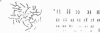Abstract
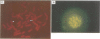
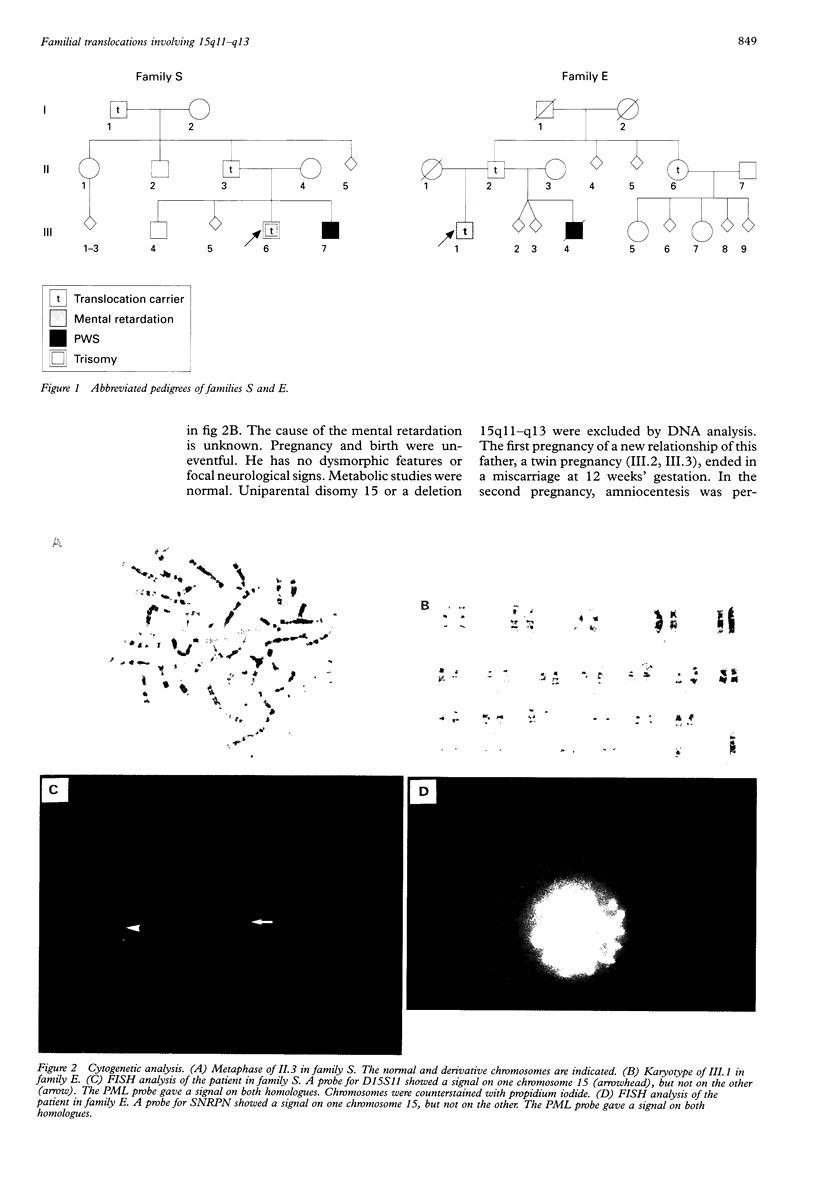
A de novo interstitial deletion of 15q11-q13 is the major cause of Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) and Angelman syndrome (AS). Here we describe two unrelated PWS patients with a typical deletion, whose fathers have a balanced translocation involving the PWS/AS region. Microsatellite data suggest that the deletion is the result of an unequal crossover between the derivative chromosome 15 and the normal chromosome 15. We conclude that familial translocations involving 15q11-q13 can give rise to interstitial deletions causing PWS or AS and that prenatal diagnosis in such families should include fluorescence in situ hybridisation or microsatellite studies or both.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckmann J. S., Tomfohrde J., Barnes R. I., Williams M., Broux O., Richard I., Weissenbach J., Bowcock A. M. A linkage map of human chromosome 15 with an average resolution of 2 cM and containing 55 polymorphic microsatellites. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Dec;2(12):2019–2030. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.12.2019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buiting K., Greger V., Brownstein B. H., Mohr R. M., Voiculescu I., Winterpacht A., Zabel B., Horsthemke B. A putative gene family in 15q11-13 and 16p11.2: possible implications for Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5457–5461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian S. L., Robinson W. P., Huang B., Mutirangura A., Line M. R., Nakao M., Surti U., Chakravarti A., Ledbetter D. H. Molecular characterization of two proximal deletion breakpoint regions in both Prader-Willi and Angelman syndrome patients. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jul;57(1):40–48. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittrich B., Buiting K., Gross S., Horsthemke B. Characterization of a methylation imprint in the Prader-Willi syndrome chromosome region. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Dec;2(12):1995–1999. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.12.1995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittrich B., Robinson W. P., Knoblauch H., Buiting K., Schmidt K., Gillessen-Kaesbach G., Horsthemke B. Molecular diagnosis of the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes by detection of parent-of-origin specific DNA methylation in 15q11-13. Hum Genet. 1992 Nov;90(3):313–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00220089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamabe J., Niikawa N. StyI polymorphism at the D15S11 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5579–5579. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm V. A., Cassidy S. B., Butler M. G., Hanchett J. M., Greenswag L. R., Whitman B. Y., Greenberg F. Prader-Willi syndrome: consensus diagnostic criteria. Pediatrics. 1993 Feb;91(2):398–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultén M., Armstrong S., Challinor P., Gould C., Hardy G., Leedham P., Lee T., McKeown C. Genomic imprinting in an Angelman and Prader-Willi translocation family. Lancet. 1991 Sep 7;338(8767):638–639. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90652-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano A., Mutirangura A., Dittrich B., Buiting K., Horsthemke B., Saitoh S., Niikawa N., Ledbetter S. A., Greenberg F., Chinault A. C. Molecular dissection of the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome region (15q11-13) by YAC cloning and FISH analysis. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Sep;1(6):417–425. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.6.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter D. H., Engel E. Uniparental disomy in humans: development of an imprinting map and its implications for prenatal diagnosis. Hum Mol Genet. 1995;4(Spec No):1757–1764. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.suppl_1.1757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutirangura A., Greenberg F., Butler M. G., Malcolm S., Nicholls R. D., Chakravarti A., Ledbetter D. H. Multiplex PCR of three dinucleotide repeats in the Prader-Willi/Angelman critical region (15q11-q13): molecular diagnosis and mechanism of uniparental disomy. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Feb;2(2):143–151. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.2.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D. Genomic imprinting and candidate genes in the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Jun;3(3):445–456. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90119-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polymeropoulos M. H., Xiao H., Rath D. S., Merril C. R. Tetranucleotide repeat polymorphism at the human aromatase cytochrome P-450 gene (CYP19). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):195–195. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeets D. F., Hamel B. C., Nelen M. R., Smeets H. J., Bollen J. H., Smits A. P., Ropers H. H., van Oost B. A. Prader-Willi syndrome and Angelman syndrome in cousins from a family with a translocation between chromosomes 6 and 15. N Engl J Med. 1992 Mar 19;326(12):807–811. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199203193261206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]