Abstract
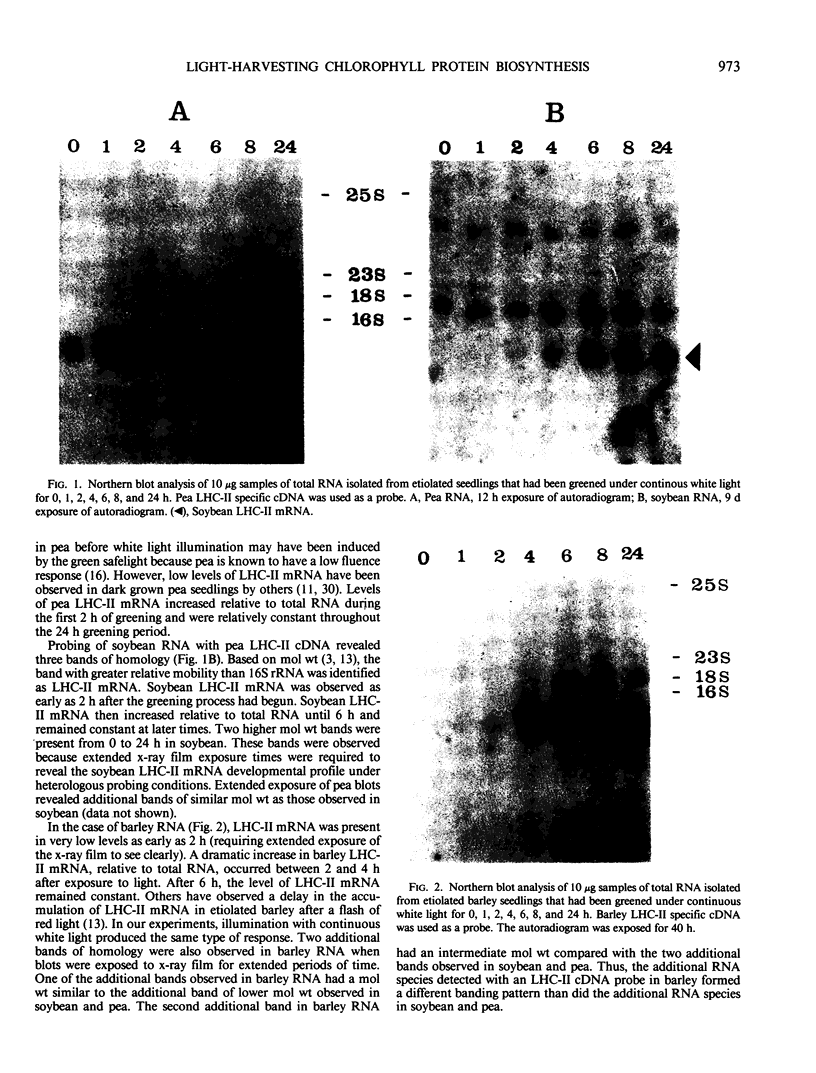
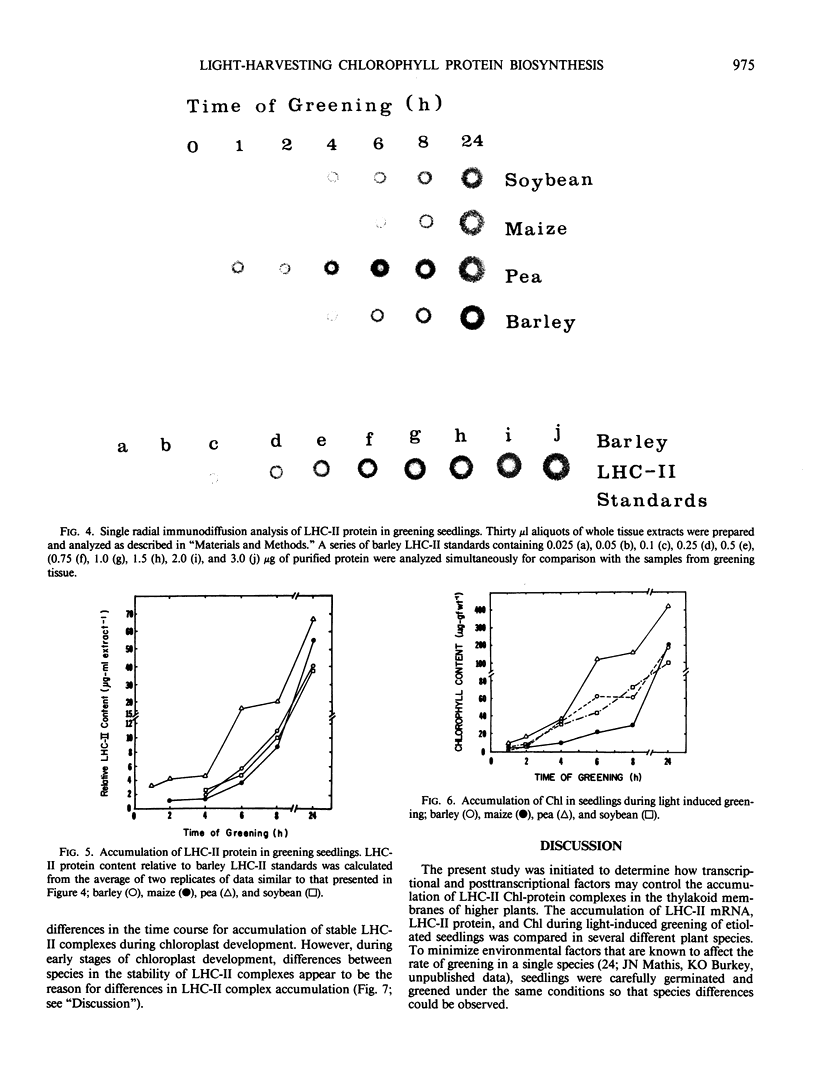
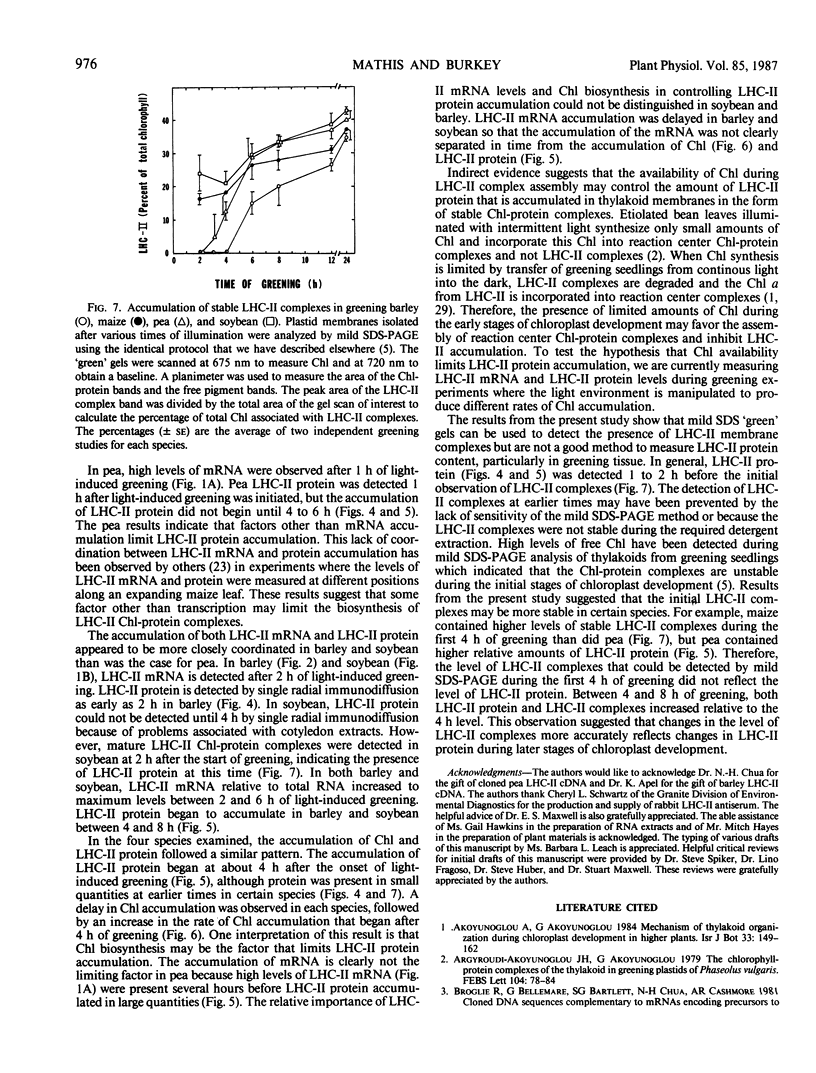
The biosynthesis of the chlorophyll a/b binding protein associated with photosystem II (LHC-II) was characterized during light-induced greening of etiolated barley (Hordeum vulgare [L.] cv Boone), maize (Zea mays [L.] Pioneer 3148), pea (Pisum sativum [L.] cv Progress 9), and soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr. cv Ransom 2). Northern blot analysis revealed that pea LHC-II mRNA was present in dark-grown seedlings and accumulated rapidly within 1 hour following illumination with white light. In contrast, the accumulation of LHC-II mRNA was delayed in barley and soybean until 2 to 4 hours after illumination began. Single radial immunodiffusion analysis revealed that LHC-II polypeptides began to accumulate in all species between 4 and 8 hours although the protein was present in detectable levels at earlier times in certain species. In a pattern similar to the LHC-II protein accumulation, chlorophyll accumulated at increased rates between 4 and 8 hours of greening in all species following an initial delay. The absence of coordination between LHC-II mRNA and LHC-II protein accumulation that was clearly observed in pea suggested that transcription is not the factor that limits LHC-II complex formation during chloroplast development. The accumulation of chlorophyll and LHC-II protein appeared to coincide suggesting that chlorophyll biosynthesis may be a factor that limits LHC-II complex formation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Camm E. L., Green B. R. Fractionation of Thylakoid Membranes with the Nonionic Detergent Octyl-beta-d-glucopyranoside: RESOLUTION OF CHLOROPHYLL-PROTEIN COMPLEX II INTO TWO CHLOROPHYLL-PROTEIN COMPLEXES. Plant Physiol. 1980 Sep;66(3):428–432. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.3.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashmore A. R. Structure and expression of a pea nuclear gene encoding a chlorophyll a/b-binding polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):2960–2964. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.2960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Werner-Washburne M., Lubben T. H., Keegstra K. Precursors to two nuclear-encoded chloroplast proteins bind to the outer envelope membrane before being imported into chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3691–3696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coruzzi G., Broglie R., Cashmore A., Chua N. H. Nucleotide sequences of two pea cDNA clones encoding the small subunit of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and the major chlorophyll a/b-binding thylakoid polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1399–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuming A. C., Bennett J. Biosynthesis of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein. Control of messenger RNA activity by light. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(1):71–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunsmuir P., Smith S. M., Bedbrook J. The major chlorophyll a/b binding protein of petunia is composed of several polypeptides encoded by a number of distinct nuclear genes. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(3):285–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollmer I., Apel K. The phytochrome-controlled accumulation of mRNA sequences encoding the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 15;133(2):309–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07463.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. R., Bartlett S. G., Schmidt G. W., Mullet J. E., Chua N. H. Optimal conditions for post-translational uptake of proteins by isolated chloroplasts. In vitro synthesis and transport of plastocyanin, ferredoxin-NADP+ oxidoreductase, and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1558–1563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin-Neumann G. A., Kohorn B. D., Thornber J. P., Tobin E. M. A chlorophyll a/b-protein encoded by a gene containing an intron with characteristics of a transposable element. J Mol Appl Genet. 1985;3(1):45–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L. S., Thompson W. F., Briggs W. R. Different Red Light Requirements for Phytochrome-Induced Accumulation of cab RNA and rbcS RNA. Science. 1984 Dec 21;226(4681):1447–1449. doi: 10.1126/science.226.4681.1447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchanski S. J., Park R. B. Comparative Studies of the Thylakoid Proteins of Mesophyll and Bundle Sheath Plastids of Zea mays. Plant Physiol. 1976 Sep;58(3):345–349. doi: 10.1104/pp.58.3.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupa Z., Huner N. P., Williams J. P., Maissan E., James D. R. Development at Cold-Hardening Temperatures : The Structure and Composition of Purified Rye Light Harvesting Complex II. Plant Physiol. 1987 May;84(1):19–24. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martineau B., Taylor W. C. Photosynthetic gene expression and cellular differentiation in developing maize leaves. Plant Physiol. 1985 Jun;78(2):399–404. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.2.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. A., Zalik S. Effect of Light Quality, Light Intensity and Temperature on Pigment Accumulation in Barley Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1965 May;40(3):569–574. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran R. Formulae for determination of chlorophyllous pigments extracted with n,n-dimethylformamide. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jun;69(6):1376–1381. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.6.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V. Rapid and simple removal of contaminating RNA from plasmid DNA without the use of RNase. Anal Biochem. 1981 May 1;113(1):34–42. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichersky E., Bernatzky R., Tanksley S. D., Breidenbach R. B., Kausch A. P., Cashmore A. R. Molecular characterization and genetic mapping of two clusters of genes encoding chlorophyll a/b-binding proteins in Lycopersicon esculentum (tomato). Gene. 1985;40(2-3):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang R., Lis J., Wu R. Elution of DNA from agarose gels after electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:176–182. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]