Abstract
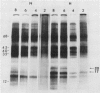
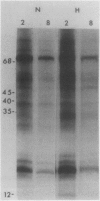
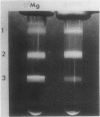
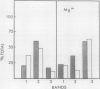
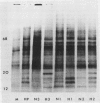
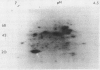
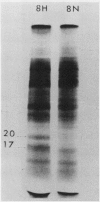
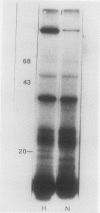
Brassica napus suspension-cultured cells can be hardened to a lethal temperature for 50% of the sample of −20°C in eight days at room temperature with abscisic acid. During the induction of freezing tolerance, changes were observed in the electrophoretic pattern of [35S]methionine labeled polypeptides. In hardening cells, a 20 kilodalton polypeptide was induced on day 2 and its level increased during hardening. The induction of freezing tolerance with nonmaximal hardening regimens also resulted in increases in the 20 kilodalton polypeptide. The 20 kilodalton polypeptide was associated with a membrane fraction enriched in endoplasmic reticulum and was resolved as a single spot by two-dimensional electrophoresis. In vitro translation of mRNA indicate alteration of gene expression during abscisic acid induction of freezing tolerance. The new mRNA encodes a 20 kilodalton polypeptide associated with increased freezing tolerance induced by either abscisic acid or high sucrose. A 20 kilodalton polypeptide was also translated by mRNA isolated from cold-hardened B. napus plants.
Full text
PDF

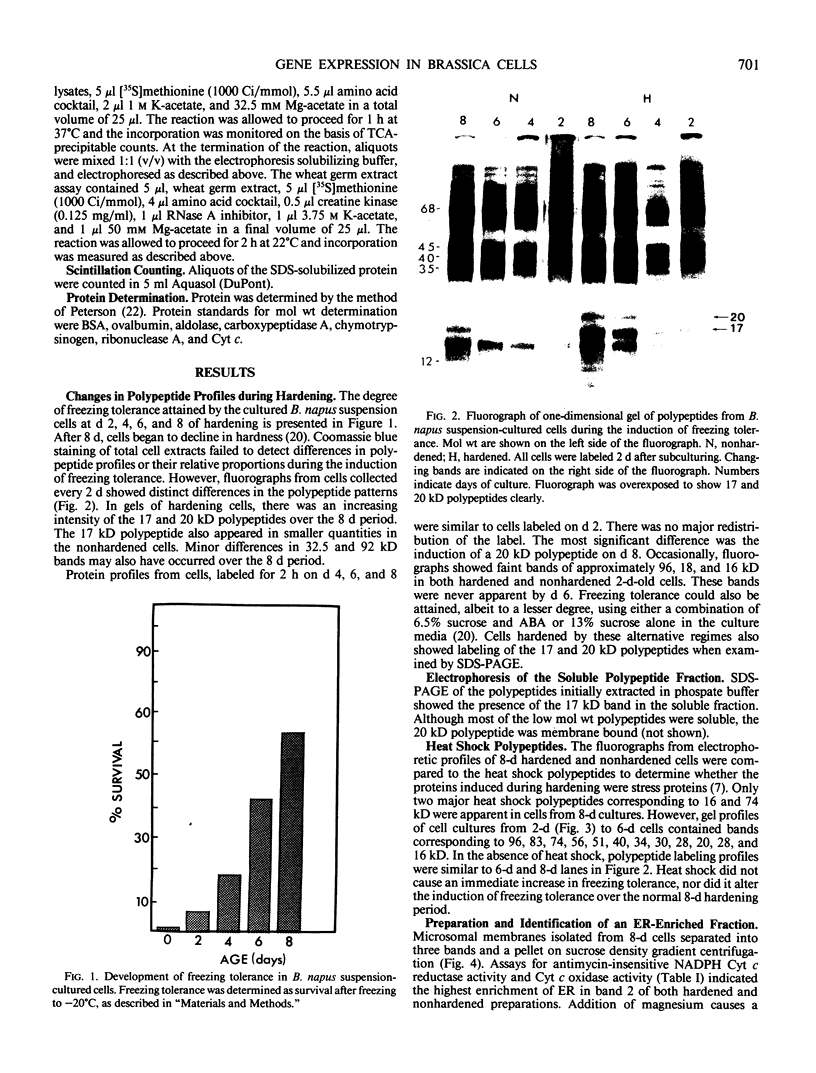
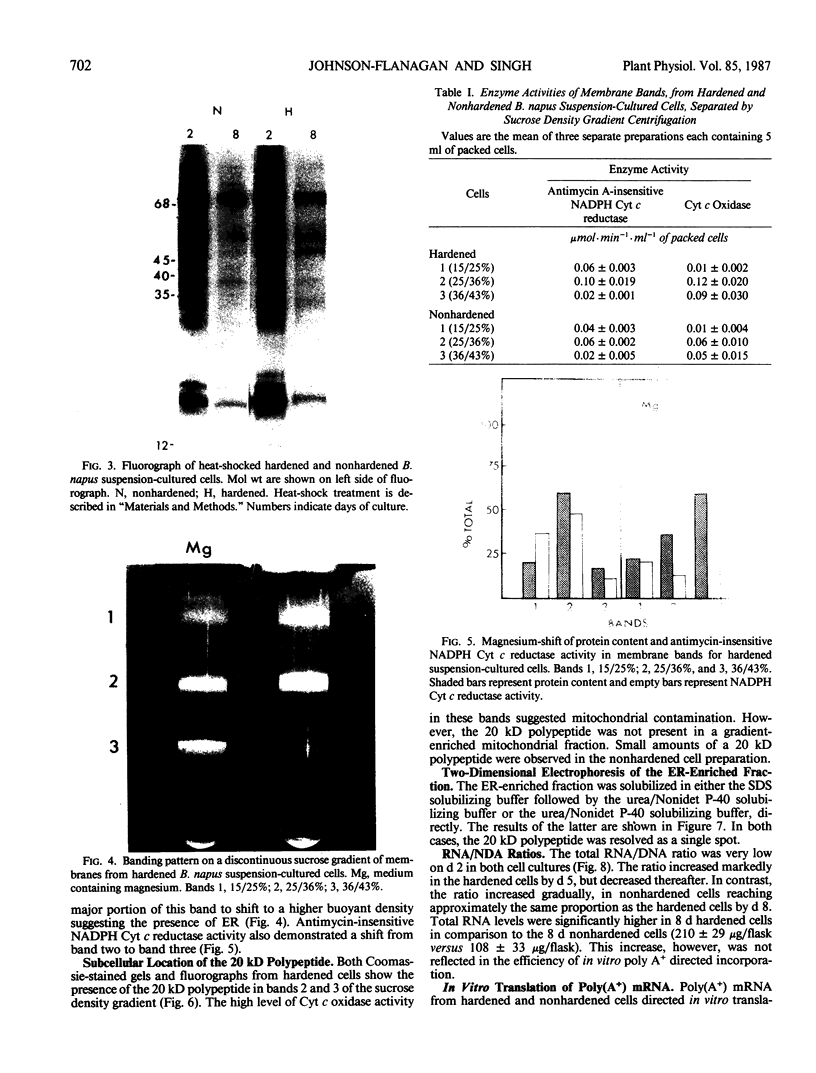
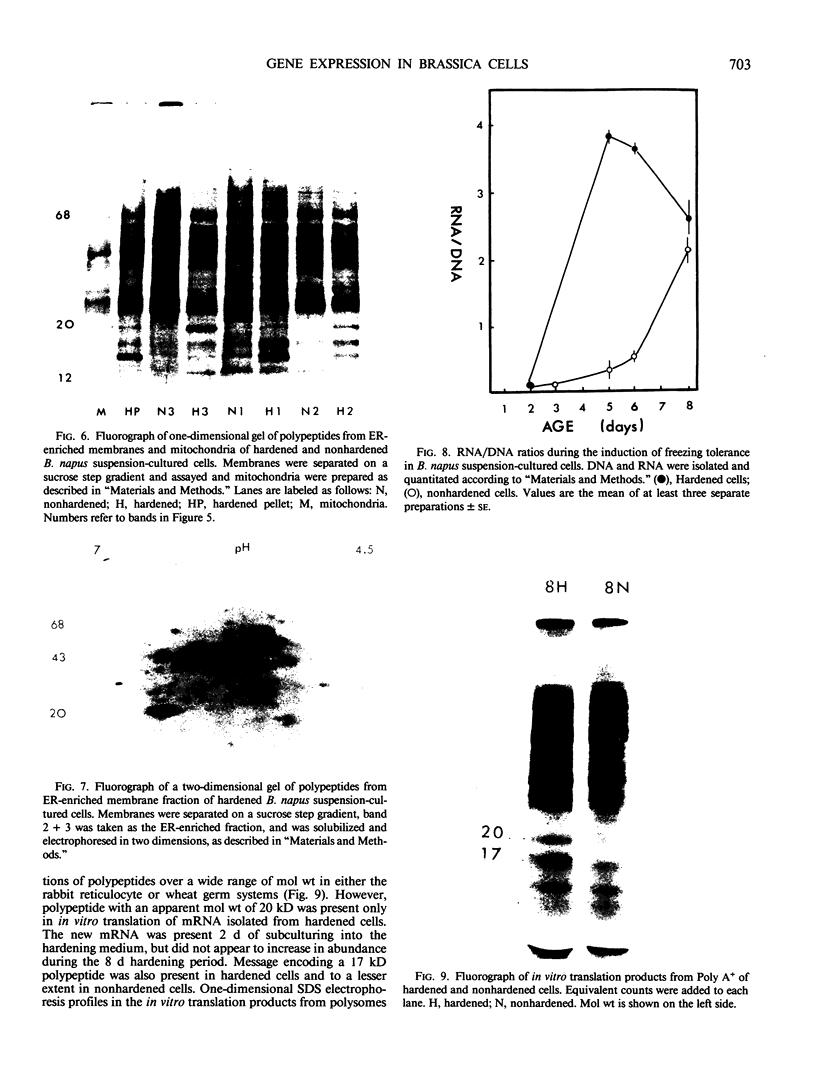
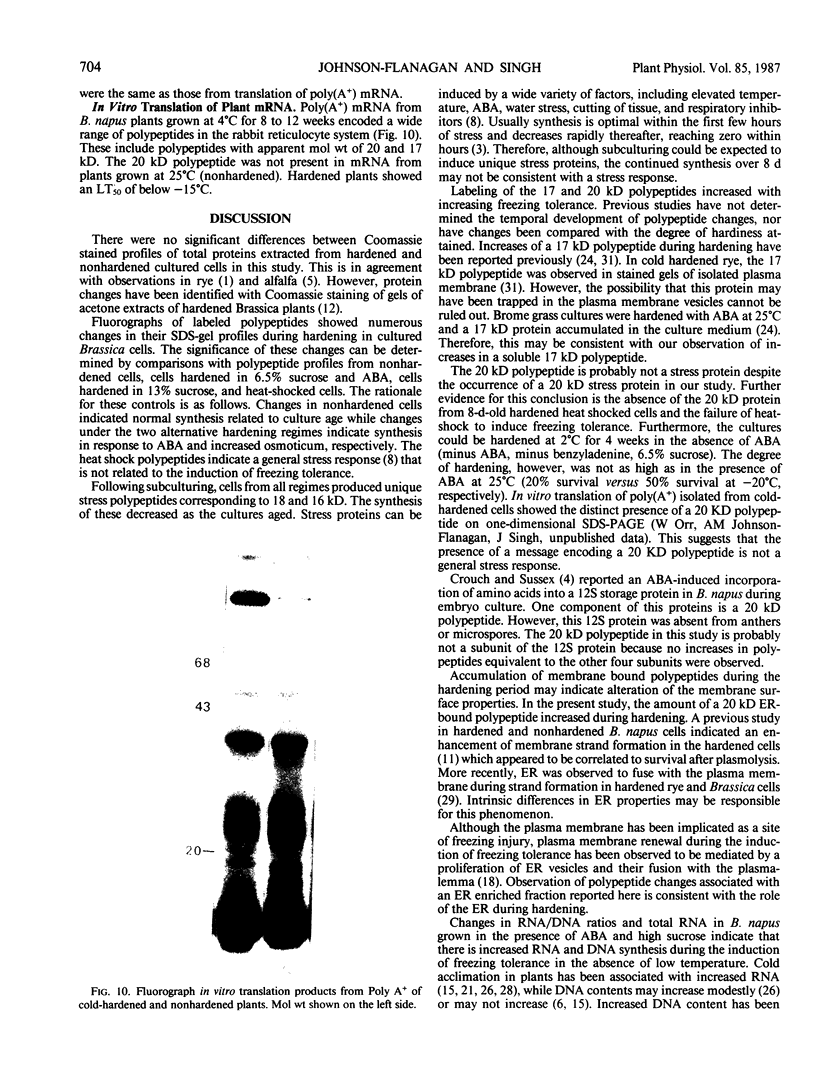

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cloutier Y. Changes in the Electrophoretic Patterns of the Soluble Proteins of Winter Wheat and Rye following Cold Acclimation and Desiccation Stress. Plant Physiol. 1983 Feb;71(2):400–403. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.2.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbert J. T., Hershey H. P., Quail P. H. Autoregulatory control of translatable phytochrome mRNA levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2248–2252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P., Ho T. H. Heat shock proteins in maize. Plant Physiol. 1983 Feb;71(2):215–222. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faw W. F., Shih S. C., Jung G. A. Extractant Influence on the Relationship between Extractable Proteins and Cold Tolerance of Alfalfa. Plant Physiol. 1976 May;57(5):720–723. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.5.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusta L. V., Weiser C. J. Nucleic Acid and protein changes in relation to cold acclimation and freezing injury of korean boxwood leaves. Plant Physiol. 1972 Jan;49(1):91–96. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy C. L., Niemi K. J., Brambl R. Altered gene expression during cold acclimation of spinach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3673–3677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila J. J., Papp J. E., Schultz G. A., Bewley J. D. Induction of heat shock protein messenger RNA in maize mesocotyls by water stress, abscisic Acid, and wounding. Plant Physiol. 1984 Sep;76(1):270–274. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.1.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Leonard R. T. Purification of a plasma membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase from plant roots. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:392–406. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson-Flanagan A. M., Spencer M. S. The effect of rotenone on respiration in pea cotyledon mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1981 Dec;68(6):1211–1217. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.6.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meza-Basso L., Alberdi M., Raynal M., Ferrero-Cadinanos M. L., Delseny M. Changes in Protein Synthesis in Rapeseed (Brassica napus) Seedlings during a Low Temperature Treatment. Plant Physiol. 1986 Nov;82(3):733–738. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.3.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. M. Auxin-binding Sites of Maize Coleoptiles Are Localized on Membranes of the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Plant Physiol. 1977 Apr;59(4):594–599. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.4.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarhan F., Chevrier N. Regulation of RNA Synthesis by DNA-Dependent RNA Polymerases and RNases during Cold Acclimation in Winter and Spring Wheat. Plant Physiol. 1985 Jun;78(2):250–255. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.2.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siminovitch D., Rheaume B., Pomeroy K., Lepage M. Phospholipid, protein, and nucleic acid increases in protoplasm and membrane structures associated with development of extreme freezing resistance in black locust tree cells. Cryobiology. 1968 Nov-Dec;5(3):202–225. doi: 10.1016/s0011-2240(68)80164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura M., Yoshida S. Involvement of Plasma Membrane Alterations in Cold Acclimation of Winter Rye Seedlings (Secale cereale L. cv Puma). Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):818–826. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma D. P., Marcus A. Activation of Protein Synthesis upon Dilution of an Arachis Cell Culture from the Stationary Phase. Plant Physiol. 1974 Jan;53(1):83–87. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widholm J. M. The use of fluorescein diacetate and phenosafranine for determining viability of cultured plant cells. Stain Technol. 1972 Jul;47(4):189–194. doi: 10.3109/10520297209116483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]