Abstract
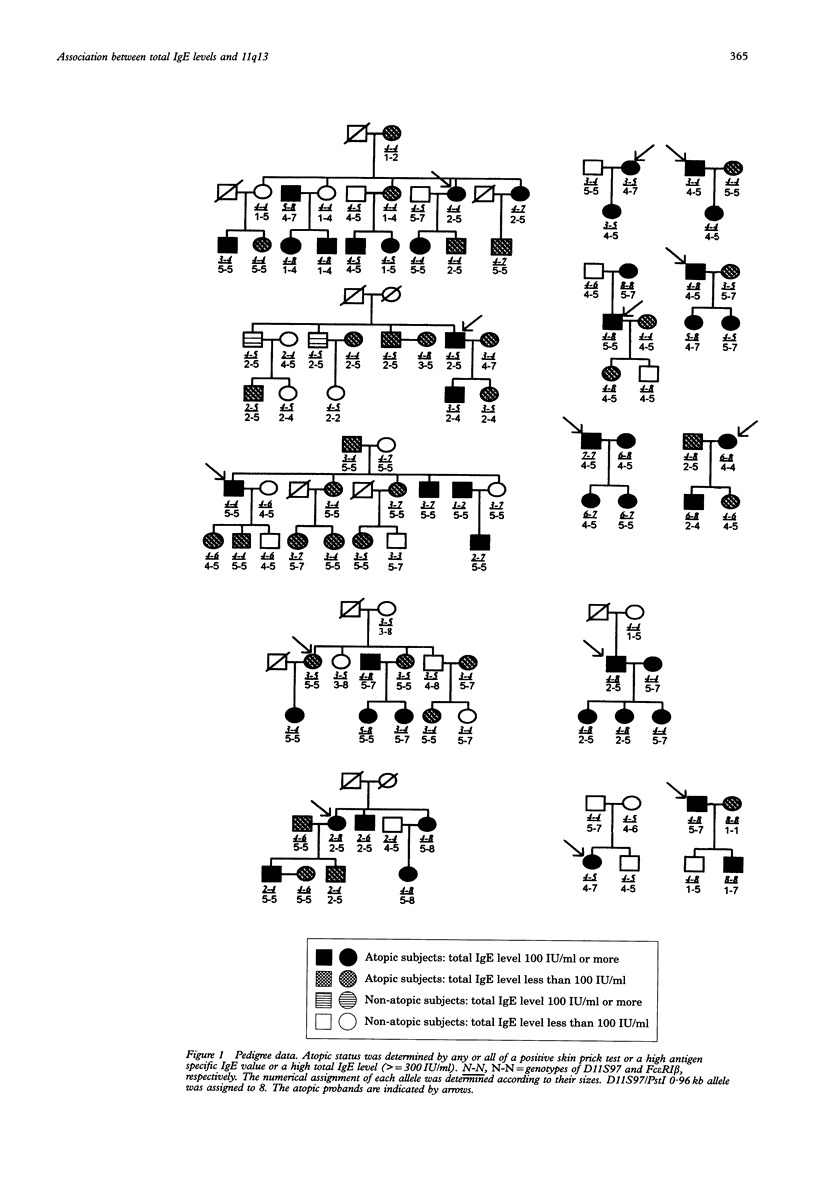
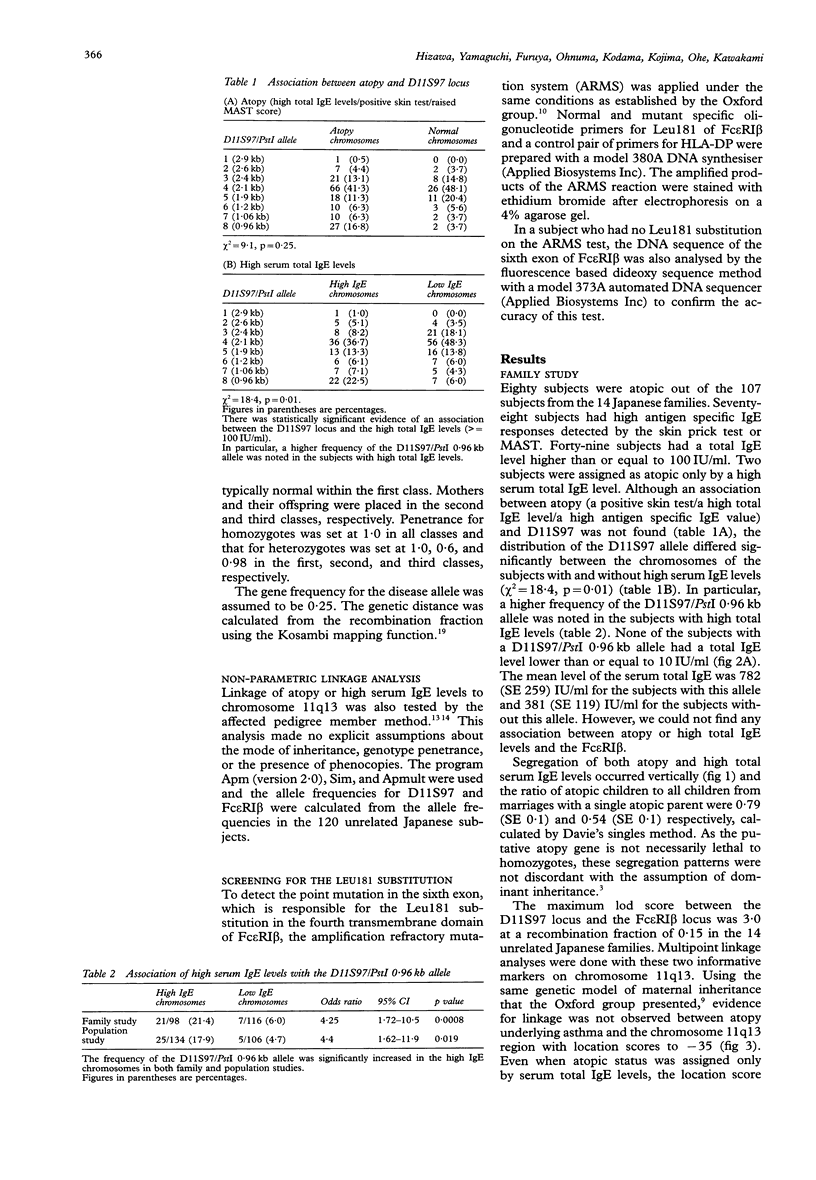
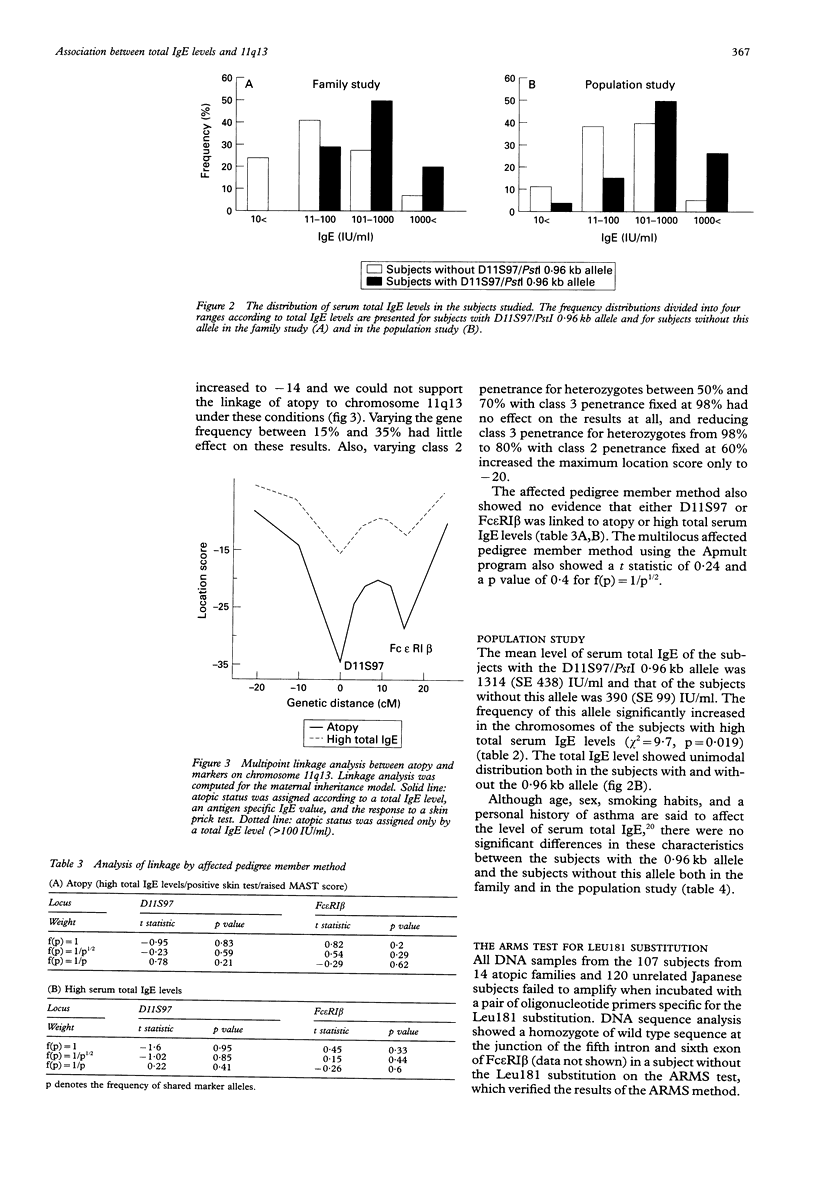
The genetic linkage of atopy to chromosome 11q13 through maternally derived alleles has been previously reported. Linkage analysis in Japanese families did not confirm the existence of a major gene for atopy at this locus under the model of autosomal dominant inheritance. However, we observed a significant association between serum total IgE levels and genetic markers at this locus both in 14 Japanese atopic families and in 120 unrelated Japanese subjects. We detected eight alleles at the D11S97 locus and eight alleles in the CA/GT repeat region in the fifth intron of the Fc epsilon RI beta gene. A significantly increased frequency of the D11S97/PstI 0.96 kb allele was observed in the chromosomes of the subjects with high serum total IgE levels both in the family study (p < 0.001) and in the population study (p < 0.05). However, multipoint linkage analysis again did not show any evidence for the existence of a major gene regulating atopy on chromosome 11q13 with location scores to -35 under the model of maternal inheritance. Evidence against linkage was confirmed by the non-parametric linkage analysis, using the affected pedigree member method. Also, there was no substitution of isoleucine for leucine in the fourth transmembrane domain of Fc epsilon RI beta (Leu181), which was reported to be responsible for a subset of atopy in the British population. Therefore, the association of serum total IgE levels with chromosome 11q13 indicates that a gene or genes at this locus may contribute to the expression of high IgE levels in the Japanese population as well as in the British population, but the heterogeneity of the genetic regulation of serum total IgE levels is evident between the two populations.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amelung P. J., Panhuysen C. I., Postma D. S., Levitt R. C., Koeter G. H., Francomano C. A., Bleecker E. R., Meyers D. A. Atopy and bronchial hyperresponsiveness: exclusion of linkage to markers on chromosomes 11q and 6p. Clin Exp Allergy. 1992 Dec;22(12):1077–1084. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1992.tb00133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal M. N., Amos D. B. Genetic and immunologic basis of atopic responses. Chest. 1987 Jun;91(6 Suppl):176S–184S. doi: 10.1378/chest.91.6_supplement.176s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borecki I. B., Rao D. C., Lalouel J. M., McGue M., Gerrard J. W. Demonstration of a common major gene with pleiotropic effects on immunoglobulin E levels and allergy. Genet Epidemiol. 1985;2(4):327–338. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370020402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. R., Higgins K. W., Frazer K., Schoelz L. K., Dyminski J. W., Marinkovich V. A., Miller S. P., Burd J. F. Simultaneous determination of total IgE and allergen-specific IgE in serum by the MAST chemiluminescent assay system. Clin Chem. 1985 Sep;31(9):1500–1505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman R., Trembath R. C., Harper J. I. Chromosome 11q13 and atopy underlying atopic eczema. Lancet. 1993 May 1;341(8853):1121–1122. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)93130-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collée J. M., ten Kate L. P., de Vries H. G., Kliphuis J. W., Bouman K., Scheffer H., Gerritsen J. Allele sharing on chromosome 11q13 in sibs with asthma and atopy. Lancet. 1993 Oct 9;342(8876):936–936. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91988-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson W. O., Sharp P. A., Faux J. A., Hopkin J. M. Linkage between immunoglobulin E responses underlying asthma and rhinitis and chromosome 11q. Lancet. 1989 Jun 10;1(8650):1292–1295. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92687-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson W. O., Young R. P., Sandford A. J., Moffatt M. F., Shirakawa T., Sharp P. A., Faux J. A., Julier C., Nakumuura Y., Nakumura Y. Maternal inheritance of atopic IgE responsiveness on chromosome 11q. Lancet. 1992 Aug 15;340(8816):381–384. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91468-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criqui M. H., Seibles J. A., Hamburger R. N., Coughlin S. S., Gabriel S. Epidemiology of immunoglobulin E levels in a defined population. Ann Allergy. 1990 Mar;64(3):308–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie A. M. The 'singles' method for segregation analysis under incomplete ascertainment. Ann Hum Genet. 1979 May;42(4):507–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1979.tb00683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A. Linkage analysis of "necessary" disease loci versus "susceptibility" loci. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jan;52(1):135–143. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hizawa N., Yamaguchi E., Ohe M., Itoh A., Furuya K., Ohnuma N., Kawakami Y. Lack of linkage between atopy and locus 11q13. Clin Exp Allergy. 1992 Dec;22(12):1065–1069. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1992.tb00131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lympany P., Welsh K. I., Cochrane G. M., Kemeny D. M., Lee T. H. Genetic analysis of the linkage between chromosome 11q and atopy. Clin Exp Allergy. 1992 Dec;22(12):1085–1092. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1992.tb00134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. G., Meyers D. A. A major gene for allergy--fact or fancy? Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):252–254. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. G., Meyers D. A., Bias W. B. The epidemiology and genetics of atopic allergy. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 24;305(26):1551–1559. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112243052603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. G., Neely J. D., Breazeale D. R., Ghosh B., Freidhoff L. R., Ehrlich-Kautzky E., Schou C., Krishnaswamy G., Beaty T. H. Linkage analysis of IL4 and other chromosome 5q31.1 markers and total serum immunoglobulin E concentrations. Science. 1994 May 20;264(5162):1152–1156. doi: 10.1126/science.8178175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers D. A., Beaty T. H., Freidhoff L. R., Marsh D. G. Inheritance of total serum IgE (basal levels) in man. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Jul;41(1):51–62. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nöthen M. M., Propping P., Fimmers R. Association versus linkage studies in psychosis genetics. J Med Genet. 1993 Aug;30(8):634–637. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.8.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. J., McGuffin P. Association and linkage: complementary strategies for complex disorders. J Med Genet. 1993 Aug;30(8):638–639. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.8.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S. S., Roitman-Johnson B., Greenberg B., Roberts S., Blumenthal M. N. Genetic analysis of atopy in three large kindreds: no evidence of linkage to D11S97. Clin Exp Allergy. 1992 Dec;22(12):1070–1076. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1992.tb00132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risch N. Genetic linkage: interpreting lod scores. Science. 1992 Feb 14;255(5046):803–804. doi: 10.1126/science.1536004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandford A. J., Shirakawa T., Moffatt M. F., Daniels S. E., Ra C., Faux J. A., Young R. P., Nakamura Y., Lathrop G. M., Cookson W. O. Localisation of atopy and beta subunit of high-affinity IgE receptor (Fc epsilon RI) on chromosome 11q. Lancet. 1993 Feb 6;341(8841):332–334. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90136-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa T., Li A., Dubowitz M., Dekker J. W., Shaw A. E., Faux J. A., Ra C., Cookson W. O., Hopkin J. M. Association between atopy and variants of the beta subunit of the high-affinity immunoglobulin E receptor. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2):125–129. doi: 10.1038/ng0694-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. E., Lange K. A multilocus extension of the affected-pedigree-member method of linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Apr;50(4):859–868. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. E., Lange K. The affected-pedigree-member method of linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):315–326. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


