Abstract
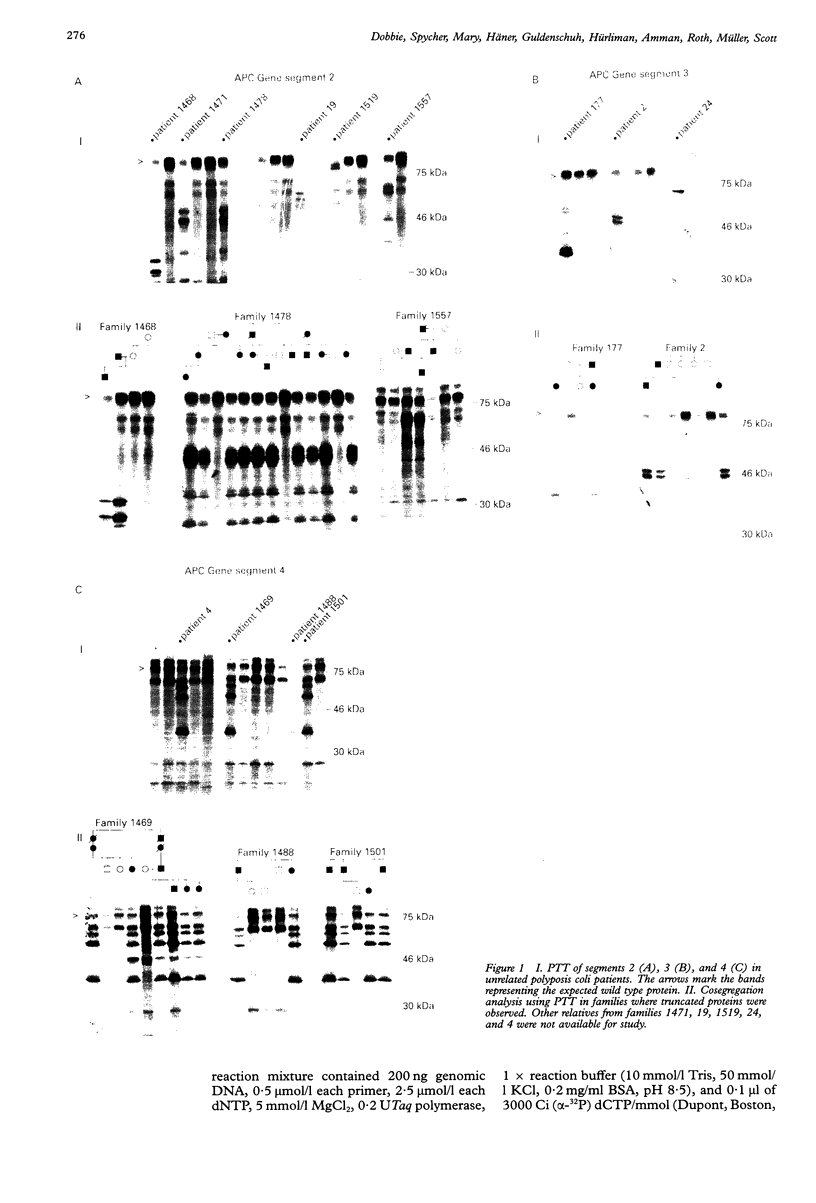
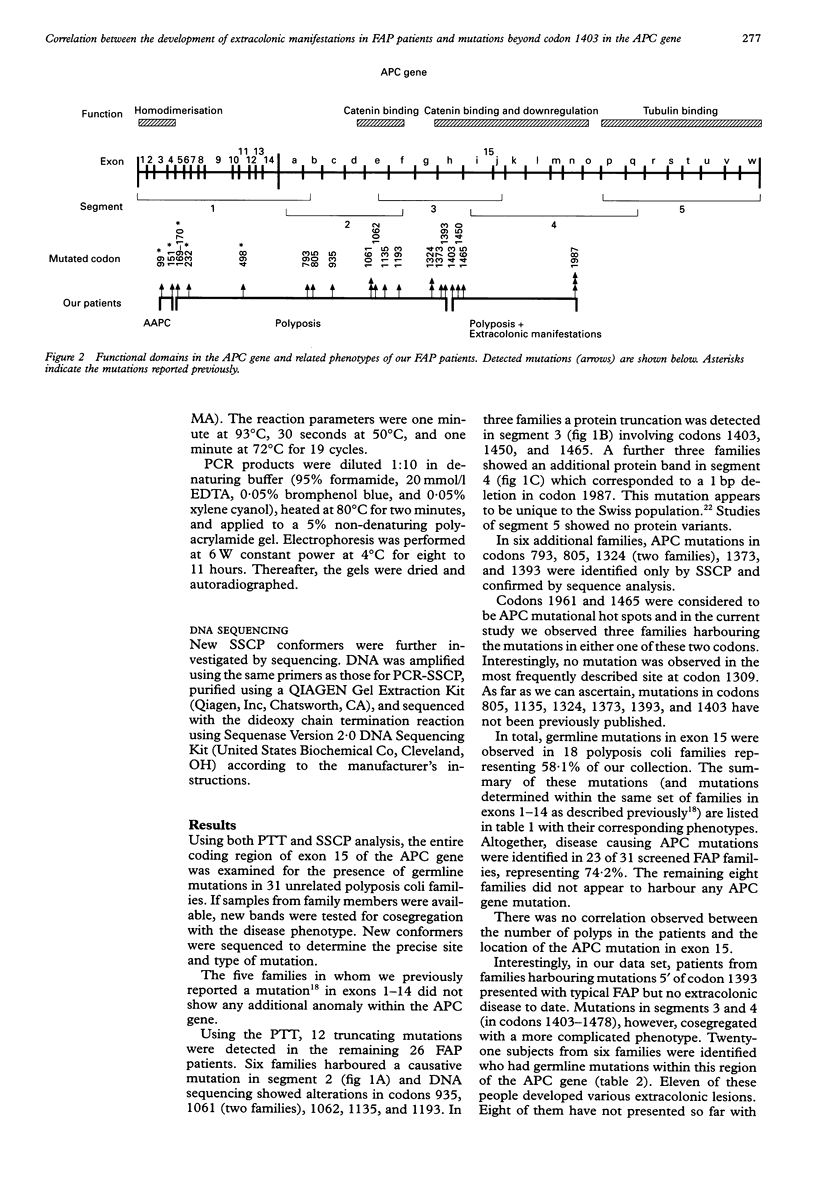
The APC gene was investigated in 31 unrelated polyposis coli families by SSCP analysis and the protein truncation test. Twenty-three germline mutations were identified which gave rise to a variety of different phenotypes. Some of these mutations have already been described; however we report six previously unpublished mutations. Typical disease symptoms were observed in families who harboured mutations between exon 4 (codon 169) and codon 1393 of exon 15. Mutations beyond codon 1403 were associated with more varied phenotype with respect to the development of extracolonic symptoms. In this report we provide support for the notion that there appears to be a correlation between the location of an APC mutation (beyond codon 1403) and extracolonic manifestations of familial adenomatous polyposis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodmer W. F., Bailey C. J., Bodmer J., Bussey H. J., Ellis A., Gorman P., Lucibello F. C., Murday V. A., Rider S. H., Scambler P. Localization of the gene for familial adenomatous polyposis on chromosome 5. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):614–616. doi: 10.1038/328614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülow S. Familial polyposis coli. Dan Med Bull. 1987 Mar;34(1):1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspari R., Friedl W., Mandl M., Möslein G., Kadmon M., Knapp M., Jacobasch K. H., Ecker K. W., Kreissler-Haag D., Timmermanns G. Familial adenomatous polyposis: mutation at codon 1309 and early onset of colon cancer. Lancet. 1994 Mar 12;343(8898):629–632. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92634-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspari R., Olschwang S., Friedl W., Mandl M., Boisson C., Böker T., Augustin A., Kadmon M., Möslein G., Thomas G. Familial adenomatous polyposis: desmoid tumours and lack of ophthalmic lesions (CHRPE) associated with APC mutations beyond codon 1444. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Mar;4(3):337–340. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.3.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich W. F., Lander E. S., Smith J. S., Moser A. R., Gould K. A., Luongo C., Borenstein N., Dove W. Genetic identification of Mom-1, a major modifier locus affecting Min-induced intestinal neoplasia in the mouse. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):631–639. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90484-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbie Z., Spycher M., Hürliman R., Ammann R., Ammann T., Roth J., Müller A., Müller H., Scott R. J. Mutational analysis of the first 14 exons of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene. Eur J Cancer. 1994;30A(11):1709–1713. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(94)00294-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gayther S. A., Wells D., SenGupta S. B., Chapman P., Neale K., Tsioupra K., Delhanty J. D. Regionally clustered APC mutations are associated with a severe phenotype and occur at a high frequency in new mutation cases of adenomatous polyposis coli. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jan;3(1):53–56. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groden J., Thliveris A., Samowitz W., Carlson M., Gelbert L., Albertsen H., Joslyn G., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification and characterization of the familial adenomatous polyposis coli gene. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):589–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurbuz A. K., Giardiello F. M., Petersen G. M., Krush A. J., Offerhaus G. J., Booker S. V., Kerr M. C., Hamilton S. R. Desmoid tumours in familial adenomatous polyposis. Gut. 1994 Mar;35(3):377–381. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.3.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joslyn G., Carlson M., Thliveris A., Albertsen H., Gelbert L., Samowitz W., Groden J., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification of deletion mutations and three new genes at the familial polyposis locus. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):601–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Nilbert M. C., Su L. K., Vogelstein B., Bryan T. M., Levy D. B., Smith K. J., Preisinger A. C., Hedge P., McKechnie D. Identification of FAP locus genes from chromosome 5q21. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):661–665. doi: 10.1126/science.1651562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert M., Dobbs M., Scambler P., O'Connell P., Nakamura Y., Stauffer D., Woodward S., Burt R., Hughes J., Gardner E. The gene for familial polyposis coli maps to the long arm of chromosome 5. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1411–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.3479843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luongo C., Gould K. A., Su L. K., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B., Dietrich W., Lander E. S., Moser A. R. Mapping of multiple intestinal neoplasia (Min) to proximal chromosome 18 of the mouse. Genomics. 1993 Jan;15(1):3–8. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch H. T., Smyrk T. C., Lanspa S. J., Jenkins J. X., Lynch P. M., Cavalieri J., Lynch J. F. Upper gastrointestinal manifestations in families with hereditary flat adenoma syndrome. Cancer. 1993 May 1;71(9):2709–2714. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930501)71:9<2709::aid-cncr2820710904>3.0.co;2-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhee M., Chepenik K. P., Liddell R. A., Nelson K. K., Siracusa L. D., Buchberg A. M. The secretory phospholipase A2 gene is a candidate for the Mom1 locus, a major modifier of ApcMin-induced intestinal neoplasia. Cell. 1995 Jun 16;81(6):957–966. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser A. R., Pitot H. C., Dove W. F. A dominant mutation that predisposes to multiple intestinal neoplasia in the mouse. Science. 1990 Jan 19;247(4940):322–324. doi: 10.1126/science.2296722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munemitsu S., Albert I., Souza B., Rubinfeld B., Polakis P. Regulation of intracellular beta-catenin levels by the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumor-suppressor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):3046–3050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.3046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munemitsu S., Souza B., Müller O., Albert I., Rubinfeld B., Polakis P. The APC gene product associates with microtubules in vivo and promotes their assembly in vitro. Cancer Res. 1994 Jul 15;54(14):3676–3681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase H., Miyoshi Y., Horii A., Aoki T., Ogawa M., Utsunomiya J., Baba S., Sasazuki T., Nakamura Y. Correlation between the location of germ-line mutations in the APC gene and the number of colorectal polyps in familial adenomatous polyposis patients. Cancer Res. 1992 Jul 15;52(14):4055–4057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y. The role of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene in human cancers. Adv Cancer Res. 1993;62:65–87. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60315-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent K. P., Phillips R. K., Hodgson S. V., Cottrell S., Smith-Ravin J., Pack K., Bodmer W. F. Phenotypic expression in familial adenomatous polyposis: partial prediction by mutation analysis. Gut. 1994 Nov;35(11):1622–1623. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.11.1622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. W., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. The F-type 5' motif of mouse L1 elements: a major class of L1 termini similar to the A-type in organization but unrelated in sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):739–749. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul P., Letteboer T., Gelbert L., Groden J., White R., Coppes M. J. Identical APC exon 15 mutations result in a variable phenotype in familial adenomatous polyposis. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2(7):925–931. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.7.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polakis P. Mutations in the APC gene and their implications for protein structure and function. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995 Feb;5(1):66–71. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(95)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell S. M., Petersen G. M., Krush A. J., Booker S., Jen J., Giardiello F. M., Hamilton S. R., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. Molecular diagnosis of familial adenomatous polyposis. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 30;329(27):1982–1987. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312303292702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser J., Condie A., Wright M., Horn J. M., Fantes J. A., Wyllie A. H., Dunlop M. G. APC mutation analysis by chemical cleavage of mismatch and a protein truncation assay in familial adenomatous polyposis. Br J Cancer. 1994 Nov;70(5):841–846. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinfeld B., Souza B., Albert I., Munemitsu S., Polakis P. The APC protein and E-cadherin form similar but independent complexes with alpha-catenin, beta-catenin, and plakoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 10;270(10):5549–5555. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.10.5549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinfeld B., Souza B., Albert I., Müller O., Chamberlain S. H., Masiarz F. R., Munemitsu S., Polakis P. Association of the APC gene product with beta-catenin. Science. 1993 Dec 10;262(5140):1731–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.8259518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. J., Levy D. B., Maupin P., Pollard T. D., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. Wild-type but not mutant APC associates with the microtubule cytoskeleton. Cancer Res. 1994 Jul 15;54(14):3672–3675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirio L., Olschwang S., Groden J., Robertson M., Samowitz W., Joslyn G., Gelbert L., Thliveris A., Carlson M., Otterud B. Alleles of the APC gene: an attenuated form of familial polyposis. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):951–957. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90538-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirio L., Otterud B., Stauffer D., Lynch H., Lynch P., Watson P., Lanspa S., Smyrk T., Cavalieri J., Howard L. Linkage of a variant or attenuated form of adenomatous polyposis coli to the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jul;51(1):92–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su L. K., Johnson K. A., Smith K. J., Hill D. E., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. Association between wild type and mutant APC gene products. Cancer Res. 1993 Jun 15;53(12):2728–2731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su L. K., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B., Preisinger A. C., Moser A. R., Luongo C., Gould K. A., Dove W. F. Multiple intestinal neoplasia caused by a mutation in the murine homolog of the APC gene. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):668–670. doi: 10.1126/science.1350108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su L. K., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. Association of the APC tumor suppressor protein with catenins. Science. 1993 Dec 10;262(5140):1734–1737. doi: 10.1126/science.8259519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Luijt R., Khan P. M., Vasen H., van Leeuwen C., Tops C., Roest P., den Dunnen J., Fodde R. Rapid detection of translation-terminating mutations at the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene by direct protein truncation test. Genomics. 1994 Mar 1;20(1):1–4. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]