Abstract
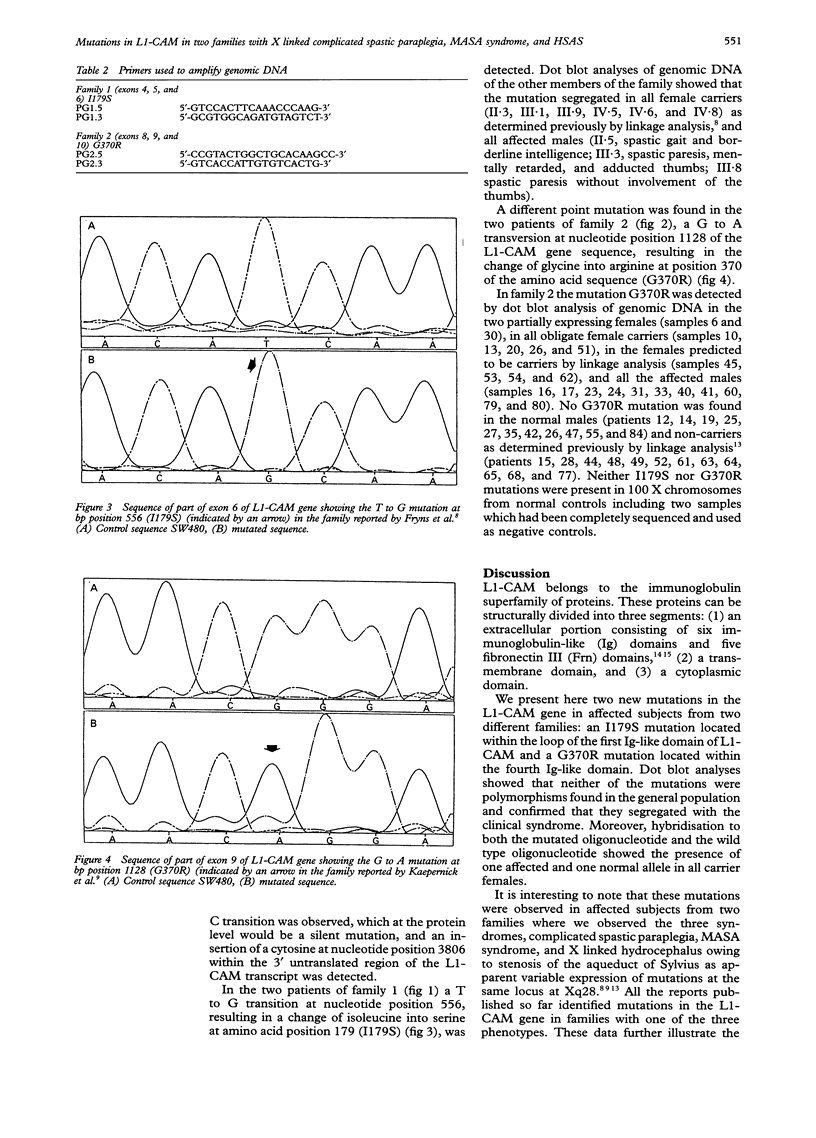
The suggestion that the three X linked syndromes X linked spastic paraplegia (MIM 312900), MASA syndrome (MIM 303350), and X linked hydrocephalus owing to stenosis of the aqueduct of Sylvius (MIM 307000) are variable clinical manifestations of mutations at the same locus at Xq28 was confirmed by the finding of mutations in the L1-CAM gene in the three syndromes. Recently, two families in which different subjects showed a clearly different phenotype within the same family of the three X linked syndromes were described. A reverse transcription PCR assay was developed for the analysis of the L1-CAM cDNA in two of the members of these families. RNA isolated from EBV transformed cell lines and a colon carcinoma derived cell line was used as a starting material. The L1-CAM cDNA of two male patients from each family was sequenced. We report two new mutations in the L1-CAM gene in these two families showing that the three different phenotypes observed in different generations within the same family are variable phenotypic expressions of the same mutation.
Full text
PDF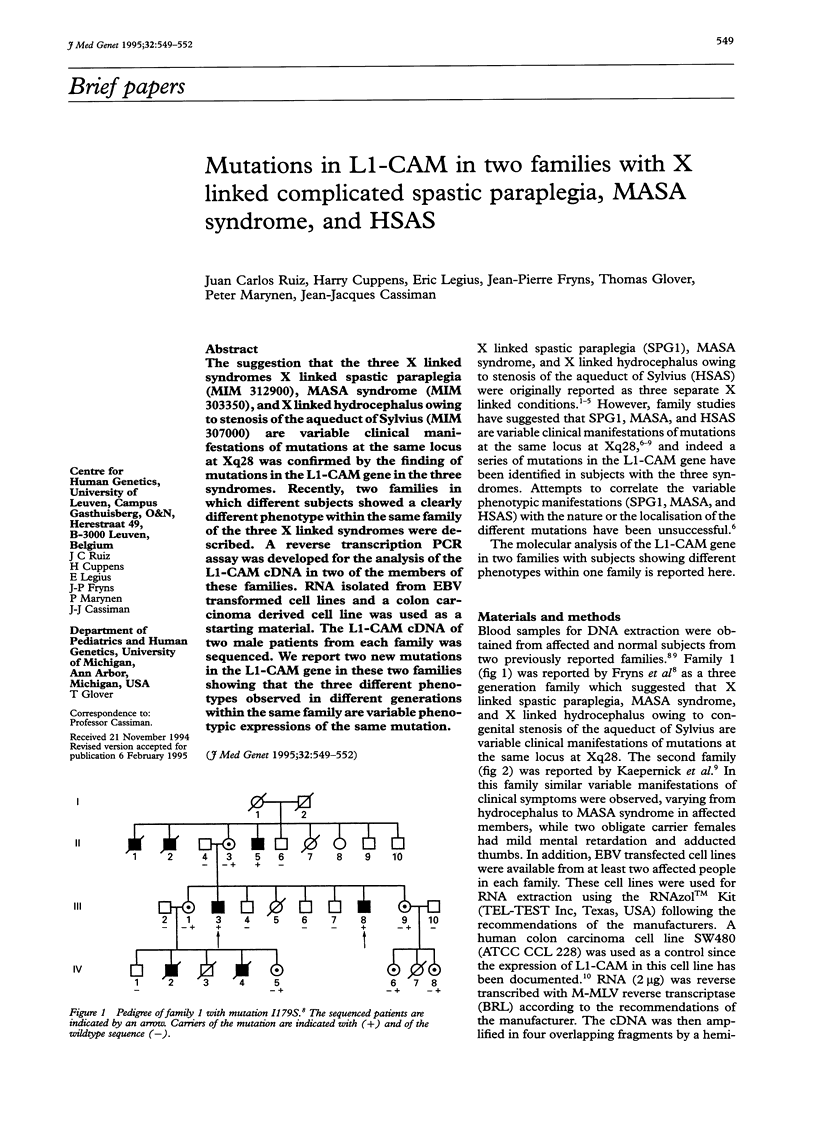

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coucke P., Vits L., Van Camp G., Serville F., Lyonnet S., Kenwrick S., Rosenthal A., Wehnert M., Munnich A., Willems P. J. Identification of a 5' splice site mutation in intron 4 of the L1CAM gene in an X-linked hydrocephalus family. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Apr;3(4):671–673. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.4.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Cho K. R., Nigro J. M., Kern S. E., Simons J. W., Ruppert J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Thomas G., Kinzler K. W. Identification of a chromosome 18q gene that is altered in colorectal cancers. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):49–56. doi: 10.1126/science.2294591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., Spaepen A., Cassiman J. J., van den Berghe H. X linked complicated spastic paraplegia, MASA syndrome, and X linked hydrocephalus owing to congenital stenosis of the aqueduct of Sylvius: variable expression of the same mutation at Xq28. J Med Genet. 1991 Jun;28(6):429–431. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.6.429-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hlavin M. L., Lemmon V. Molecular structure and functional testing of human L1CAM: an interspecies comparison. Genomics. 1991 Oct;11(2):416–423. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90150-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouet M., Rosenthal A., Armstrong G., MacFarlane J., Stevenson R., Paterson J., Metzenberg A., Ionasescu V., Temple K., Kenwrick S. X-linked spastic paraplegia (SPG1), MASA syndrome and X-linked hydrocephalus result from mutations in the L1 gene. Nat Genet. 1994 Jul;7(3):402–407. doi: 10.1038/ng0794-402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouet M., Rosenthal A., MacFarlane J., Kenwrick S., Donnai D. A missense mutation confirms the L1 defect in X-linked hydrocephalus (HSAS) Nat Genet. 1993 Aug;4(4):331–331. doi: 10.1038/ng0893-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
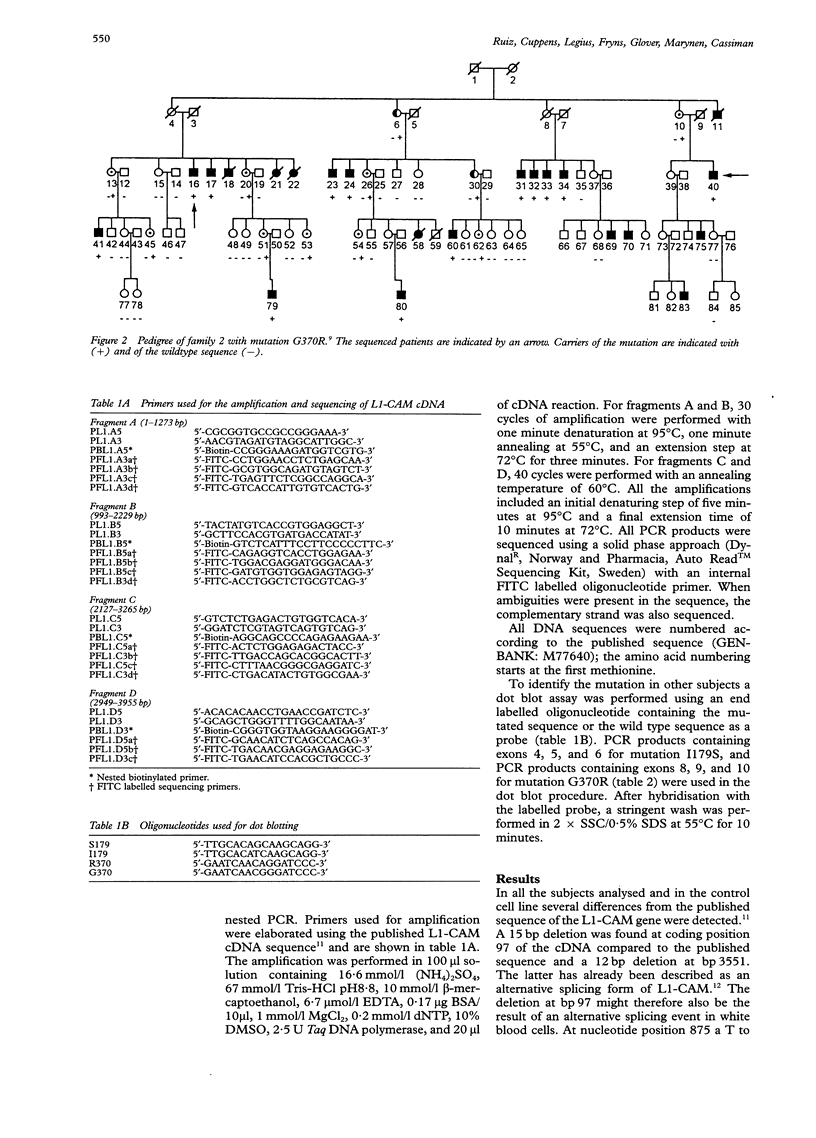
- Kaepernick L., Legius E., Higgins J., Kapur S. Clinical aspects of the MASA syndrome in a large family, including expressing females. Clin Genet. 1994 Apr;45(4):181–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1994.tb04019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krog L., Bock E. Glycosylation of neural cell adhesion molecules of the immunoglobulin superfamily. APMIS Suppl. 1992;27:53–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legius E., Kaepernick L., Higgins J. V., Glover T. W. Fine mapping of X-linked clasped thumb and mental retardation (MASA syndrome) in Xq28. Clin Genet. 1994 Apr;45(4):165–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1994.tb04016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid R. A., Hemperly J. J. Variants of human L1 cell adhesion molecule arise through alternate splicing of RNA. J Mol Neurosci. 1992;3(3):127–135. doi: 10.1007/BF02919404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Jouet M., Kenwrick S. Aberrant splicing of neural cell adhesion molecule L1 mRNA in a family with X-linked hydrocephalus. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):107–112. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrander-Stumpel C., Fryns J., Cassiman J. J., Legius E., Spaepen A., Höweler C. J. MASA syndrome (a form of complicated spastic paraplegia) and X linked hydrocephalus: variable expression of the same mutation at Xq28? Call for families. J Med Genet. 1992 Mar;29(3):215–215. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.3.215-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straussberg R., Blatt I., Brand N., Kessler D., Katznelson M. B., Goodman R. M. X-linked mental retardation with bilateral clasped thumbs: report of another affected family. Clin Genet. 1991 Nov;40(5):337–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1991.tb03105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Camp G., Vits L., Coucke P., Lyonnet S., Schrander-Stumpel C., Darby J., Holden J., Munnich A., Willems P. J. A duplication in the L1CAM gene associated with X-linked hydrocephalus. Nat Genet. 1993 Aug;4(4):421–425. doi: 10.1038/ng0893-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vits L., Van Camp G., Coucke P., Fransen E., De Boulle K., Reyniers E., Korn B., Poustka A., Wilson G., Schrander-Stumpel C. MASA syndrome is due to mutations in the neural cell adhesion gene L1CAM. Nat Genet. 1994 Jul;7(3):408–413. doi: 10.1038/ng0794-408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


