Abstract
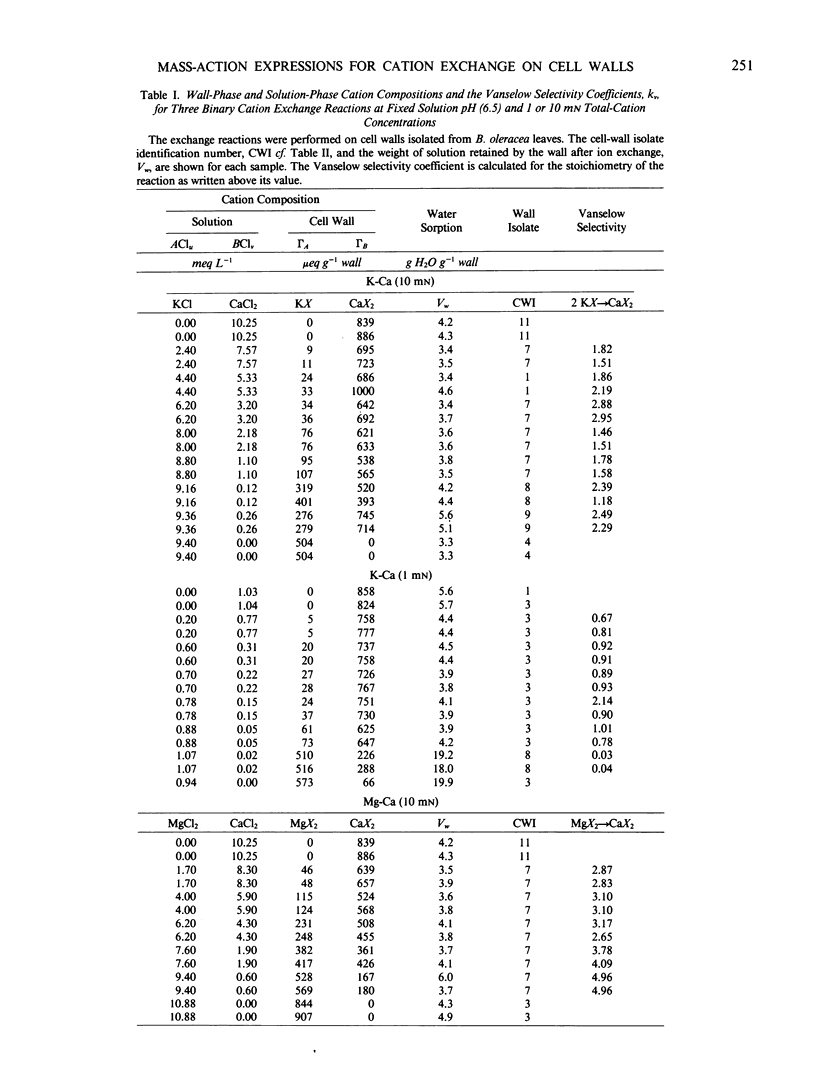
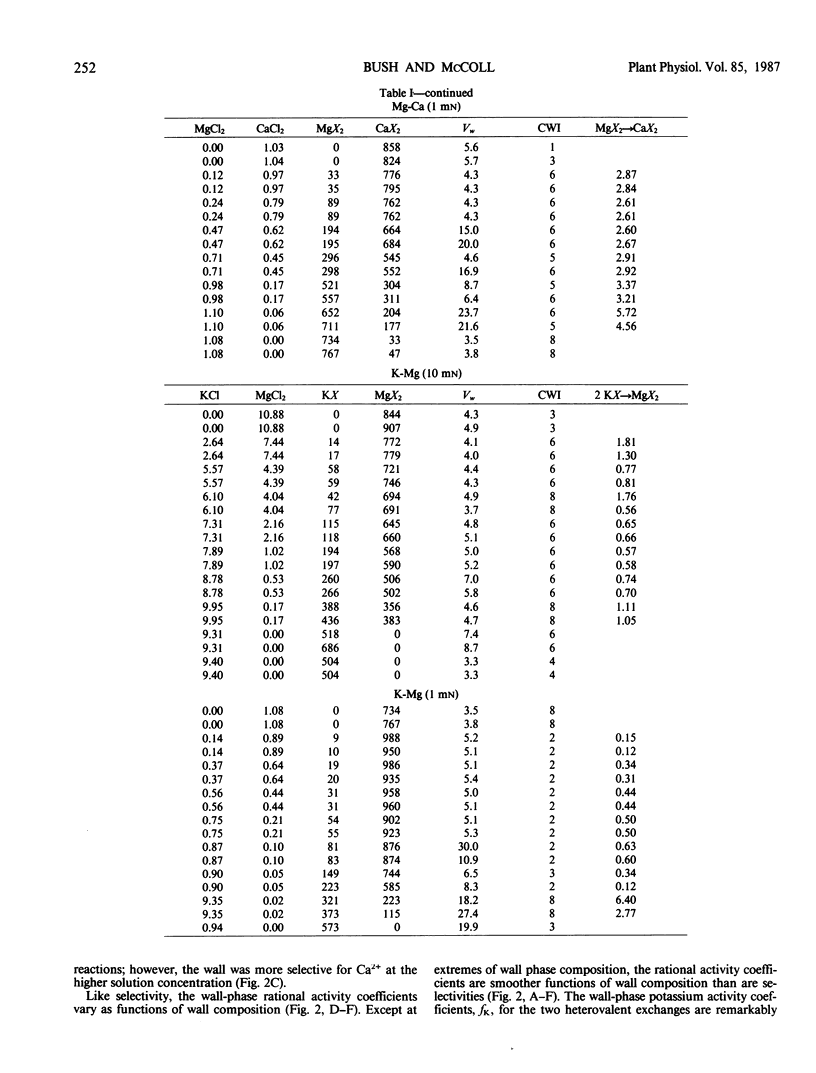
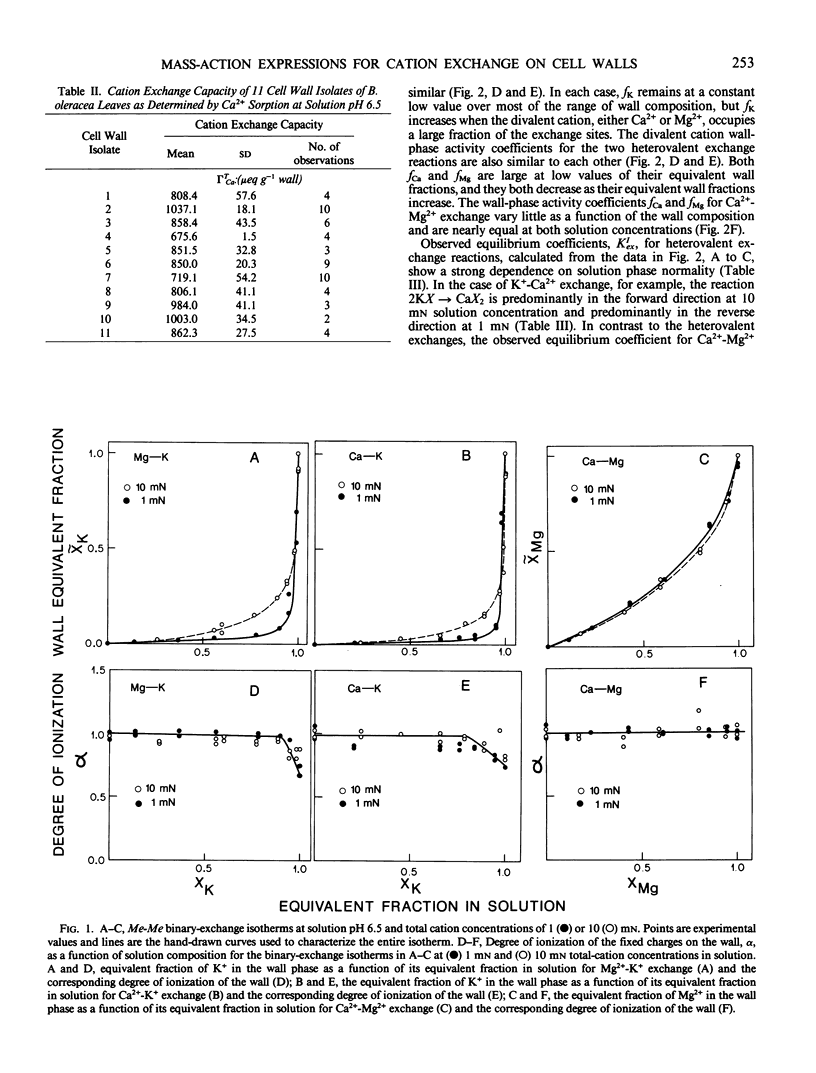
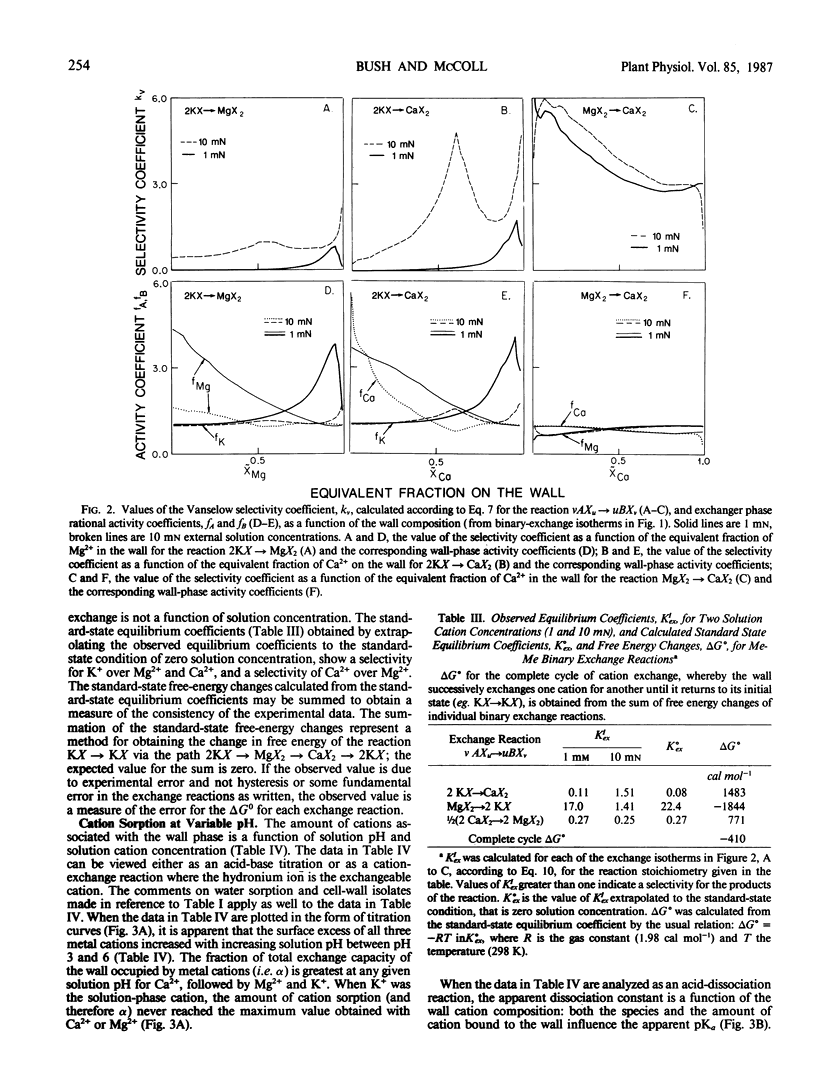
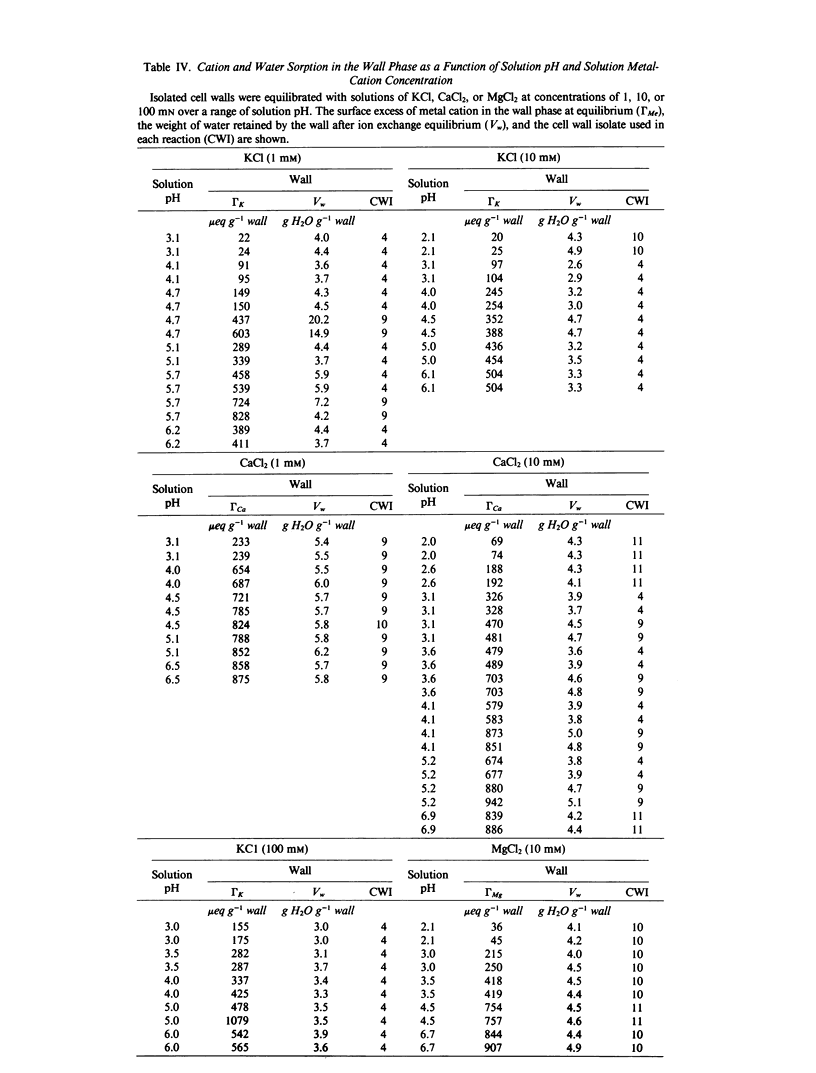
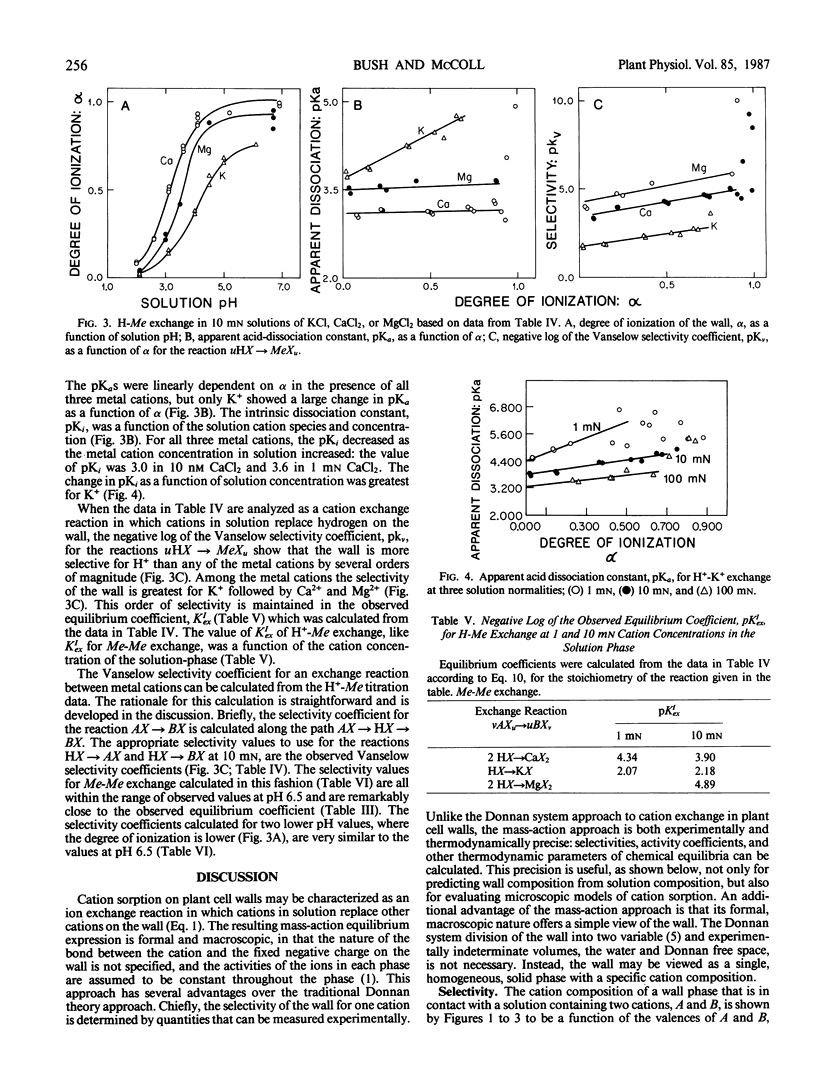
The cation exchange properties of cell walls isolated from collard (Bassica oleracea var acephala D.C.) leaves were investigated. Cation sorption on cell walls was described by mass-action expressions of ion exchange, rather than by the traditional Donnan equilibrium. The mass-action expressions enable the selectivity of the wall for one cation over another to be determined unambiguously from ion exchange isotherms. We found that: (a) the cation composition of the wall varied as a function of the solution cation concentration, solution cation composition, and pH in a way predicted by mass action; (b) the affinity of the wall for divalent cations increased as the equivalent fraction of divalent cation on the wall increased, and as the concentration of divalent cations in solution increased; (c) the selectivity of the wall for any metal cation pair was not altered by the concentration of H+ in solution or on the wall; (d) H+ sorption on the wall may be treated as a cation exchange reaction making it possible to calculate the relative affinity of the wall for metal cation pairs from H+-metal (Me) titration curves; and (e) the relative affinity of the wall for the cations we studied was: H+ ≫ (K+ ≥ Ca2+) > Mg2+. A cation-exchange model including surface complexes is consistent with observed cation selectivity. We conclude that metal cations interact with the wall to minimize or eliminate long-range electrostatic interactions and suggest that this may be due to the formation of site-specific cation-wall surface complexes.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Demarty M., Morvan C., Thellier M. Exchange Properties of Isolated Cell Walls of Lemna minor L. Plant Physiol. 1978 Oct;62(4):477–481. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.4.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentenac H., Grignon C. A model for predicting ionic equilibrium concentrations in cell walls. Plant Physiol. 1981 Aug;68(2):415–419. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge K. W., Keegstra K., Bauer W. D., Albersheim P. The Structure of Plant Cell Walls: I. The Macromolecular Components of the Walls of Suspension-cultured Sycamore Cells with a Detailed Analysis of the Pectic Polysaccharides. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):158–173. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


