Abstract
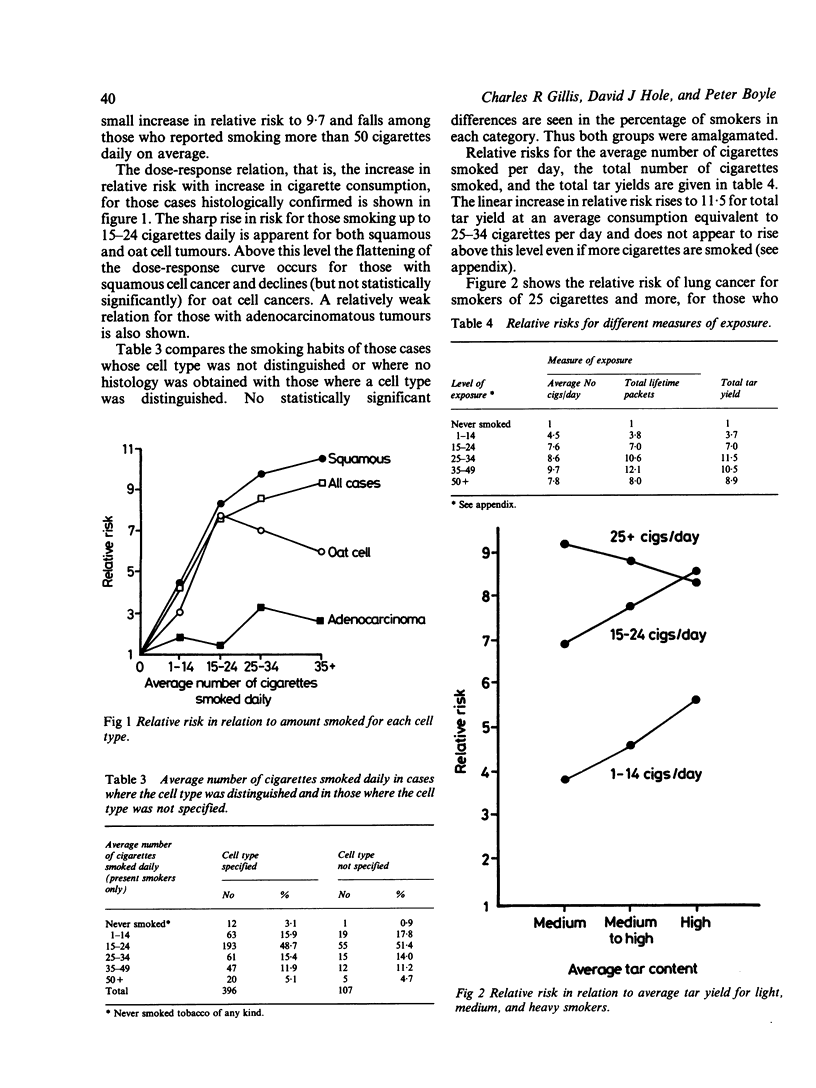
Altogether 656 male lung cancer cases and 1312 age and sex matched controls were interviewed between 1976 and 1981 in a case-control study of cigarette smoking habits and lung cancer in Glasgow and the West of Scotland, an area with the highest recorded incidence in the world. The relative risk of lung cancer increased significantly for smokers whose consumption was below 20 cigarettes per day but did not rise significantly in those who smoked more than 20 cigarettes per day. Other smoking characteristics such as inhalation and tar yields of brands smoked did not explain this finding. Additionally, the relative risks observed at all levels of cigarette consumption were low in comparison with those in the published literature. By constructing an index of cigarette exposure which included the tar yields of brands smoked, an assessment of the risk of lung cancer in relation to tar exposure independent of amount smoked was derived. Only in smokers of less than 15 cigarettes per day was there a statistically significant reduction in risk of lung cancer associated with lower levels of tar yield.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breslow N. E., Day N. E., Halvorsen K. T., Prentice R. L., Sabai C. Estimation of multiple relative risk functions in matched case-control studies. Am J Epidemiol. 1978 Oct;108(4):299–307. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLL R., HILL A. B. A study of the aetiology of carcinoma of the lung. Br Med J. 1952 Dec 13;2(4797):1271–1286. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4797.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLL R., HILL A. B., KREYBERG L. The significance of cell type in relation to the aetiology of lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 1957 Mar;11(1):43–48. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1957.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doll R., Peto R. Mortality in relation to smoking: 20 years' observations on male British doctors. Br Med J. 1976 Dec 25;2(6051):1525–1536. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6051.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis C. R., Hole D. J., Hawthorne V. M. Cigarette smoking and male lung cancer in an area of very high incidence. II. Report of a general population cohort study in the West of Scotland. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1988 Mar;42(1):44–48. doi: 10.1136/jech.42.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald N., Doll R., Copeland G. Trends in tar, nicotine, and carbon monoxide yields of UK cigarettes manufactured since 1934. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Mar 7;282(6266):763–765. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6266.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss W., Boucot K. R., Seidman H., Carnahan W. J. Risk of lung cancer according to histologic type and cigarette dosage. JAMA. 1972 Nov 13;222(7):799–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynder E. L., Stellman S. D. Comparative epidemiology of tobacco-related cancers. Cancer Res. 1977 Dec;37(12):4608–4622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


