Abstract
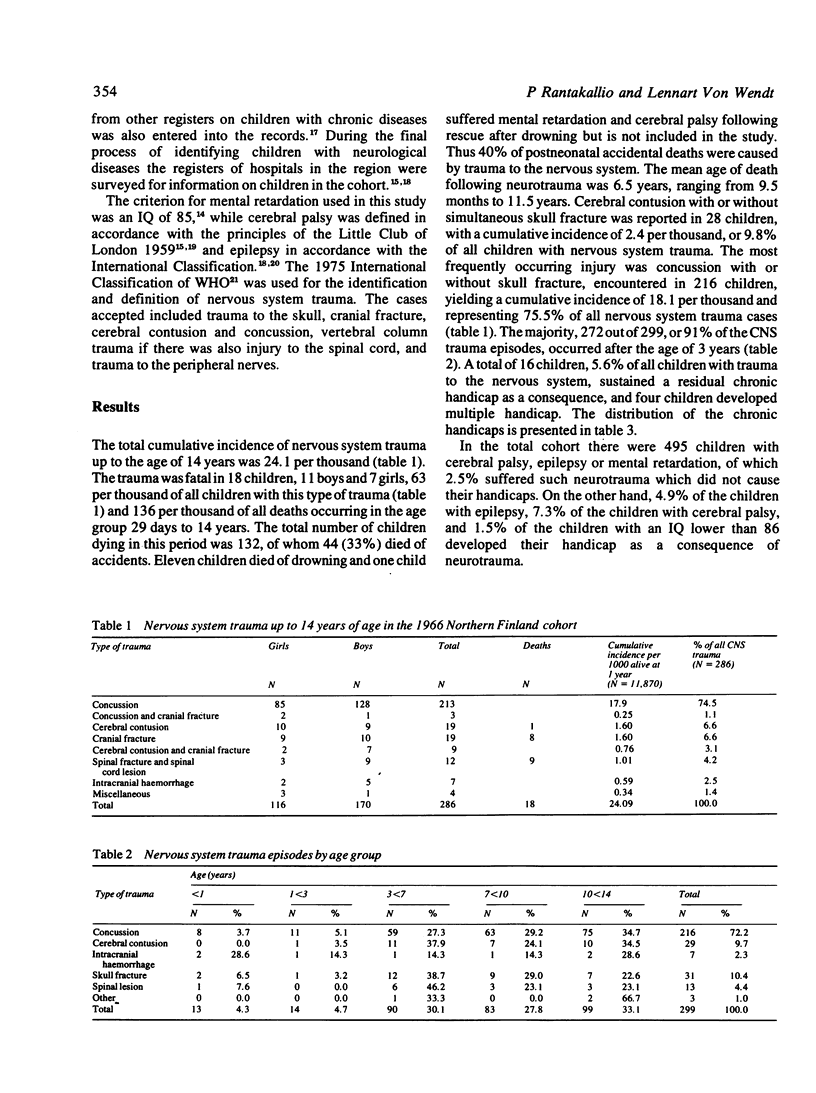
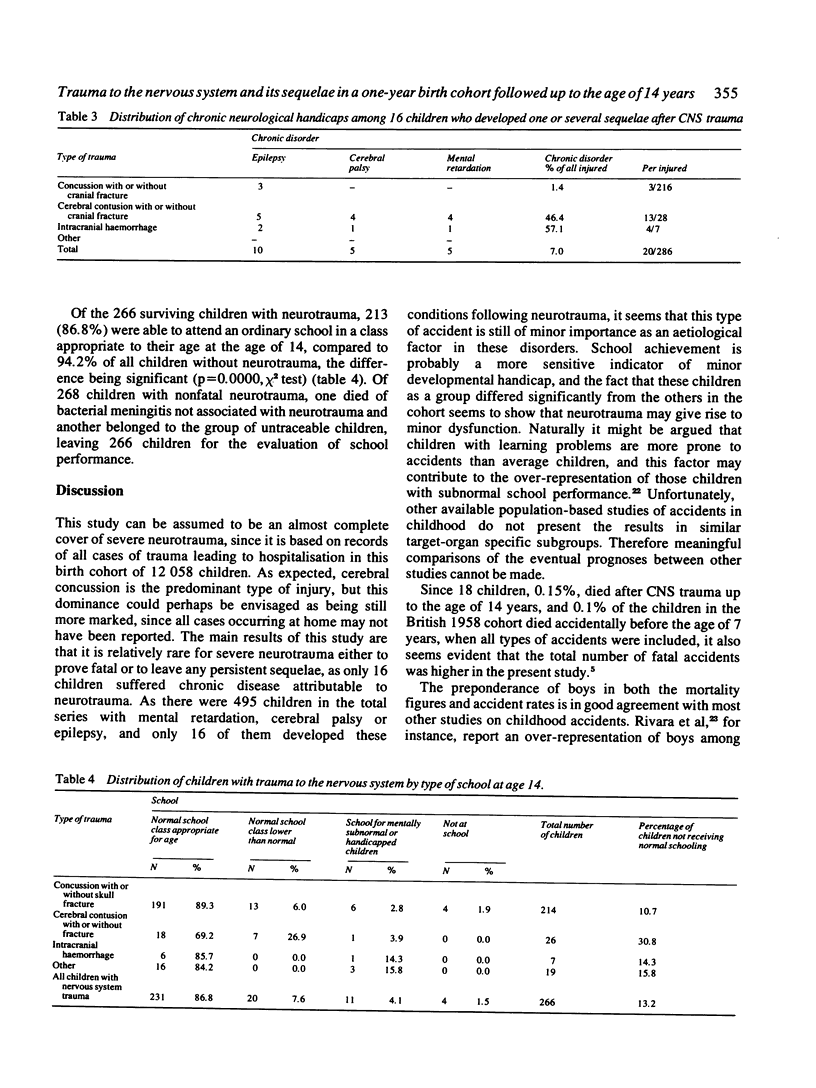
The one-year birth cohort of 12 058 children, 96% of all children born in the two northernmost provinces of Finland, Oulu and Lapland, in 1966 was studied prospectively up to the age of 14 years. During this period 14 children, 1.2 per thousand, were lost from the follow-up. Data on development, mortality, and morbidity were collected prospectively by means of questionnaires and from various registers, the most important of which was the National Hospital Discharge Register. A total of 299 cases of trauma to the nervous system (skull fracture, cerebral contusion, concussion, fracture of the vertebral column with spinal lesion, injury to the cranial or peripheral nerves) occurred in 286 children, 116 girls and 170 boys, which yields a cumulative incidence of nervous system trauma of 24.1 per thousand. The trauma was fatal in 11 boys and 7 girls, 63 per thousand of all children with neurotrauma, and 136 per thousand of all cases of death occurring in the age group 29 days to 14 years. Spinal injury occurred in 12 children, cerebral contusion in 28, skull fracture in 19, and concussion in 216. Such trauma resulted in chronic disease, cerebral palsy, mental retardation, and epilepsy in 16 children, 5.6% of all children with neurotrauma and 3.2% of the 495 children in the cohort with cerebral palsy, epilepsy or mental retardation only.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gallagher S. S., Finison K., Guyer B., Goodenough S. The incidence of injuries among 87,000 Massachusetts children and adolescents: results of the 1980-81 Statewide Childhood Injury Prevention Program Surveillance System. Am J Public Health. 1984 Dec;74(12):1340–1347. doi: 10.2105/ajph.74.12.1340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gastaut H. Clinical and electroencephalographical classification of epileptic seizures. Epilepsia. 1970 Mar;11(1):102–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1970.tb03871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratz R. R. Accidental injury in childhood: a literature review on pediatric trauma. J Trauma. 1979 Aug;19(8):551–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson L. H. Childhood accidents. Three epidemiological studies on the etiology. Scand J Soc Med. 1977;5(1):5–13. doi: 10.1177/140349487700500102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiskanen O., Kaste M. Late prognosis of severe brain injury in children. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1974 Feb;16(1):11–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1974.tb02705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janec M. The rate of accidental injuries in childhood morbidity and lethality. Acta Chir Acad Sci Hung. 1979;20(2-3):301–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer H. Prognosis of severe head injuries in childhood and adolescence. Neuropediatrics. 1983 Aug;14(3):176–181. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1059574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcusson H., Oehmisch W. La mortalité causée par les accidents chez les enfants: données provenant d'un choix de pays de différents continents 1950-1971. World Health Stat Rep. 1977;30(1):57–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rantakallio P. A 14-year follow-up of children with normal and abnormal birth weight for their gestational age. A population study. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1985 Jan;74(1):62–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1985.tb10922.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivara F. P., Bergman A. B., LoGerfo J. P., Weiss N. S. Epidemiology of childhood injuries. II. Sex differences in injury rates. Am J Dis Child. 1982 Jun;136(6):502–506. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1982.03970420026004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivara F. P. Childhood injuries. III: Epidemiology of non-motor vehicle head trauma. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1984 Feb;26(1):81–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1984.tb04410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth J., Burnell I., Taylor B., Butler N. Family type and accidents in preschool children. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1983 Jun;37(2):100–104. doi: 10.1136/jech.37.2.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink C., Karsten J., von Törne J., Zink A., Korporal J. Epidemiologische und sozialpsychologische Aspekte von Unfällen im Kindesalter. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1980 Jul;128(7):496–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


