Abstract
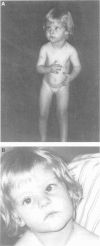
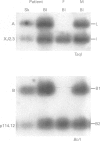
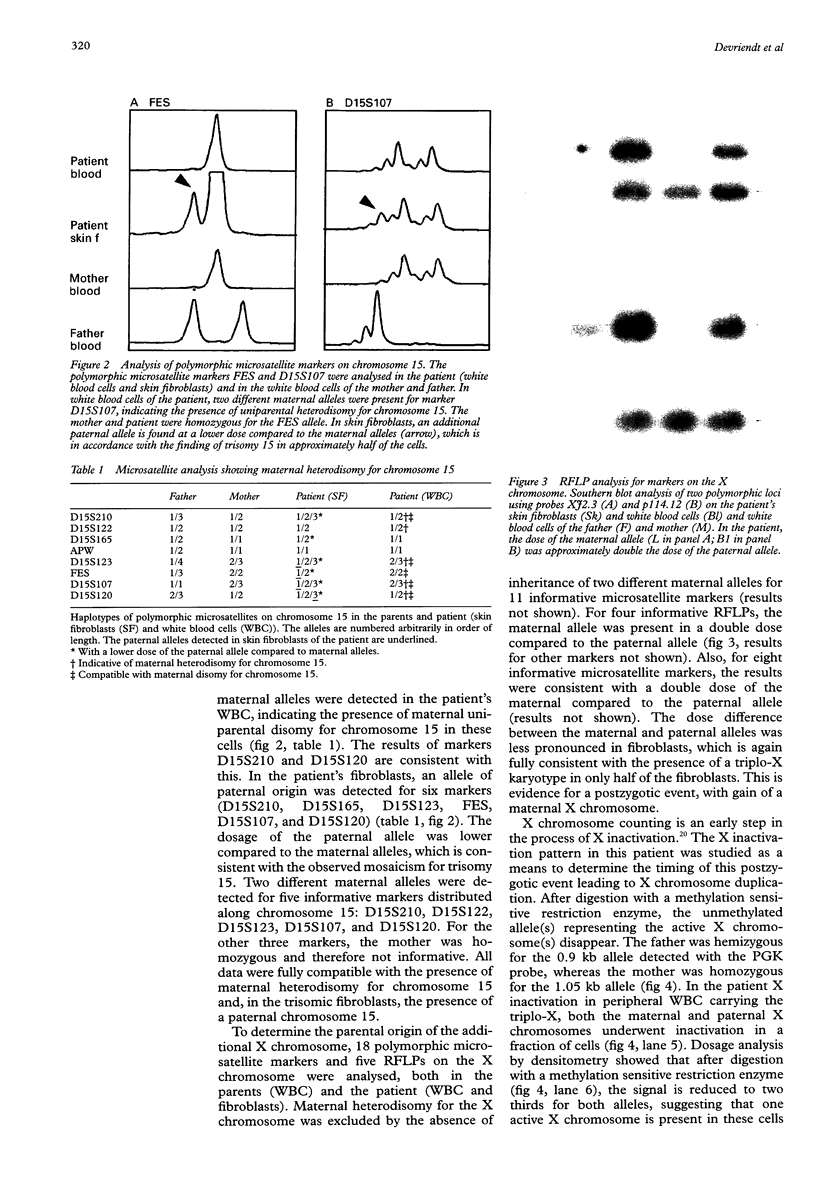
A 3.3 year old girl with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) and mosaicism for two aneuploidies, 47,XXX and 47,XX,+15, is presented. The triplo-X cell line was found in white blood cells and fibroblasts, the trisomy 15 cell line in 50% of the fibroblasts. Using methylation studies of the PWS critical region and by polymorphic microsatellite analysis, the existence of uniparental maternal heterodisomy for chromosome 15 was shown in white blood cells. This provided a molecular explanation for the PWS in this child. In fibrolasts, an additional paternal allele was detected for markers on chromosome 15, which is in agreement with the presence of mosaicism for trisomy 15 in these cells. This example provides direct evidence for trisomic rescue by reduction to disomy as a possible basis for PWS. Whereas the trisomy 15 was caused by a maternal meiosis I error, the triplo-X resulted from a postzygotic gain of a maternal X chromosome, as shown by the finding of two identical maternal X chromosomes in the 47,XXX cell line. Because the triplo-X and the trisomy 15 were present in different cell lines, gain of an X chromosome occurred either in the same cell division as the trisomy 15 rescue or shortly before or after.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cassidy S. B., Lai L. W., Erickson R. P., Magnuson L., Thomas E., Gendron R., Herrmann J. Trisomy 15 with loss of the paternal 15 as a cause of Prader-Willi syndrome due to maternal disomy. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Oct;51(4):701–708. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian S. L., Smith A. C., Macha M., Black S. H., Elder F. F., Johnson J. M., Resta R. G., Surti U., Suslak L., Verp M. S. Prenatal diagnosis of uniparental disomy 15 following trisomy 15 mosaicism. Prenat Diagn. 1996 Apr;16(4):323–332. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0223(199604)16:4<323::AID-PD856>3.0.CO;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittrich B., Robinson W. P., Knoblauch H., Buiting K., Schmidt K., Gillessen-Kaesbach G., Horsthemke B. Molecular diagnosis of the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes by detection of parent-of-origin specific DNA methylation in 15q11-13. Hum Genet. 1992 Nov;90(3):313–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00220089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. J., Waters M. F., Williams C. A., Zori R. T., Glenn C. C., Avidano K. M., Nicholls R. D. A DNA methylation imprint, determined by the sex of the parent, distinguishes the Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel E. Uniparental disomy revisited: the first twelve years. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Jul 1;46(6):670–674. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320460613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., Kleczkowska A., Lagae L., Kenis H., van den Berghe H. A specific phenotype associated with trisomy 15 mosaicism. Ann Genet. 1993;36(2):129–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillessen-Kaesbach G., Robinson W., Lohmann D., Kaya-Westerloh S., Passarge E., Horsthemke B. Genotype-phenotype correlation in a series of 167 deletion and non-deletion patients with Prader-Willi syndrome. Hum Genet. 1995 Dec;96(6):638–643. doi: 10.1007/BF00210291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison K., Eisenger K., Anyane-Yeboa K., Brown S. Maternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 2 in a baby with trisomy 2 mosaicism in amniotic fluid culture. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Aug 28;58(2):147–151. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320580211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm V. A., Cassidy S. B., Butler M. G., Hanchett J. M., Greenswag L. R., Whitman B. Y., Greenberg F. Prader-Willi syndrome: consensus diagnostic criteria. Pediatrics. 1993 Feb;91(2):398–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter D. H., Riccardi V. M., Airhart S. D., Strobel R. J., Keenan B. S., Crawford J. D. Deletions of chromosome 15 as a cause of the Prader-Willi syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 5;304(6):325–329. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102053040604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M., Hassold T., Harvey J., Wang L. H., Morton N. E., Jacobs P. The origin of 47,XXY and 47,XXX aneuploidy: heterogeneous mechanisms and role of aberrant recombination. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Aug;3(8):1365–1371. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.8.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Jeppesen P., Torchia B. S., Fu S., Dunn M. A., Axelman J., Schmeckpeper B. J., Fantes J., Zori R. T., Driscoll D. J. Lack of X inactivation associated with maternal X isodisomy: evidence for a counting mechanism prior to X inactivation during human embryogenesis. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jan;58(1):161–170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milunsky J. M., Wyandt H. E., Huang X. L., Kang X. Z., Elias E. R., Milunsky A. Trisomy 15 mosaicism and uniparental disomy (UPD) in a liveborn infant. Am J Med Genet. 1996 Jan 22;61(3):269–273. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19960122)61:3<269::AID-AJMG12>3.0.CO;2-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morichon-Delvallez N., Mussat P., Dumez Y., Vekemans M. Trisomy 15 in chorionic villi and Prader-Willi syndrome at birth. Prenat Diagn. 1993 Apr;13(4):307–308. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970130410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutirangura A., Greenberg F., Butler M. G., Malcolm S., Nicholls R. D., Chakravarti A., Ledbetter D. H. Multiplex PCR of three dinucleotide repeats in the Prader-Willi/Angelman critical region (15q11-q13): molecular diagnosis and mechanism of uniparental disomy. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Feb;2(2):143–151. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.2.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D., Knoll J. H., Butler M. G., Karam S., Lalande M. Genetic imprinting suggested by maternal heterodisomy in nondeletion Prader-Willi syndrome. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):281–285. doi: 10.1038/342281a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purvis-Smith S. G., Saville T., Manass S., Yip M. Y., Lam-Po-Tang P. R., Duffy B., Johnston H., Leigh D., McDonald B. Uniparental disomy 15 resulting from "correction" of an initial trisomy 15. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jun;50(6):1348–1350. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. P., Lorda-Sanchez I., Malcolm S., Langlois S., Schuffenhauer S., Knoblauch H., Horsthemke B., Schinzel A. A. Increased parental ages and uniparental disomy 15: a paternal age effect? Eur J Hum Genet. 1993;1(4):280–286. doi: 10.1159/000472425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J., Ali Z., Bower S., Bennett P., Chard T., Moore G. Human maternal uniparental disomy for chromosome 16 and fetal development. Prenat Diagn. 1994 Aug;14(8):751–756. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970140817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Willard H. F., Michelson A. M., Riggs A. D., Orkin S. H. Clonal analysis using recombinant DNA probes from the X-chromosome. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 15;47(18):4806–4813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb A., Beard J., Wright C., Robson S., Wolstenholme J., Goodship J. A case of paternal uniparental disomy for chromosome 11. Prenat Diagn. 1995 Aug;15(8):773–777. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970150816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willatt L. R., Davison B. C., Goudie D., Alexander J., Dyson H. M., Jenks P. E., Ferguson-Smith M. E. A male with trisomy 9 mosaicism and maternal uniparental disomy for chromosome 9 in the euploid cell line. J Med Genet. 1992 Oct;29(10):742–744. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.10.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]