Abstract
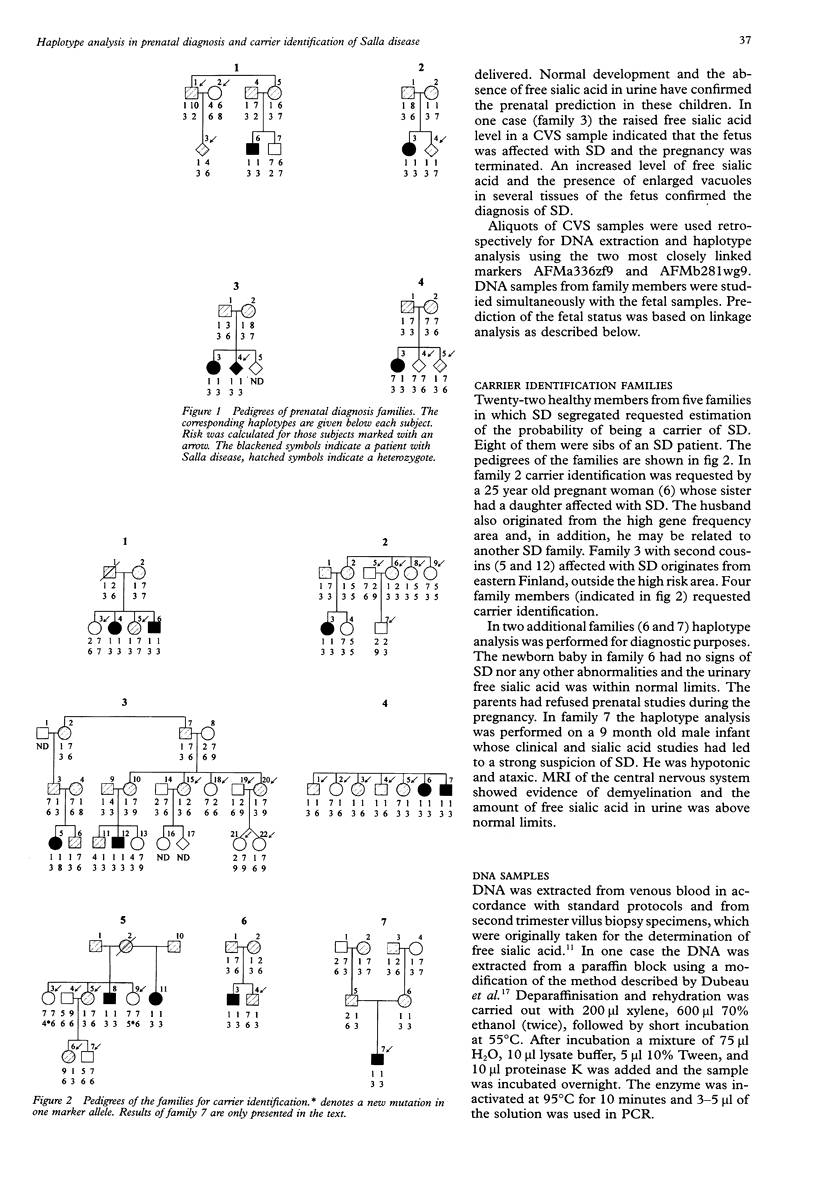
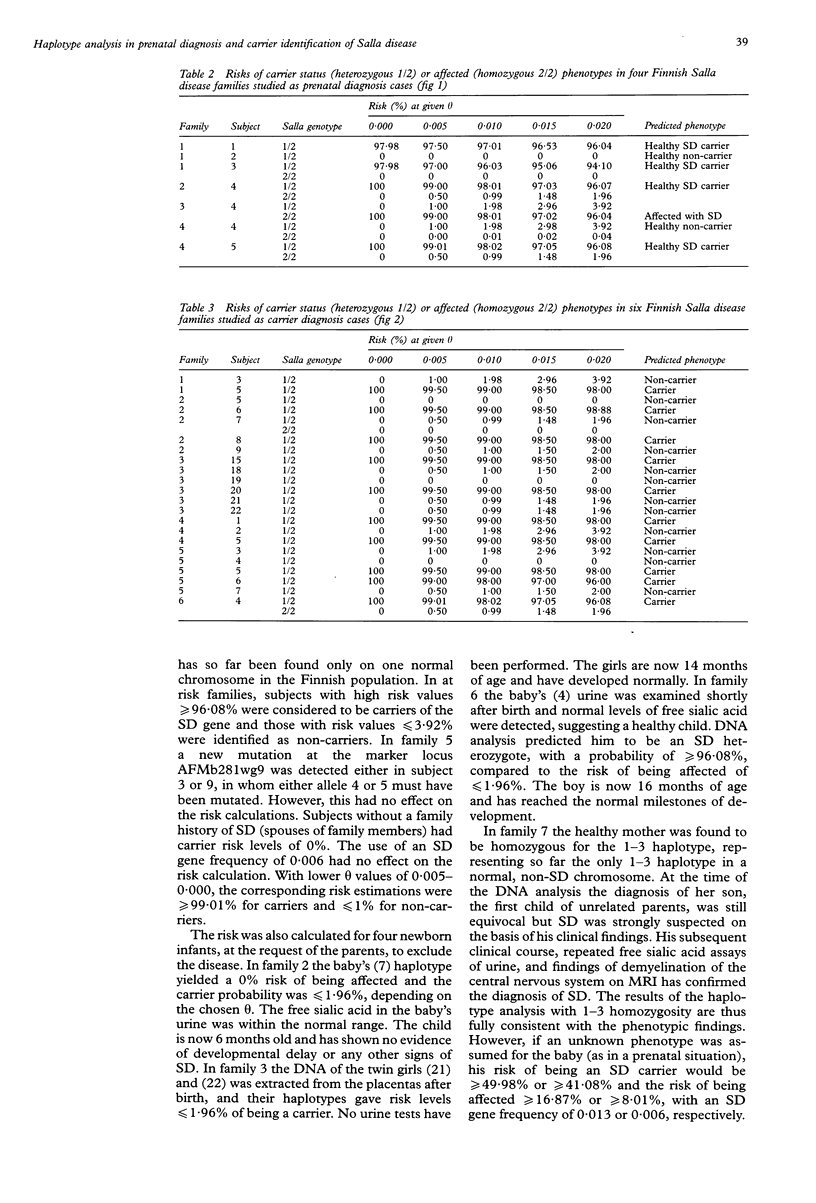
Salla disease (SD) is an autosomal recessive disorder in which free sialic acid (N-acetyl neuraminic acid) accumulates in lysosomes. A specific transport mechanism for acidic monosaccharides on the lysosomal membrane has recently been described, but the molecular deficiency causing SD is still unknown. We have previously mapped the SD gene to 6q14-q15 by means of genetic linkage analysis and restricted the positive chromosomal area to less than 100 kb with linkage disequilibrium mapping. The two best allelic association markers have now retrospectively been used in five prenatal analyses originally studied with sialic acid assays in chorionic villus specimens. In four cases an unaffected fetus was predicted with a probability level of more than 94%, which was in concordance with the biochemical data. One fetus was predicted to be affected with over 96% probability, as was shown by free sialic acid assays in a CVS sample and in fetal tissues after termination of the pregnancy. Risk calculations incorporating disequilibrium were also used to predict the carrier status in members of six families with previous SD cases, and also in a few cases with no known family history of SD. DNA marker based analysis thus provides a reliable method for risk estimations in prenatal cases and for carrier identification of SD.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aula P., Autio S., Raivio K. O., Rapola J., Thodén C. J., Koskela S. L., Yamashina I. "Salla disease": a new lysosomal storage disorder. Arch Neurol. 1979 Feb;36(2):88–94. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1979.00500380058006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aula P., Renlund M., Raivio K. O., Koskela S. L. Screening of inherited oligosaccharidurias among mentally retarded patients in northern Finland. J Ment Defic Res. 1986 Dec;30(Pt 4):365–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1986.tb01332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements P. R., Taylor J. A., Hopwood J. J. Biochemical characterization of patients and prenatal diagnosis of sialic acid storage disease for three families. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1988;11(1):30–44. doi: 10.1007/BF01800055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodelson de Kremer R., Depetris de Boldini C., Paschini de Capra A., Hliba E. Enfermedad de Salla (sialuria, tipo Finlandés). Nueva variante clínica en un primer reconocimiento Argentino. Medicina (B Aires) 1990;50(2):107–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubeau L., Chandler L. A., Gralow J. R., Nichols P. W., Jones P. A. Southern blot analysis of DNA extracted from formalin-fixed pathology specimens. Cancer Res. 1986 Jun;46(6):2964–2969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echenne B., Vidal M., Maire I., Michalski J. C., Baldet P., Astruc J. Salla disease in one non-Finnish patient. Eur J Pediatr. 1986 Sep;145(4):320–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00439413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haataja L., Schleutker J., Laine A. P., Renlund M., Savontaus M. L., Dib C., Weissenbach J., Peltonen L., Aula P. The genetic locus for free sialic acid storage disease maps to the long arm of chromosome 6. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Jun;54(6):1042–1049. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hästbacka J., Salonen R., Laurila P., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I. Prenatal diagnosis of diastrophic dysplasia with polymorphic DNA markers. J Med Genet. 1993 Apr;30(4):265–268. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.4.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorde L. B., Watkins W. S., Viskochil D., O'Connell P., Ward K. Linkage disequilibrium in the neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) region: implications for gene mapping. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Nov;53(5):1038–1050. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake B. D., Young E. P., Nicolaides K. Prenatal diagnosis of infantile sialic acid storage disease in a twin pregnancy. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1989;12(2):152–156. doi: 10.1007/BF01800718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G. M., Beerens C. E., Aula P. P., Verheijen F. W. Sialic acid storage diseases. A multiple lysosomal transport defect for acidic monosaccharides. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1329–1335. doi: 10.1172/JCI115136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renlund M., Aula P. Prenatal detection of Salla disease based upon increased free sialic acid in amniocytes. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Oct;28(2):377–384. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renlund M., Aula P., Raivio K. O., Autio S., Sainio K., Rapola J., Koskela S. L. Salla disease: a new lysosomal storage disorder with disturbed sialic acid metabolism. Neurology. 1983 Jan;33(1):57–66. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renlund M. Clinical and laboratory diagnosis of Salla disease in infancy and childhood. J Pediatr. 1984 Feb;104(2):232–236. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80998-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renlund M., Tietze F., Gahl W. A. Defective sialic acid egress from isolated fibroblast lysosomes of patients with Salla disease. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):759–762. doi: 10.1126/science.3961501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleutker J., Laine A. P., Haataja L., Renlund M., Weissenbach J., Aula P., Peltonen L. Linkage disequilibrium utilized to establish a refined genetic position of the Salla disease locus on 6q14-q15. Genomics. 1995 May 20;27(2):286–292. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulisalo T., Sillence D., Wilson M., Ryynänen M., Kaitila I. Early prenatal diagnosis of cartilage-hair hypoplasia (CHH) with polymorphic DNA markers. Prenat Diagn. 1995 Feb;15(2):135–140. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970150205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tondeur M., Libert J., Vamos E., Van Hoof F., Thomas G. H., Strecker G. Infantile form of sialic acid storage disorder: clinical, ultrastructural, and biochemical studies in two siblings. Eur J Pediatr. 1982 Oct;139(2):142–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00441499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vamos E., Libert J., Elkhazen N., Jauniaux E., Hustin J., Wilkin P., Baumkötter J., Mendla K., Cantz M., Strecker G. Prenatal diagnosis and confirmation of infantile sialic acid storage disease. Prenat Diagn. 1986 Nov-Dec;6(6):437–446. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970060607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesa J., Hellsten E., Mäkelä T. P., Järvelä I., Airaksinen T., Santavuori P., Peltonen L. A single PCR marker in strong allelic association with the infantile form of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis facilitates reliable prenatal diagnostics and disease carrier identification. Eur J Hum Genet. 1993;1(2):125–132. doi: 10.1159/000472399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Chapelle A. Disease gene mapping in isolated human populations: the example of Finland. J Med Genet. 1993 Oct;30(10):857–865. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.10.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


