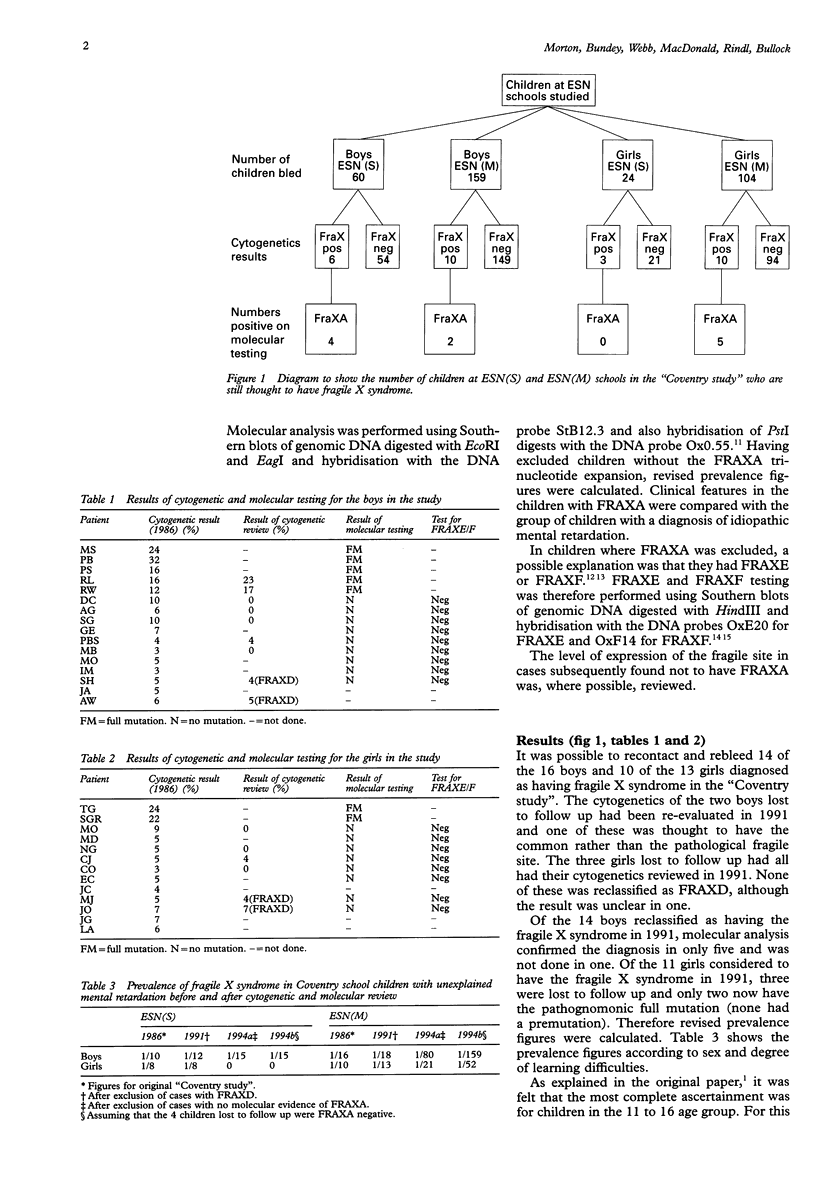
Abstract
In 1986, a population study of school children in the city of Coventry gave an overall prevalence in males and females for fragile X syndrome of 1/952. The 29 children diagnosed as having fragile X syndrome in this study have been re-evaluated with molecular diagnostic techniques. Eighteen of the original 29 children have been found not to have the expansion of the FMR1 gene associated with fragile X syndrome. Revised prevalence figures have been calculated giving rise to an overall prevalence figure of 1/2720 (range 1/2198-1/3089). If the four children lost to follow up are also assumed not to have the fragile X syndrome, the revised prevalence figure was 1/5714 (range 1/4762-1/6349). Clinical review of boys with severe mental retardation from this and a subsidiary study show that the clinical features of head circumference greater than the 50th centile, testicular volume greater than the 50th centile, and IQ between 35 and 70 remain helpful in distinguishing boys with fragile X syndrome from those who have non-specific mental retardation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allingham-Hawkins D. J., Ray P. N. FRAXE expansion is not a common etiological factor among developmentally delayed males. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jul;57(1):72–76. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnicoat A. J., Docherty Z., Bobrow M. Where have all the fragile X boys gone? Dev Med Child Neurol. 1993 Jun;35(6):532–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1993.tb11684.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn G. A., Hirst M. C., Knight S. J., Macpherson J. N., Barber J. C., Flannery A. V., Davies K. E., Buckle V. J. Identification of the FRAXE fragile site in two families ascertained for X linked mental retardation. J Med Genet. 1993 Feb;30(2):97–100. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.2.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustavson K. H., Blomquist H. K., Holmgren G. Prevalence of the fragile-X syndrome in mentally retarded boys in a Swedish county. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Jan-Feb;23(1-2):581–587. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320230152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman R. J., Amiri K., Cronister A. Fragile X checklist. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Feb-Mar;38(2-3):283–287. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320380223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst M. C., Barnicoat A., Flynn G., Wang Q., Daker M., Buckle V. J., Davies K. E., Bobrow M. The identification of a third fragile site, FRAXF, in Xq27--q28 distal to both FRAXA and FRAXE. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Feb;2(2):197–200. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Bullman H., Macpherson J., Youings S., Rooney V., Watson A., Dennis N. R. Population studies of the fragile X: a molecular approach. J Med Genet. 1993 Jun;30(6):454–459. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.6.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight S. J., Flannery A. V., Hirst M. C., Campbell L., Christodoulou Z., Phelps S. R., Pointon J., Middleton-Price H. R., Barnicoat A., Pembrey M. E. Trinucleotide repeat amplification and hypermethylation of a CpG island in FRAXE mental retardation. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90300-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight S. J., Voelckel M. A., Hirst M. C., Flannery A. V., Moncla A., Davies K. E. Triplet repeat expansion at the FRAXE locus and X-linked mild mental handicap. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Jul;55(1):81–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kähkönen M., Alitalo T., Airaksinen E., Matilainen R., Launiala K., Autio S., Leisti J. Prevalence of the fragile X syndrome in four birth cohorts of children of school age. Hum Genet. 1987 Sep;77(1):85–87. doi: 10.1007/BF00284720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laing S., Partington M., Robinson H., Turner G. Clinical screening score for the fragile X (Martin-Bell) syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Feb-Mar;38(2-3):256–259. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320380219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulley J. C., Yu S., Loesch D. Z., Hay D. A., Donnelly A., Gedeon A. K., Carbonell P., López I., Glover G., Gabarrón I. FRAXE and mental retardation. J Med Genet. 1995 Mar;32(3):162–169. doi: 10.1136/jmg.32.3.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish J. E., Oostra B. A., Verkerk A. J., Richards C. S., Reynolds J., Spikes A. S., Shaffer L. G., Nelson D. L. Isolation of a GCC repeat showing expansion in FRAXF, a fragile site distal to FRAXA and FRAXE. Nat Genet. 1994 Nov;8(3):229–235. doi: 10.1038/ng1194-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie R. J., Knight S. J., Hirst M. C., Grewal P. K., Bobrow M., Cross G. S., Davies K. E. The cloning of FRAXF: trinucleotide repeat expansion and methylation at a third fragile site in distal Xqter. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Dec;3(12):2115–2121. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.12.2115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau F., Heitz D., Biancalana V., Blumenfeld S., Kretz C., Boué J., Tommerup N., Van Der Hagen C., DeLozier-Blanchet C., Croquette M. F. Direct diagnosis by DNA analysis of the fragile X syndrome of mental retardation. N Engl J Med. 1991 Dec 12;325(24):1673–1681. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199112123252401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simko A., Hornstein L., Soukup S., Bagamery N. Fragile X syndrome: recognition in young children. Pediatrics. 1989 Apr;83(4):547–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaney S. F., Wilkie A. O., Hirst M. C., Charlton R., McKinley M., Pointon J., Christodoulou Z., Huson S. M., Davies K. E. DNA testing for fragile X syndrome in schools for learning difficulties. Arch Dis Child. 1995 Jan;72(1):33–37. doi: 10.1136/adc.72.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart R. D. Fragile X syndrome: as common as first thought? J Med Genet. 1992 Apr;29(4):287–287. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.4.287-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Baker E. Characterisation of a new rare fragile site easily confused with the fragile X. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 May;1(2):111–113. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.2.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Baker E. The common fragile site in band q27 of the human X chromosome is not coincident with the fragile X. Clin Genet. 1990 Mar;37(3):167–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1990.tb03498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thake A., Todd J., Bundey S., Webb T. Is it possible to make a clinical diagnosis of the fragile X syndrome in a boy? Arch Dis Child. 1985 Nov;60(11):1001–1007. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.11.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranebjaerg L., Hilling S., Jessen J., Lind D., Hansen M. S. Prevalence of fra(X) in the county of Funen in Denmark is lower than expected. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Jul 15;51(4):423–427. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320510424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Robinson H., Laing S., Purvis-Smith S. Preventive screening for the fragile X syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1986 Sep 4;315(10):607–609. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198609043151002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkerk A. J., Pieretti M., Sutcliffe J. S., Fu Y. H., Kuhl D. P., Pizzuti A., Reiner O., Richards S., Victoria M. F., Zhang F. P. Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):905–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90397-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb T. P., Bundey S., Thake A., Todd J. The frequency of the fragile X chromosome among schoolchildren in Coventry. J Med Genet. 1986 Oct;23(5):396–399. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.5.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb T., Bundey S. Prevalence of fragile X syndrome. J Med Genet. 1991 May;28(5):358–358. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.5.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S., Pritchard M., Kremer E., Lynch M., Nancarrow J., Baker E., Holman K., Mulley J. C., Warren S. T., Schlessinger D. Fragile X genotype characterized by an unstable region of DNA. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1179–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


