Abstract
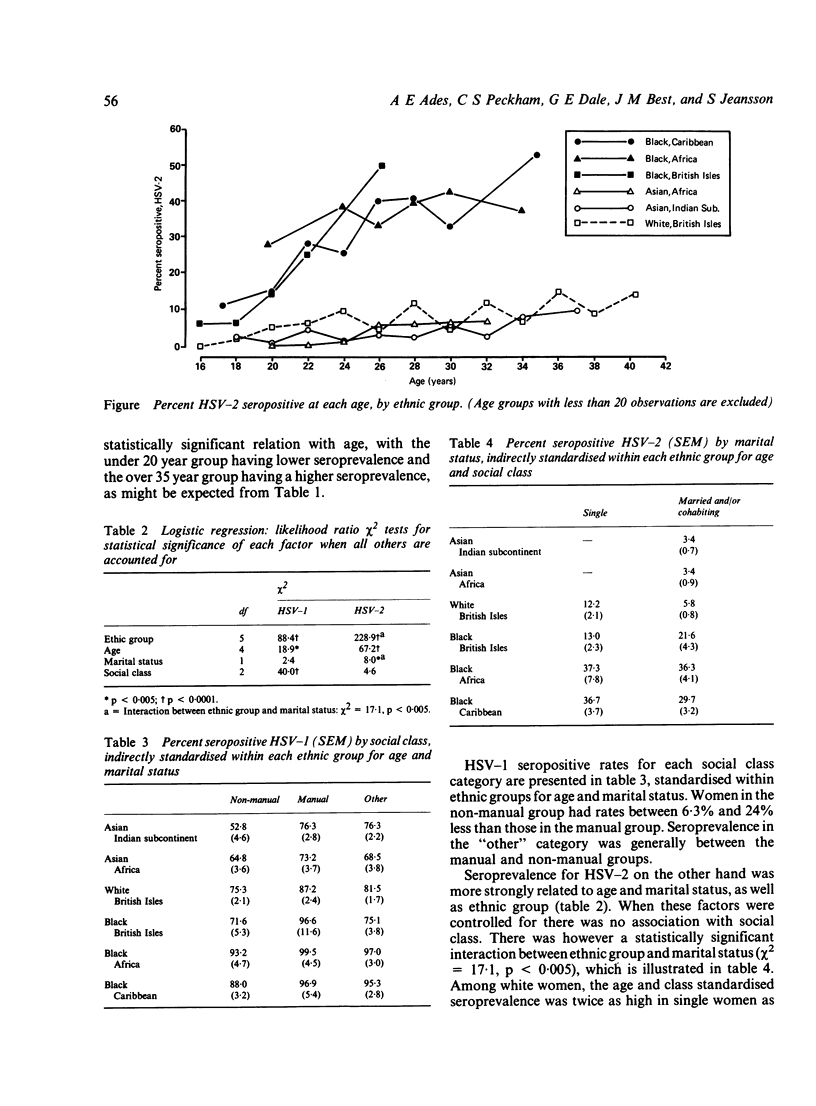
There has been a recent increase in notifications of genital herpes but it is not known whether this has been reflected in the pregnant population. We have therefore carried out a study to determine the prevalence of herpes simplex antibodies in pregnant women and to estimate the incidence of primary infection. Sera were collected from 3533 women at antenatal clinics and tested for total antibodies to herpes simples virus (HSV), and if positive, for specific antibodies to HSV-2. Estimates of HSV-1 seroprevalence were derived from the HSV-2 seronegative population. HSV-1 seroprevalence was nearly 100% in black women born in Africa or the Caribbean and 60-80% in white, Asian and UK born black women. It was lower in women in non-manual employment. HSV-2 seroprevalence was related to age, rising from 0 at age 16 to 40% at age 35 in black women, and to about 10% in Asian and white women. The estimated incidence of primary HSV-2 infection during pregnancy, per 1000 pregnancies, was about 2.4 in Asian women, 5 in white women, and 20 in black women. Estimates of the incidence of neonatal infection were derived from these figures and compared to the nationally reported rates.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam E., Kaufman R. H., Melnick J. L., Levy A. H., Rawls W. E. Seroepidemiologic studies of herpesvirus type 2 and carcinoma of the cervix. 3. Houston, Texas. Am J Epidemiol. 1972 Dec;96(6):427–442. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Committee on fetus and newborn. Committee on infectious diseases. Perinatal herpes simplex virus infections. Pediatrics. 1980 Jul;66(1):147–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. M., May R. M. Vaccination against rubella and measles: quantitative investigations of different policies. J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Apr;90(2):259–325. doi: 10.1017/s002217240002893x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey L., Spear P. G. Infections with herpes simplex viruses (1). N Engl J Med. 1986 Mar 13;314(11):686–691. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198603133141105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham S., Rawls W., Swanson M., McCurtis J. Sex partners and herpes simplex virus type 2 in the epidemiology of cancer of the cervix. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 May;115(5):729–735. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenfell B. T., Anderson R. M. The estimation of age-related rates of infection from case notifications and serological data. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Oct;95(2):419–436. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400062859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindley D. J., Adler M. W. Genital herpes: an increasing problem? Genitourin Med. 1985 Feb;61(1):56–58. doi: 10.1136/sti.61.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeansson S., Forsgren M., Svennerholm B. Evaluation of solubilized herpes simplex virus membrane antigen by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1160–1166. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1160-1166.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClung H., Seth P., Rawls W. E. Relative concentrations in human sera of antibodies to cross-reacting and specific antigens of Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Am J Epidemiol. 1976 Aug;104(2):192–201. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald A. D., Williams M. C., West R., Stewart J. Neutralizing antibodies to herpesvirus types 1 and 2 in Montreal women. Am J Epidemiol. 1974 Aug;100(2):124–129. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. E., Coleman R. M., Best J. M., Benetato B. B., Nahmias A. J. Persistence of serum IgA antibodies to herpes simplex, varicella-zoster, cytomegalovirus, and rubella virus detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. J Med Virol. 1985 Aug;16(4):343–349. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890160407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Alford C. A., Korones S. B. Infection of the newborn with herpesvirus hominis. Adv Pediatr. 1970;17:185–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Josey W. E., Naib Z. M., Freeman M. G., Fernandez R. J., Wheeler J. H. Perinatal risk associated with maternal genital herpes simplex virus infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1971 Jul 15;110(6):825–837. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(71)90580-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Josey W. E., Naib Z. M., Luce C. F., Duffey A. Antibodies to Herpesvirus hominis types 1 and 2 in humans. I. Patients with genital herpetic infections. Am J Epidemiol. 1970 Jun;91(6):539–546. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Roizman B. Infection with herpes-simplex viruses 1 and 2. 1. N Engl J Med. 1973 Sep 27;289(13):667–674. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197309272891305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papoz L., Simondon F., Saurin W., Sarmini H. A simple model relevant to toxoplasmosis applied to epidemiologic results in France. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Jan;123(1):154–161. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peckham C. S., Chin K. S., Coleman J. C., Henderson K., Hurley R., Preece P. M. Cytomegalovirus infection in pregnancy: preliminary findings from a prospective study. Lancet. 1983 Jun 18;1(8338):1352–1355. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92138-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prober C. G., Hensleigh P. A., Boucher F. D., Yasukawa L. L., Au D. S., Arvin A. M. Use of routine viral cultures at delivery to identify neonates exposed to herpes simplex virus. N Engl J Med. 1988 Apr 7;318(14):887–891. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198804073181404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prober C. G., Sullender W. M., Yasukawa L. L., Au D. S., Yeager A. S., Arvin A. M. Low risk of herpes simplex virus infections in neonates exposed to the virus at the time of vaginal delivery to mothers with recurrent genital herpes simplex virus infections. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jan 29;316(5):240–244. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198701293160503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I. W., Peutherer J. F., MacCallum F. O. The incidence of Herpesvirus hominis antibody in the population. J Hyg (Lond) 1967 Sep;65(3):395–408. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400045915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavraky K. M., Rawls W. E., Chiavetta J., Donner A. P., Wanklin J. M. Sexual and socioeconomic factors affecting the risk of past infections with herpes simplex virus type 2. Am J Epidemiol. 1983 Jul;118(1):109–121. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm B., Olofsson S., Jeansson S., Vahlne A., Lycke E. Herpes simplex virus type-selective enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with Helix pomatia lectin-purified antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):235–239. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.235-239.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wacholder S. Binomial regression in GLIM: estimating risk ratios and risk differences. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Jan;123(1):174–184. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., Alexander E. R. Seroepidemiology of infectious due to members of the herpesvirus group. Am J Epidemiol. 1971 Nov;94(5):496–507. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley R. J., Nahmias A. J., Visintine A. M., Fleming C. L., Alford C. A. The natural history of herpes simplex virus infection of mother and newborn. Pediatrics. 1980 Oct;66(4):489–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeager A. S., Arvin A. M. Reasons for the absence of a history of recurrent genital infections in mothers of neonates infected with herpes simplex virus. Pediatrics. 1984 Feb;73(2):188–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeager A. S., Arvin A. M., Urbani L. J., Kemp J. A., 3rd Relationship of antibody to outcome in neonatal herpes simplex virus infections. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):532–538. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.532-538.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


