Abstract
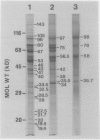
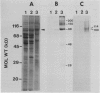
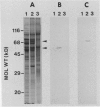
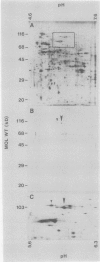
Tonoplast and plasma membranes (PM) were isolated from barley roots (Hordeum vulgare L. cv California Mariout 72) using sucrose step gradients. The isolation procedure yielded sufficient quantities of PM and tonoplast vesicles that were sealed and of the right orientation to measure ATP-dependent proton transport in vitro. The proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum, tonoplast-plus-Golgi membrane (TG) and PM fractions were separated on sodium dodecyl sulfate gels, and immunoblots were used to test for cross-contamination between the fractions. Proteins that cross-reacted with antibodies to the PM ATPase from corn roots and Neurospora were greatly enriched in the PM fraction, as were proteins that cross-reacted with monoclonal antibodies to an arabinogalactan protein from the PM of tobacco cells. Proteins that cross-reacted with antibodies to the 58- and 72-kilodalton subunits of the tonoplast ATPase of red beet storage tissue were greatly enriched in the TG fraction. The results with immunoblots and enzyme assays indicated that there was little cross-contamination between the tonoplast and PM vesicles. The molecular weights and isoelectric points of the PM ATPase and the tonoplast ATPase subunits were also determined using immunoblots of two-dimensional gels of the PM and TG proteins.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthon G. E., Spanswick R. M. Purification and properties of the h-translocating ATPase from the plasma membrane of tomato roots. Plant Physiol. 1986 Aug;81(4):1080–1085. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.4.1080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A. B., O'neill S. D., Spanswick R. M. H-ATPase Activity from Storage Tissue of Beta vulgaris: I. Identification and Characterization of an Anion-Sensitive H-ATPase. Plant Physiol. 1984 Mar;74(3):538–544. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.3.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill K. A., Holaway B., Sze H. Separation of two types of electrogenic h-pumping ATPases from oat roots. Plant Physiol. 1983 Dec;73(4):921–928. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.4.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Michelis M. I., Spanswick R. M. H-pumping driven by the vanadate-sensitive ATPase in membrane vesicles from corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jun;81(2):542–547. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Hurkman W. J. Separation of the Mg-ATPases from the Ca-Phosphatase Activity of Microsomal Membranes Prepared from Barley Roots. Plant Physiol. 1985 Apr;77(4):857–862. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.4.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M. Variable Effects of Nitrate on ATP-Dependent Proton Transport by Barley Root Membranes. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jun;84(2):526–534. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.2.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Norlyn J. D. Seawater-based crop production: a feasibility study. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):249–251. doi: 10.1126/science.197.4300.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher S. R., Leonard R. T. Electrophoretic characterization of a detergent-treated plasma membrane fraction from corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1987 Feb;83(2):265–271. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbarino J., Dupont F. M. NaCl Induces a Na/H Antiport in Tonoplast Vesicles from Barley Roots. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jan;86(1):231–236. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I. Two dimensional gel electrophoresis and computer analysis of proteins synthesized by clonal cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7961–7977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannini J. L., Gildensoph L. H., Briskin D. P. Selective production of sealed plasma membrane vesicles from red beet (Beta vulgaris L.) storage tissue. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 May 1;254(2):621–630. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goffeau A., Slayman C. W. The proton-translocating ATPase of the fungal plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 30;639(3-4):197–223. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(81)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager K. M., Mandala S. M., Davenport J. W., Speicher D. W., Benz E. J., Jr, Slayman C. W. Amino acid sequence of the plasma membrane ATPase of Neurospora crassa: deduction from genomic and cDNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7693–7697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurkman W. J., Tanaka C. K. Solubilization of plant membrane proteins for analysis by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jul;81(3):802–806. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.3.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurkman W. J., Tanaka C. K. The effects of salt on the pattern of protein synthesis in barley roots. Plant Physiol. 1987 Mar;83(3):517–524. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.3.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Körner L. E., Kjellbom P., Larsson C., Møller I. M. Surface properties of right side-out plasma membrane vesicles isolated from barley roots and leaves. Plant Physiol. 1985 Sep;79(1):72–79. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBel D., Poirier G. G., Beaudoin A. R. A convenient method for the ATPase assay. Anal Biochem. 1978 Mar;85(1):86–89. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90277-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandala S., Taiz L. Characterization of the subunit structure of the maize tonoplast ATPase. Immunological and inhibitor binding studies. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12850–12855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs D. Protein contaminants of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Dec;135(2):470–474. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90714-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleski N. A., Bennett A. B. H-ATPase Activity from Storage Tissue of Beta vulgaris: IV. N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide Binding and Inhibition of the Plasma Membrane H-ATPase. Plant Physiol. 1987 Mar;83(3):569–572. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasi-Caldogno F., Pugliarello M. C., De Michelis M. I. Electrogenic transport of protons driven by the plasma membrane ATPase in membrane vesicles from radish : biochemical characterization. Plant Physiol. 1985 Jan;77(1):200–205. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salinovich O., Montelaro R. C. Reversible staining and peptide mapping of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose after separation by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 1;156(2):341–347. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]