Abstract
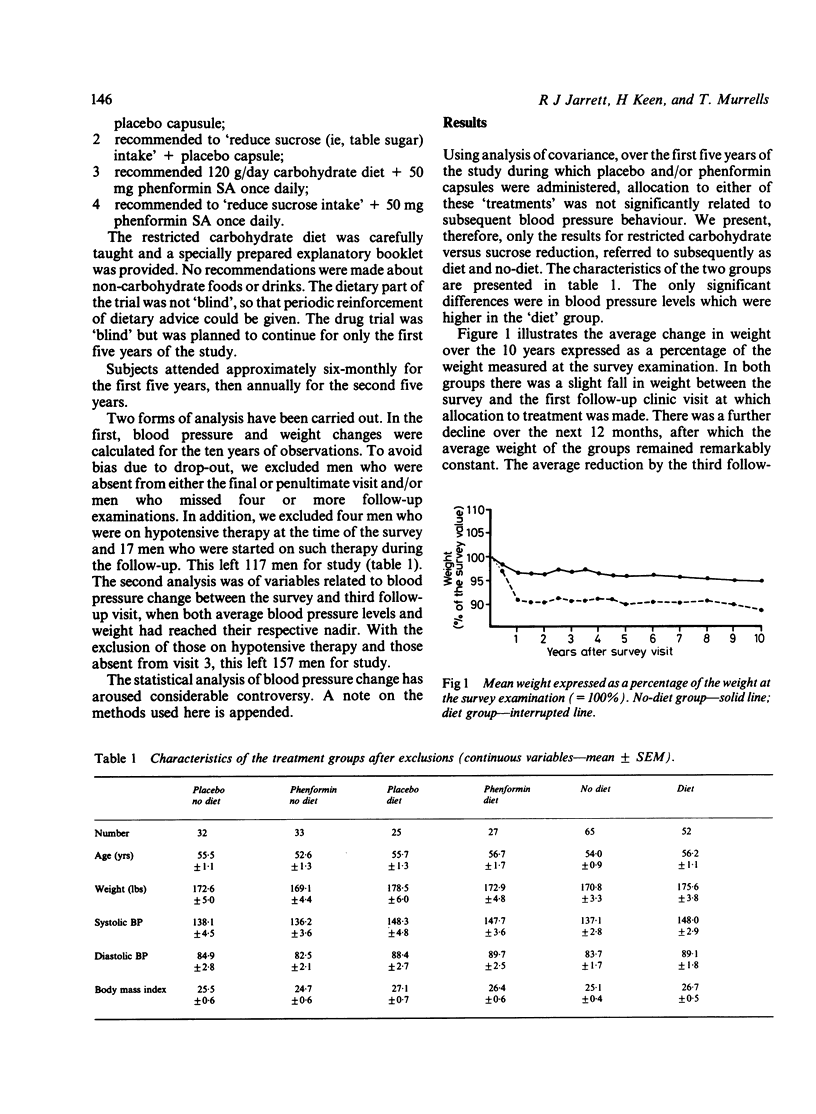
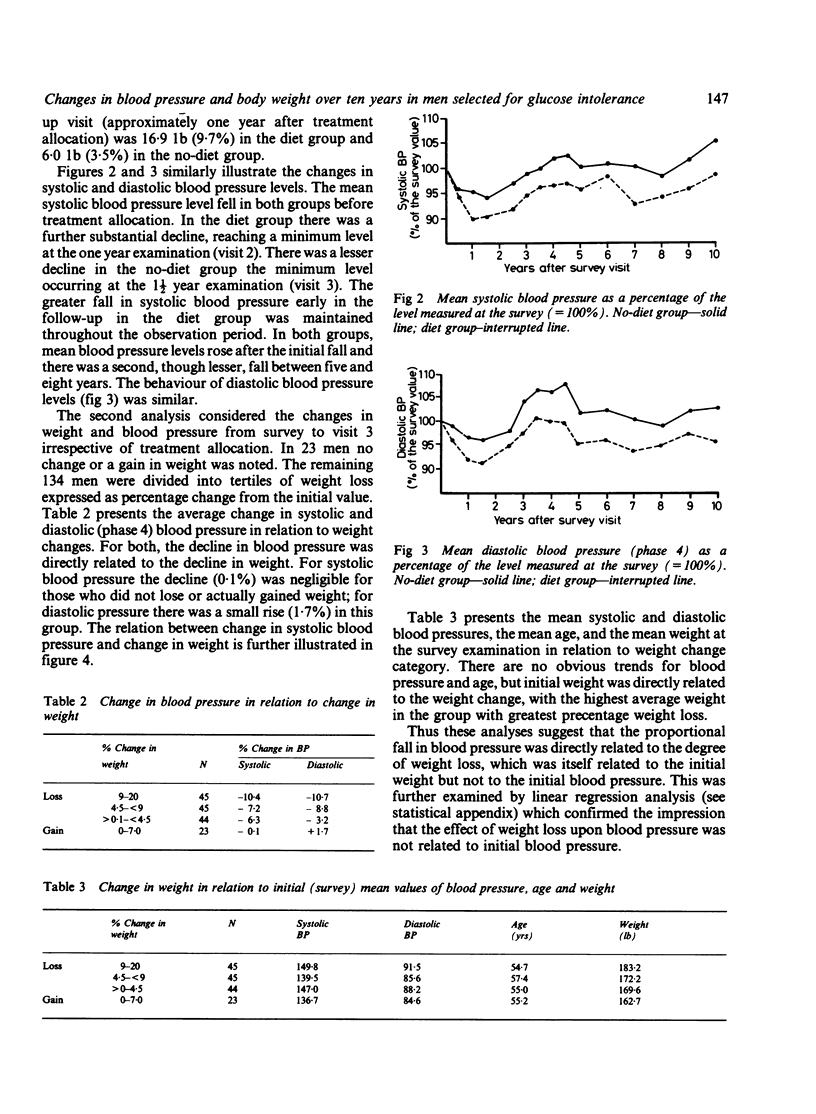
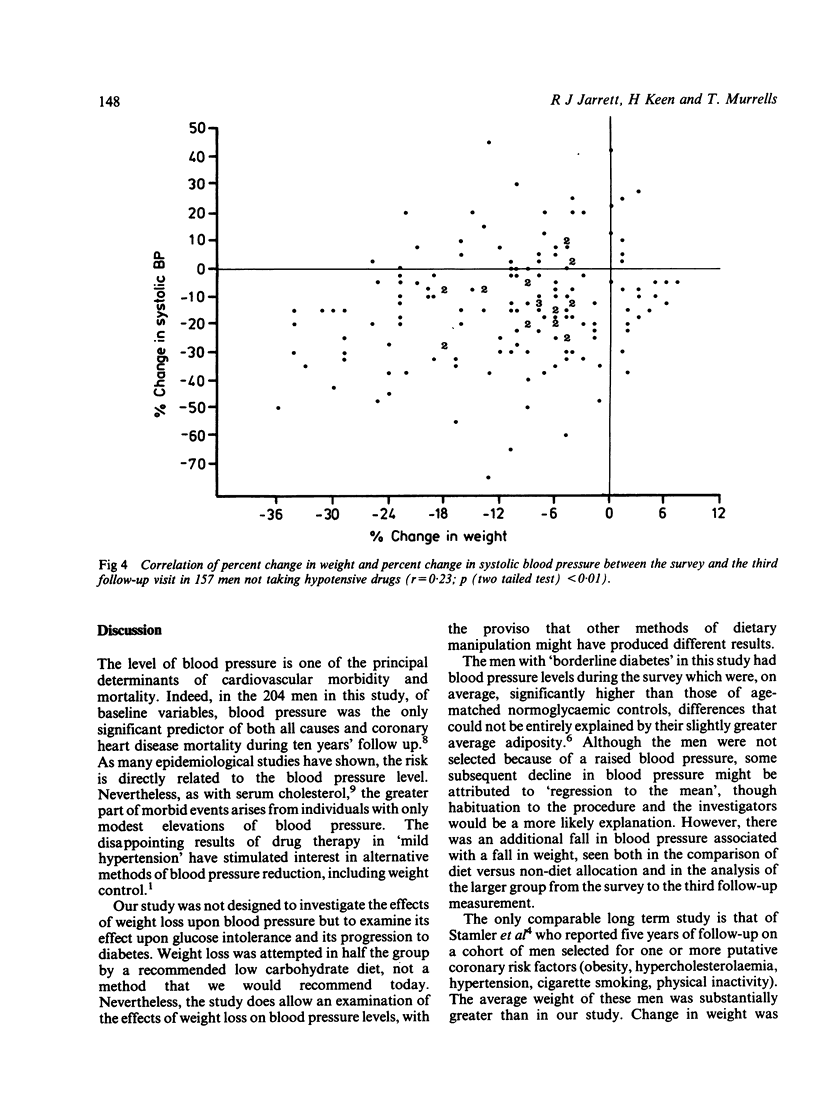
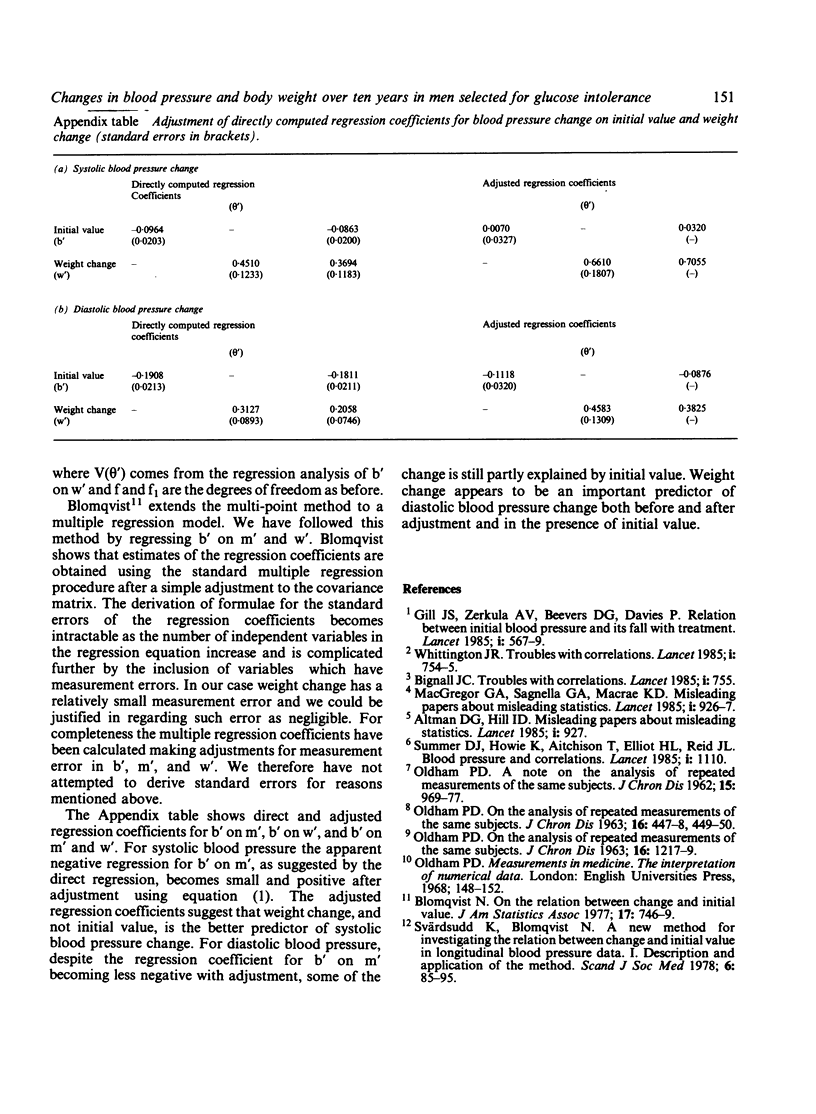
Relative changes in body weight and blood pressure over ten years of observation are reported in men recruited for a trial of therapy in relation to the natural history of glucose intolerance. Half were recommended a diet restricting carbohydrate to 120 g daily (diet group) and half were recommended to 'limit use of table sugar' (no diet). In both groups average weight and blood pressure fell over the 12 to 18 months after treatment allocation, the decline being proportionately greater for both variables in the diet group. Subsequently, average weight remained constant up to the end of the ten year study, but blood pressure levels rose, though remaining below baseline levels in the diet group. Statistical analysis of changes in blood pressure and weight between initial (pre-treatment) and third follow-up visit measurement indicated that the proportional change in blood pressure was related principally to change in weight, with little relation to initial level of blood pressure. Although a reduction in weight results in a fall in blood pressure, it does not necessarily prevent a subsequent age related increase in blood pressure.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashley F. W., Jr, Kannel W. B. Relation of weight change to changes in atherogenic traits: the Framingham Study. J Chronic Dis. 1974 Mar;27(3):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(74)90079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan P. J., Greenberg G., Miall W. E., Thompson S. G. Seasonal variation in arterial blood pressure. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Oct 2;285(6346):919–923. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6346.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. S., Zezulka A. V., Beevers D. G., Davies P. Relation between initial blood pressure and its fall with treatment. Lancet. 1985 Mar 9;1(8428):567–569. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyden S., Borhani N. O., Tyroler H. A., Schneider K. A., Langford H. G., Hames C. G., Hutchinson R., Oberman A. The relationship of weight change to changes in blood pressure, serum uric acid, cholesterol and glucose in the treatment of hypertension. J Chronic Dis. 1985;38(4):281–288. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(85)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. J., Keen H., Fuller J. H., McCartney M. Treatment of borderline diabetes: controlled trial using carbohydrate restriction and phenformin. Br Med J. 1977 Oct 1;2(6091):861–865. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6091.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. J., Keen H., McCartney M., Fuller J. H., Hamilton P. J., Reid D. D., Rose G. Glucose tolerance and blood pressure in two population samples: their relation to diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Int J Epidemiol. 1978 Mar;7(1):15–24. doi: 10.1093/ije/7.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. J., Keen H., McCartney P. The Whitehall Study: ten year follow-up report on men with impaired glucose tolerance with reference to worsening to diabetes and predictors of death. Diabet Med. 1984 Nov;1(4):279–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1984.tb01973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misleading paper about misleading statistics. Lancet. 1985 Apr 20;1(8434):926–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLDHAM P. D. A note on the analysis of repeated measurements of the same subjects. J Chronic Dis. 1962 Oct;15:969–977. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(62)90116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preferential efficacy of cyclosporin? Lancet. 1985 Mar 30;1(8431):755–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay L. E., Ramsay M. H., Hettiarachchi J., Davies D. L., Winchester J. Weight reduction in a blood pressure clinic. Br Med J. 1978 Jul 22;2(6132):244–245. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6132.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid D. D., Brett G. Z., Hamilton P. J., Jarrett R. J., Keen H., Rose G. Cardiorespiratory disease and diabetes among middle-aged male Civil Servants. A study of screening and intervention. Lancet. 1974 Mar 23;1(7856):469–473. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92783-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisin E., Abel R., Modan M., Silverberg D. S., Eliahou H. E., Modan B. Effect of weight loss without salt restriction on the reduction of blood pressure in overweight hypertensive patients. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jan 5;298(1):1–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197801052980101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose G., Shipley M. Plasma cholesterol concentration and death from coronary heart disease: 10 year results of the Whitehall study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Aug 2;293(6542):306–307. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6542.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowers J. R., Whitfield L. A., Catania R. A., Stern N., Tuck M. L., Dornfeld L., Maxwell M. Role of the sympathetic nervous system in blood pressure maintenance in obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Jun;54(6):1181–1186. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-6-1181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamler J., Farinaro E., Mojonnier L. M., Hall Y., Moss D., Stamler R. Prevention and control of hypertension by nutritional-hygienic means. Long-term experience of the Chicago Coronary Prevention Evaluation Program. JAMA. 1980 May 9;243(18):1819–1823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner D. J., Howie K., Aitchison T., Elliott H. L., Reid J. L. Blood pressure and correlations. Lancet. 1985 May 11;1(8437):1110–1111. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92419-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svärdsudd K., Blomqvist N. A new method for investigating the relation between change and initial value in longitudinal blood pressure data. I. Description and application of the method. Scand J Soc Med. 1978;6(2):85–95. doi: 10.1177/140349487800600207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt G. C., Edwards C., Hart J. T., Hart M., Walton P., Foy C. J. Dietary sodium restriction for mild hypertension in general practice. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Feb 5;286(6363):432–436. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6363.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


