatic deletion of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene in a neurofibrosarcoma supports a tumour suppressor gene hypothesis. Nat Genet. 1993 Feb;3(2):122–126. doi: 10.1038/ng0293-122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D. A., Saulino A. M., Tavakkol R., Swaroop M., Wallace M. R., Andersen L. B., Mitchell A. L., Gutmann D. H., Boguski M., Collins F. S. cDNA cloning of the type 1 neurofibromatosis gene: complete sequence of the NF1 gene product. Genomics. 1991 Dec;11(4):931–940. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. A., Viskochil D., Bollag G., McCabe P. C., Crosier W. J., Haubruck H., Conroy L., Clark R., O'Connell P., Cawthon R. M. The GAP-related domain of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene product interacts with ras p21. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):843–849. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90150-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall S., Ramzy M. I., Curé J. K., Pai G. S. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis and the Proteus syndrome: distinct entities with overlapping manifestations. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Jul 1;43(4):662–668. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccardi V. M. Genotype, malleotype, phenotype, and randomness: lessons from neurofibromatosis-1 (NF-1) Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Aug;53(2):301–304. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccardi V. M. Type 1 neurofibromatosis and the pediatric patient. Curr Probl Pediatr. 1992 Feb;22(2):66–107. doi: 10.1016/0045-9380(92)90053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo R., Pavone L., Micali G., Nigro F., Cohen M. M., Jr Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis, Proteus syndrome, and somatic mosaicism. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Oct 1;47(5):653–655. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320470515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassabehji M., Strachan T., Sharland M., Colley A., Donnai D., Harris R., Thakker N. Tandem duplication within a neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) gene exon in a family with features of Watson syndrome and Noonan syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):90–95. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassabehji M., Strachan T., Sharland M., Colley A., Donnai D., Harris R., Thakker N. Tandem duplication within a neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) gene exon in a family with features of Watson syndrome and Noonan syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):90–95. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya M., Shen M., Cherryson A., Farnham J., Maynard J., Huson S. M., Harper P. S. Analysis of mutations at the neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) locus. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Dec;1(9):735–740. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.9.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya M., Shen M., Cherryson A., Farnham J., Maynard J., Huson S. M., Harper P. S. Analysis of mutations at the neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) locus. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Dec;1(9):735–740. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.9.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viskochil D., Buchberg A. M., Xu G., Cawthon R. M., Stevens J., Wolff R. K., Culver M., Carey J. C., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Deletions and a translocation interrupt a cloned gene at the neurofibromatosis type 1 locus. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90252-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Marchuk D. A., Andersen L. B., Letcher R., Odeh H. M., Saulino A. M., Fountain J. W., Brereton A., Nicholson J., Mitchell A. L. Type 1 neurofibromatosis gene: identification of a large transcript disrupted in three NF1 patients. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):181–186. doi: 10.1126/science.2134734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann H. R., Burgio G. R. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis and Proteus syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Oct;25(2):403–404. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320250229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G. F., Lin B., Tanaka K., Dunn D., Wood D., Gesteland R., White R., Weiss R., Tamanoi F. The catalytic domain of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene product stimulates ras GTPase and complements ira mutants of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):835–841. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]