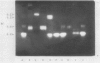
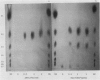
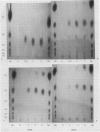
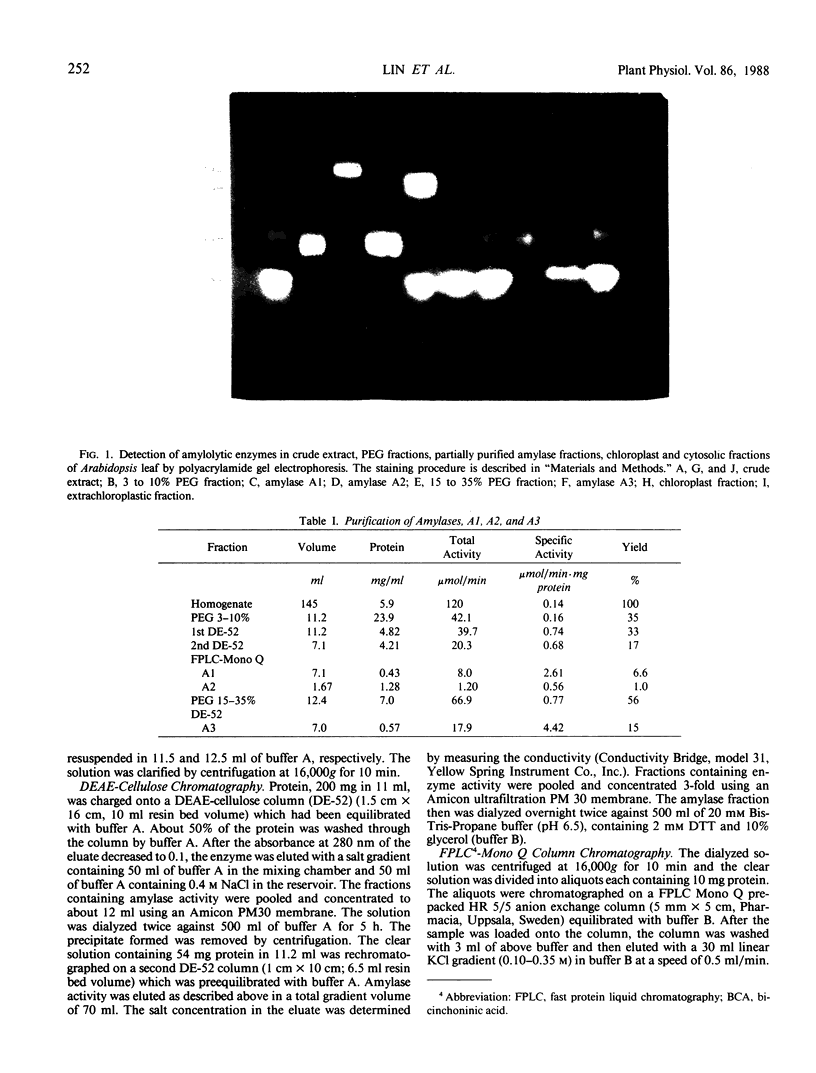
Abstract
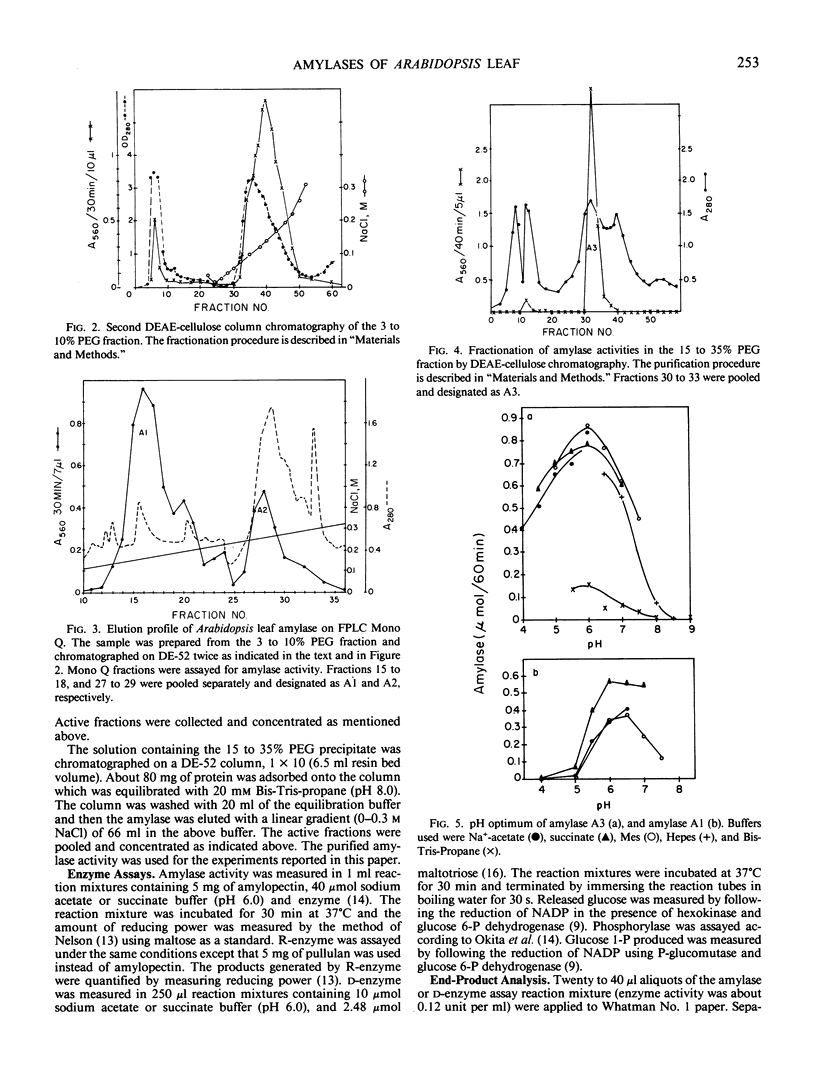
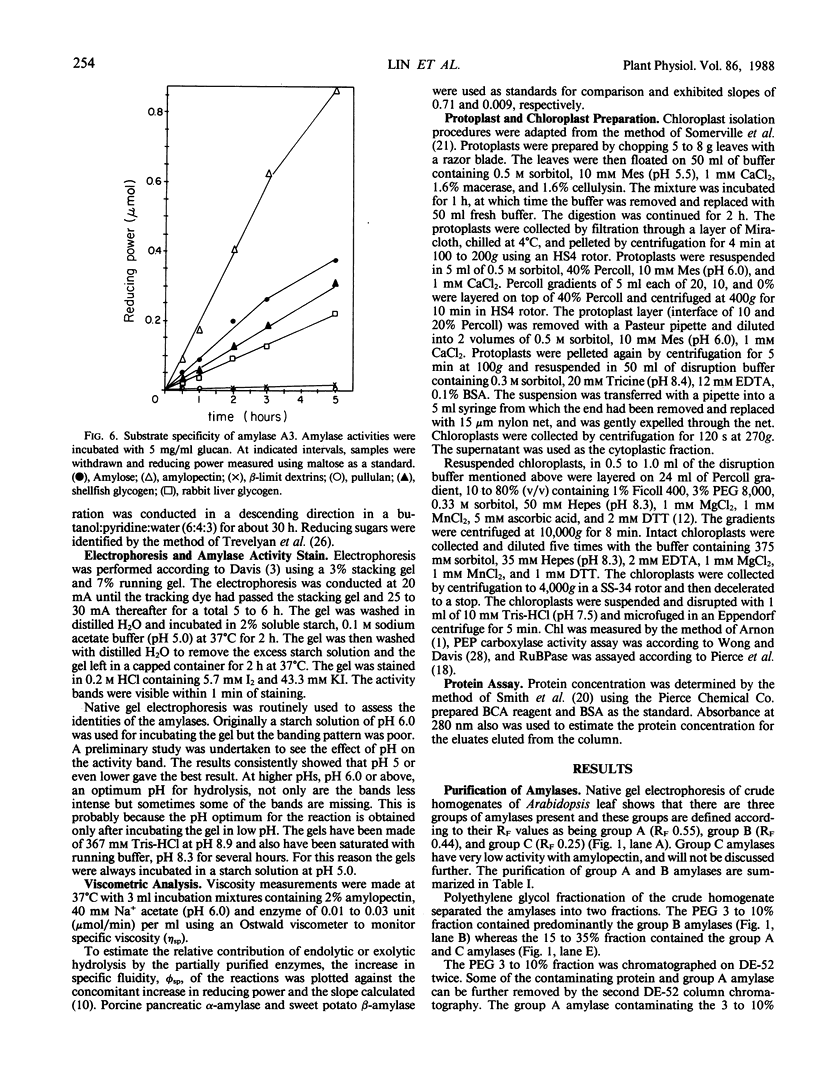
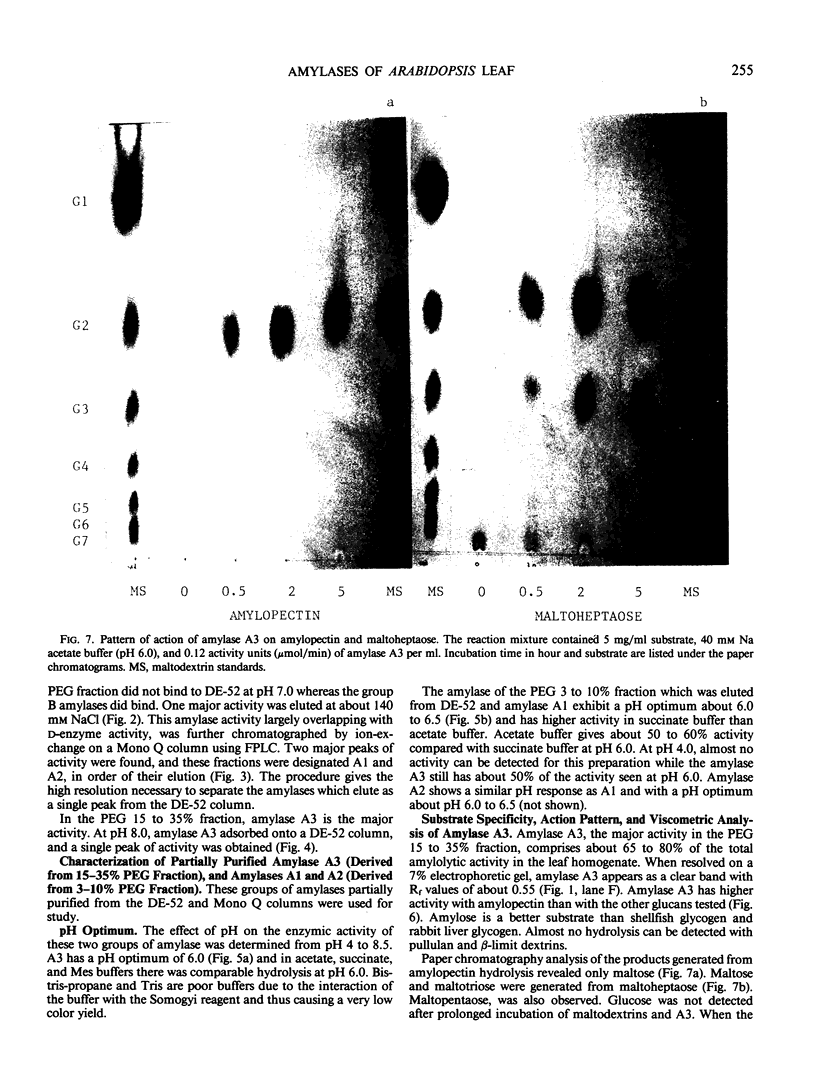
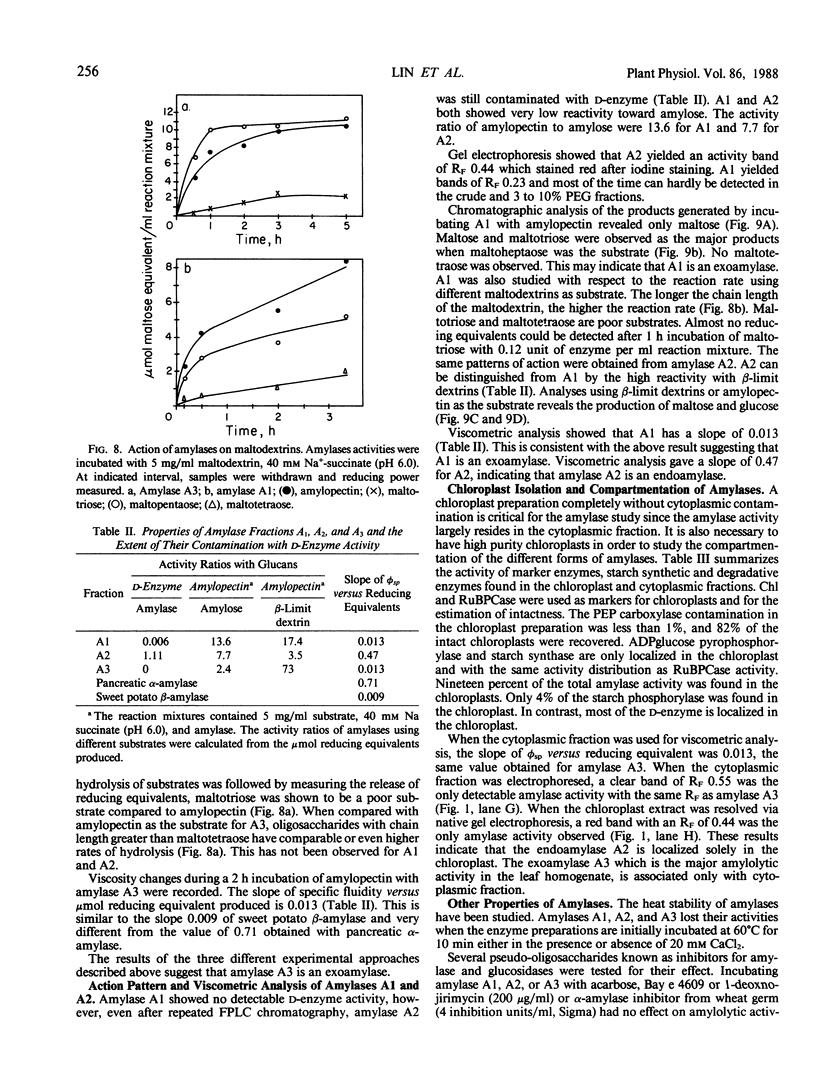
Amylolytic enzymes of Arabidopsis leaf tissue were partially purified and characterized. Endoamylase, starch phosphorylase, d-enzyme (transglycosylase), and possibly exoamylase were found in the chloroplasts. Endoamylase, fraction A2, found only in the chloroplast, was resolved from the exoamylases by chromatography on a Mono Q column and migrated with an RF of 0.44 on 7% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Exoamylase fraction, A1, has an RF of 0.23 on the polyacrylamide gel. Viscometric analysis showed that A1 has a slope of 0.013, which is same as that of A3, the extrachloroplastic amylase. A1, however, can be distinguished from A3 by having much higher amylolytic activity in succinate buffer than acetate buffer, and having much less reactivity with amylose. A1 probably is also localized in the chloroplast, and contributes to the 30 to 40% higher amylolytic activity of the chloroplast preparation in succinate than acetate buffer at pH 6.0. The high activity of d-enzyme compared to the amylolytic activity in the chloroplast suggests that transglycosylation probably has an important role during starch degradation in Arabidopsis leaf. Extrachloroplastic amylase, A3, has an RF of 0.55 on 7% electrophoretic gel and constitutes 80% of the total leaf amylolytic activity. The results of substrate specificity studies, action pattern and viscometric analyses indicate that the extrachloroplastic amylases are exolytic.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman G. W., Jr, Pallas J. E., Jr, Mendicino J. The hydrolysis of maltodextrins by a -amylase isolated from leaves of Vicia faba. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 28;276(2):491–507. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)91010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. V., Hanson A. D., Chandler P. C. Water stress enhances expression of an alpha-amylase gene in barley leaves. Plant Physiol. 1986 Feb;80(2):350–359. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakefuda G., Duke S. H. Electrophoretic transfer as a technique for the detection and identification of plant amylolytic enzymes in polyacrylamide gels. Plant Physiol. 1984 May;75(1):278–280. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.1.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi C., Gibbs M. Starch degradation in isolated spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jun;57(6):933–935. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.6.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi C., Preiss J. Amylopectin degradation in pea chloroplast extracts. Plant Physiol. 1978 Feb;61(2):218–220. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.2.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKie J. E., Brandts J. F. High precision capillary viscometry. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:257–288. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerowitz E. M., Pruitt R. E. Arabidopsis thaliana and Plant Molecular Genetics. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1214–1218. doi: 10.1126/science.229.4719.1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita T. W., Greenberg E., Kuhn D. N., Preiss J. Subcellular localization of the starch degradative and biosynthetic enzymes of spinach leaves. Plant Physiol. 1979 Aug;64(2):187–192. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita T. W., Preiss J. Starch Degradation in Spinach Leaves: ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THE AMYLASES AND R-ENZYME OF SPINACH LEAVES. Plant Physiol. 1980 Nov;66(5):870–876. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.5.870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavey D. G., Steup M., Gibbs M. Characterization of starch breakdown in the intact spinach chloroplast. Plant Physiol. 1977 Aug;60(2):305–308. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.2.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. W., McCurry S. D., Mulligan R. M., Tolbert N. E. Activation and assay of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Methods Enzymol. 1982;89(Pt 500):47–55. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)89011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Okita T. W., Greenberg E. Characterization of the spinach leaf phosphorylases. Plant Physiol. 1980 Nov;66(5):864–869. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.5.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steup M., Peavey D. G., Gibbs M. The regulation of starch metabolism by inorganic phosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 18;72(4):1554–1561. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Bulpin P. V., ap Rees T. Pathway of starch breakdown in photosynthetic tissues of Pisum sativum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 15;544(1):200–214. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Rees T. A. Carbohydrate breakdown by chloroplasts of Pisum sativum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 17;627(2):131–143. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90315-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. F., Davies D. D. Regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase of Zea mays by metabolites. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;131(3):451–458. doi: 10.1042/bj1310451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler P., Beck E. Exoamylase activity in vacuoles isolated from pea and wheat leaf protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1986 Dec;82(4):1119–1121. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.4.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]