Abstract
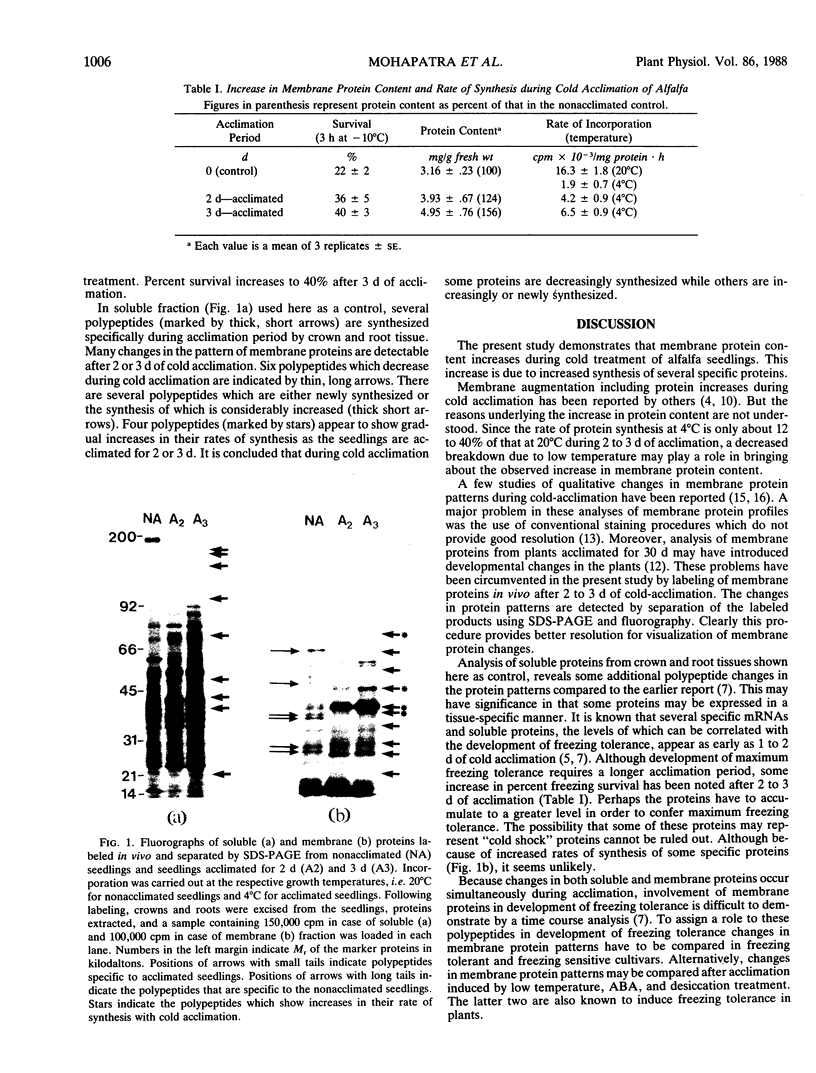
Changes in pattern of membrane proteins during cold acclimation of alfalfa have been examined. Cold acclimation for 2 to 3 days increases membrane protein content. Labeling of membrane proteins in vivo with [35S]methionine indicates increases in the rate of incorporation as acclimation progresses. Cold acclimation induces the synthesis of about 10 new polypeptides as shown by SDS-PAGE and fluorography of membrane proteins labeled in vivo.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusta L. V., Weiser C. J. Nucleic Acid and protein changes in relation to cold acclimation and freezing injury of korean boxwood leaves. Plant Physiol. 1972 Jan;49(1):91–96. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy C. L., Haskell D. Induction of freezing tolerance in spinach is associated with the synthesis of cold acclimation induced proteins. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jul;84(3):872–878. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.3.872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohapatra S. S., Poole R. J., Dhindsa R. S. Changes in Protein Patterns and Translatable Messenger RNA Populations during Cold Acclimation of Alfalfa. Plant Physiol. 1987 Aug;84(4):1172–1176. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.4.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis R. L., Berkowitz R. L. Characterization of Soybean Plasma Membrane during Development: FREE STEROL COMPOSITION AND CONCANAVALIN A BINDING STUDIES. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):871–879. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura M., Yoshida S. Involvement of Plasma Membrane Alterations in Cold Acclimation of Winter Rye Seedlings (Secale cereale L. cv Puma). Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):818–826. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S. Chemical and Biophysical Changes in the Plasma Membrane during Cold Acclimation of Mulberry Bark Cells (Morus bombycis Koidz. cv Goroji). Plant Physiol. 1984 Sep;76(1):257–265. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Uemura M. Protein and Lipid Compositions of Isolated Plasma Membranes from Orchard Grass (Dactylis glomerata L.) and Changes during Cold Acclimation. Plant Physiol. 1984 May;75(1):31–37. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Roche I. A., Pomeroy M. K., Andrews C. J. Changes in fatty acid composition in wheat cultivars of contrasting hardiness. Cryobiology. 1975 Oct;12(5):506–512. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(75)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]